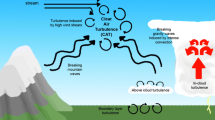
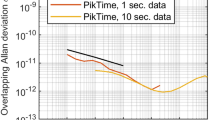
Abstract
Distribution of a high-stability clock signal is an important topic for many applications. Recently, optical frequency comb transfer through outdoor atmosphere has become a valuable tool for the clock distribution due to its versatility. To extend the benefits of comb-based open-air clock distribution, one-way radiofrequency (RF) transfer with a single optical frequency comb is an attractive approach due to its simplicity and broad application span. Here, we transfer an L-band RF signal across 820-m-scale outdoor beam path with a single optical frequency comb. We measured the absolute phase noise of the transferred RF signal, and analyzed it with Kolmogorov’s f −8/3 power law and Taylor’s hypothesis of frozen turbulence. We also show that the residual-phase noise of the transferred RF signal can be suppressed to the femtosecond regime by a delay-locked loop. Our results may benefit remote ranging at km-range, inter-building clock distribution, and optical communication through aerial drones.








Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of datas and materials
Additional data related to this paper may be requested from the author.
References
S.A. Diddams, The evolving optical frequency comb. J. Opt. Soc. Am. B 27, B51–B62 (2010)
J. Kim, Y. Song, Ultralow-noise mode-locked fiber lasers and frequency combs: principles, status, and applications. Adv. Opt. Photonics 8, 465–540 (2016)
J. Ye, H. Schnatz, L.W. Hollberg, Optical frequency combs: from frequency metrology to optical phase control. IEEE J. Sel. Top. Quantum Electron. 9, 1041–1058 (2003)
D. Kwon, I. Jeon, W.K. Lee, M.S. Heo, J. Kim, Generation of multiple ultrastable optical frequency. Sci. Adv. 6, 4457 (2020)
Y. Na et al., Ultrafast, sub-nanometre-precision and multifunctional time-of-flight detection. Nat. Photonics 14, 355–360 (2020)
K. Jung, J. Kim, Subfemtosecond synchronization of microwave oscillators with mode-locked Er-fiber lasers. Opt. Lett. 37, 2958–2960 (2012)
M. Walbran, A. Gliserin, K. Jung, J. Kim, P. Baum, 5-femtosecond laser-electron synchronization for pump-probe crystallography and diffraction. Phys. Rev. Appl. 4, 044013 (2015)
J. Kim, J.A. Cox, J. Chen, F.X. Kärtner, Drift-free femtosecond timing synchronization of remote optical and microwave sources. Nat. Photonics 2, 733–736 (2008)
S. Schulz et al., Femtosecond all-optical synchronization of an X-ray free-electron laser. Nat. Commun. 6, 5938 (2015)
A.G. Glenday et al., Operation of a broadband visible-wavelength astro-comb with a high-resolution astrophysical spectrograph. Optica 2, 250–254 (2015)
G. Marra et al., High-resolution microwave frequency transfer over an 86-km-long optical fiber network using a mode-locked laser. Opt. Lett. 36, 511–513 (2011)
F.R. Giorgetta et al., Broadband phase spectroscopy over turbulent air paths. Phys. Rev. Lett. 115, 103901 (2015)
K.D. Ridley, Measurements of laser phase fluctuations induced by atmospheric turbulence over 2 km and 17.5km distances. Appl. Opt. 50, 5085–5092 (2011)
S. Tichkule, A. Muschinski, Effects of wind-driven telescope vibrations on measurements of turbulent angle-of-arrival fluctuations. Appl. Opt. 53, 4651–4660 (2014)
W.C. Swann et al., Measurement of the impact of turbulence anisoplanatism on precision free-space optical time transfer. Phys. Rev. A 99, 023855 (2019)
J.-M. Conan, G. Rousset, P.-Y. Madec, Wave-front temporal spectra in high-resolution imaging through turbulence. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 12, 1559–1570 (1995)
D.P. Greenwood, D.O. Tarazano, Proposed form for the atmospheric turbulence spatial spectrum at large scales. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 25, 1349–1360 (2008)
L.C. Sinclair et al., Optical phase noise from atmospheric fluctuations and its impact on optical time-frequency transfer. Phys. Rev. A 89, 023805 (2014)
E.D. Caldwell et al., Optical timing jitter due to atmospheric turbulence: comparison of frequency comb measurements to predictions from micrometeorological sensors. Opt. Express 28, 26661–26675 (2020)
R. Rao, S. Wang, X. Liu, Z. Gong, Turbulence spectrum effect on wave temporal-frequency spectra for light propagating through the atmosphere. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A 16, 2755–2762 (1999)
