Abstract
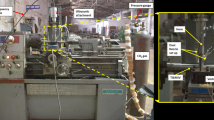
Titanium (Ti) alloys are extremely difficult-to-cut aerospace alloys due to their low thermal conductivity, high chemical reactivity, and high hardness. Making miniature holes in these alloys by traditional drilling is much difficult, because most of heat generated in the process passes through twist drill, which causes frequent failure of it. Electrical discharge machining (EDM) is an appropriate process for creating holes in these materials but it faces problem of debris flushing when hole size reaches to micro-range. All debris particles start to accumulate at bottom side, as hole progresses, which enhance arcing, short-circuiting, unusual discharges, etc. In account of all above mentioned problems, authors developed ultrasonic assisted micro-EDM (UA-MEDM) setup, in which tool is rotating and workpiece is vibrating. Further, the machining characteristics of Ti–6Al–4V have been investigated in the form of material removal rate (MRR), hole taper (Ta), tool wear rate (TWR), and surface quality (SQ) of microholes due to variation of gap current, pulse off-time, pulse on-time, tool RPM, and ultrasonic power using one factor-at-a-time (OFAT) methodology on this developed setup. On the other hand machining characteristics have been studied when ultrasonic vibration and rotation of tool are switched-off. Surface quality of microholes and micro-tools has also been observed by using scanning electron microscopy (SEM). Experimental results show that rotating tool and vibrating workpiece give microholes of better quality with higher MRR.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
E.O. Ezugwu, Z.M. Wang, Titanium alloys and their machinability—a review. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 68(3), 262–274 (1997)
B. Jabbaripour, M.H. Sadeghi, S.H. Faridvand, M.R. Shabgard, Investigating the effects of EDM parameters on surface integrity, MRR and TWR in machining of Ti–6Al–4V. Mach. Sci. Technol. 31(4), 475–482 (2012)
A.R. Machado, J. Walbank, Machining of titanium and its alloys—a review. Proc. IMechE Part B J. Eng. Manuf. 204, 53–60 (1990)
U.S. Yadav, V. Yadava, Experimental investigation on electrical discharge drilling of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mach. Sci. Technol. 19, 515–535 (2015)
V.K. Jain, Advanced Machining Processes (Allied Publisher Private Limited, New Delhi, 2004), p.127
J. Wang, Z. Jia, Efficiency improvement in electrical discharge machining (EDM) of constant section cavity based on experimental study and numerical calculations. Prod. Eng. Res. Dev. 12, 567–578 (2018)
A. Kumar, R.N. Rai, Grey-Taguchi and TOPSIS-Taguchi-based optimisation of performance parameters of spark EDM on heat-treated AA7050/5 B4C composite. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 101(1), 71–79 (2020)
Z. Wansheng, W. Zhenlong, D. Shichun, C. Guanxin, W. Hongyu, Ultrasonic and electric discharge machining to deep and small hole on titanium alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 120(1–3), 101–106 (2002)
S.Z. Chavoshi, X. Luo, Hybrid micro-machining processes: a review. Precis. Eng. 41, 1–23 (2015)
J.S. Soni, G. Chakraverti, Machining characteristics of titanium with rotary electro-discharge machining. Wear 171(1–2), 51–58 (1994)
M.P. Jahan, Y.S. Wong, M. Rahman, Experimental investigations into the influence of major operating parameters during micro-electro discharge drilling of cemented carbide. Mach. Sci. Technol. 16, 131–156 (2012)
U.S. Yadav, V. Yadava, Parametric study on electrical discharge drilling of aerospace nickel alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 29(3), 260–266 (2014)
D.K. Chung, H.S. Shin, M.S. Park, H. Kim, C.N. Chu, Recent researches in micro electrical machining. Int. J. Precis. Eng. Manuf. 12(2), 371–380 (2013)
M.R. Shabgard, H. Alenabi, Ultrasonic assisted electrical discharge machining of Ti–6Al–4V alloy. Mater. Manuf. Process. 30(8), 991–1000 (2015)
H. Huang, H. Zhang, L. Zhou, H.Y. Zheng, