Abstract
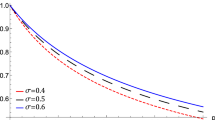
The basic features of a solitary potential (associated with the self-gravitational field), which are found to exist in a degenerate quantum plasma system (containing heavy nuclei and degenerate electrons), have been investigated by employing the pseudo-potential approach, which is valid for nonlinear structures with arbitrary amplitudes. The small-amplitude limit for such nonlinear structures has also been recovered. The degenerate quantum plasma system under consideration is found to support solitary structures with a negative self-gravitational potential; moreover, the magnitude of the amplitude of the self-gravitational solitary potential structures first increases and then decreases with increasing propagation speed whereas the width of the self-gravitational solitary potential structures increases with increasing speed. The implications of our results in some astrophysical compact objects (such as white dwarfs and neutron stars) are briefly discussed.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
S. Chandrasekhar, Philos. Mag. 11, 592 (1931)
S. Chandrasekhar, Astrophys. J. 74, 81 (1931)
S. Chandrasekhar, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 170, 405 (1935)
S. Chandrasekhar, An Introduction to the Study of Stellar Structure (Dover, New York, 1939), p. 412
S. Chandrasekhar, Phys. Rev. Lett. 12, 114 (1964)
S. Chandrasekhar, R.F. Tooper, Astrophys. J. 139, 1396 (1964)
D. Koester, G. Chanmugam, Rep. Prog. Phys. 53, 837 (1990)
S.L. Shapiro, S.A. Teukolsky, Black Holes, White Dwarfs, and Neutron Stars: The Physics of Compact Objects (Wiley, New York, 1983)
E. Garcia-Berro, S. Torres, L.G. Althaus, I. Renedo, P. Lorén-Aguiltar, A.H. Córsico, R.D. Rohrmann, M. Salaris, J. Isern, Nature (London) 465, 194 (2010)
F. Haas, Phys. Plasmas 14, 042309 (2007)
A.P. Misra, S. Samanta, Phys. Plasmas 15, 122307 (2008)
A.P. Misra, S. Banerjee, F. Haas, P.K. Shukla, L.P.G. Assis, Phys. Plasmas 17, 032307 (2010)
S.K. Chakrabarti, Astron. Astrphys. 351, 185–191 (1999)
M.A. Hossen, A.A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 22, 102710 (2015)
M.R. Hossen, A.A. Mamun, Braz. J. Phys. 44, 673–681 (2014)
M.R. Hossen, L. Nahar, S. Sultana, A.A. Mamun, High Energy Density Phys. 13, 13–19 (2014)
A.A. Mamun, P.K. Shukla, Phys. Lett. A 374, 4238 (2010)
R.H. Fowler, Mon. Not. R. Astron. Soc. 87, 114 (1926)
D. Koester, Astron. Astrophys. 11, 33 (2002)
P.K. Shukla, B. Eliasson, Rev. Mod. Phys. 83, 885 (2011)
P.K. Shukla, A.A. Mamun, D.A. Mendis, Phys. Rev. E 84, 026405 (2011)
A.A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 24, 102306 (2017)
A.A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 25, 022307 (2018)
A.A. Mamun, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 59, e201900080 (2019)
A.A. Mamun, Phys. Lett. A 375, 4029 (2011)
M. Asaduzzaman, A. Mannan, A.A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 24, 052102 (2017)
M. Asaduzzaman, A. Mannan, A.A. Mamun, Contrib. Plasma Phys. 60, e2019000104 (2020)
A.A. Mamun, R.A. Cairns, P.K. Shukla, Phys. Plasmas 3, 702 (1996)
A.A. Mamun, Astrophys. Space Sci. 268, 443 (1999)
N.S. Saini, I. Kourakis, M.A. Hellberg, Phys. Plasmas 16, 062903 (2009)
A.A. Mamun, P.K. Shukla, B. Eliasson, Phys. Rev. E 80, 046406 (2009)
N. Roy, S. Tasnim, A.A. Mamun, Phys. Plasmas 19, 033705 (2012)
E. Witt, W. Lotko, Phys. Fluids 26, 2176 (1983)
V.E. Fortov, Phys. Usp. 52, 615 (2009)
R.A. Cairns, A.A. Mamun, R. Bingham, R. Boström, R.O. Dendy, C.M.C. Nairn, P.K. Shukla, Geophys. Res. Lett 22, 2709 (1995)
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Asaduzzaman, M. Arbitrary-amplitude self-gravitational solitary potential in a degenerate quantum plasma system. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 80, 214–220 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-022-00413-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-022-00413-1