H.J. Kang et al., Free-space transfer of comb-rooted optical frequencies over an 18 km open-air link. Nat. Commun. 10, 4438 (2019)
J. Kang et al., Few-femtosecond-resolution characterization and suppression of excess timing jitter and drift in indoor atmospheric frequency comb transfer. Opt. Express 22, 26023–26031 (2014)
P. Cinquegrana et al., Optical beam transport to a remote location for low jitter pump-probe experiments with a free electron laser. Phys. Rev. Accel. Beams. 17, 040702 (2014)
J.-D. Deschênes et al., Synchronization of distant optical clocks at the femtosecond level. Phys. Rev. X 6, 021016 (2016)
R.P. Gollapalli, L. Duan, Atmospheric timing transfer using a femtosecond frequency comb. IEEE Photon. J. 2, 904–910 (2010)
J. Lee et al., Time-of-flight measurement with femtosecond light pulses. Nat. Photonics 4, 716 (2010)
M. Hulea, Z. Ghassemlooy, S. Rajbhandari, X. Tang, Compensating for optical beam scattering and wandering in fso communications. J. Light. Technol. 32, 1323–1328 (2014)
F.R. Giorgetta et al., Optical two-way time and frequency transfer over free space. Nat. Photonics 7, 434–438 (2013)
K.C. Cossel et al., Open-path dual-comb spectroscopy to an airborne retroreflector. Optica 4, 724–728 (2017)
H. Bergeron et al., Femtosecond time synchronization of optical clocks off of a flying quadcopter. Nat. Commun. 10, 1819 (2019)
L.C. Sinclair et al., Femtosecond optical two-way time-frequency transfer in the presence of motion. Phys. Rev. A 99, 023844 (2019)
D. Herman et al., Femtosecond timekeeping: slip-free clockwork for optical timescales. Phys. Rev. Appl. 9, 044002 (2018)
M.I. Bodine et al., Optical atomic clock comparison through turbulent air. Phys. Rev. Research 2, 033395 (2020)
L.C. Sinclair et al., Synchronization of clocks through 12 km of strongly turbulent air over a city. Appl. Phys. Lett. 109, 151104 (2016)
C. Hu, R.P. Gollapalli, L. Yang, L. Duan, Excess phase noise characterization in multifrequency remote clock distribution based on femtosecond frequency combs. Appl. Sci. 5, 77–87 (2015)
R.P. Gollapalli, L. Duan, Multiheterodyne characterization of excess phase noise in atmospheric transfer of a femtosecond-laser frequency comb. J. Light. Technol. 29, 3401–3407 (2011)
F. Sun et al., Femtosecond-level timing fluctuation suppression in atmospheric frequency transfer with passive phase conjunction correction. Opt. Express 25, 21312–21320 (2017)
G. Guo et al., Laser-based atmospheric radio-frequency transfer with sub-picosecond timing fluctuation using single phase compensator. Opt. Commun. 426, 526–530 (2018)
Y. Chen et al., Stable radio frequency transfer over free space by passive phase correction. IEEE Photon. J. 11, 5503308 (2019)
D.R. Gozzard, S.W. Schediwy, B. Stone, M. Messineo, M. Tobar, Stabilized free-space optical frequency transfer. Phys. Rev. Appl. 10, 024046 (2018)
W.C. Swann et al., Low-loss reciprocal optical terminals for two-way time-frequency transfer. Appl. Opt. 56, 9406 (2017)
B. P. Dix-Matthews et al. Point-to-point stabilized optical frequency transfer with active optics, arXiv200704985 [physics.ins-det] (2020)
G.-R. Kim, T.-I. Jeon, D. Grischkowsky, 910-m propagation of THz ps pulses through the atmosphere. Opt. Express 25, 25422 (2017)
Acknowledgements
The results in this work are obtained using the infrastructure and resources of Professor Jungwon Kim’s group at Korea Advanced Institute of Science and Technology (KAIST). I thank fruitful discussions and technical supports from Changmin Ahn, Jaegoan Lee and Jungwon Kim of KAIST and Myoung-Sun Heo, Sang Eon Park and Dai-Hyuk Yu of Korea Research Institute of Standards and Science (KRISS).
Funding
This work was supported by the Government Contribution Research Fund to KAERI of Republic of Korea (524450–20) and National Research Foundation of Republic of Korea (2013M1A3A3A02042273).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflicts of interest
The author declares no conflicts of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shin, J. Optical frequency comb transfer through 820-m-scale atmospheric turbulence for low-noise radiofrequency distribution. J. Korean Phys. Soc. 78, 1055–1061 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00168-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40042-021-00168-1