Abstract
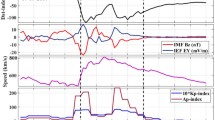
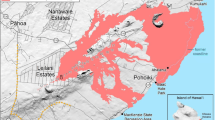
The four-dimensional variational (4D-VAR) technique, originally developed for weather forecasting applications, has been utilized in a data-assimilated model to estimate rocket exhaust emission from observed ionospheric disturbances. In this study, we improved the 4D-VAR method by utilizing a more realistic chemical model in the ionosphere and applied it to characterize ionosphere disturbances caused by the Hwasung-15 (H-15) rocket exhaust chemicals. The H-15 rocket was launched southeastward from North Korea at 18:17 UT on 28 November 2017. During the first hours of the launch, the total electron content (TEC) derived from the Korean ground-based GNSS receiver network exhibited ionospheric disturbances along the Rocket’s trajectory. The disturbances were most distinct along the GLONASS (Global Orbiting Navigational Satellite System) line of site. By assimilating the measured TEC data into the 4D-VAR model, we were able to characterize the ionospheric depletion and recovery with respect to the standard ionospheric model, IRI-2016. In addition, the rocket exhaust emissions were estimated to be ~ 1.5 × 1027 molecules per sec, with a number ratio of 2:1 for water to hydrogen in the rocket’s exhaust gas.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
M.C. Kelley, The Earth’s ionosphere: plasma physics and electrodynamics (Academic Press, Amsterdam, 2009)
H.G. Booker, J. Geophys. Res. 66, 1073 (1961)
M. Mendillo, G.S. Hawkins, J.A. Klobuchar, J. Geophys. Res. 80, 2217 (1975)
T. Furuya, K. Heki, Earth Planets Space. 60, 235 (2008)
M. Ozeki, K. Heki, Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 115, A9 (2010)
C.H. Lin et al., Ann. Geophys. 32, 1145 (2014)
Y. Kakinami et al., J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 118, 5184 (2013)
Y. Nakashim, K. Heki, Radio Sci. 49, 497 (2014)
B.K. Choi, H. Kil, Adv. Space Res. 59, 532 (2017)
N. Ssessanga, Y.H. Kim, B. Choi, J.K. Chung, J. Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 123, 2315 (2018)
B.K. Choi, J. Hong. Adv. Space Res. 63, 2598 (2019)
P. Vergados et al., Radio Sci. 51, 1010 (2016)
E.E. Ferguson, At. Data Nucl. Data Tables. 12, 159 (1973)
E.P. Olaguer, Atmos. Environ. 45, 6980 (2011)
E.E. Ferguson, Rev. Geophys. 12, 703 (1974)
A.E. Hedin, Geophys. Res. Space Phys. 96, 1159 (1991)
X. Zou, F. Vandenberghe, M. Pondeca, Y.H. Kuo, Introduction to adjoint techniques and the MM5 adjoint modeling system. NCAR Tech. Note NCAR/TN-435STR (1997)
Acknowledgements
The GLONASS STEC data sets in this work were provided by the Korea Astronomy and Space Science Institute (KASI). This work was supported by a research fund, FA2386-19-1-0123, in the Department of Astronomy and Space Science of Chungnam National University awarded by the Air Force Research Laboratory of the USA.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, G.S., Kim, Y.H., Choi, BK. et al. Characterizing ionospheric disturbances caused by the North Korean rocket (Hwasung-15) using a four-dimensional variational (4D-VAR) data-assimilation model. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 79, 785–794 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00282-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00282-0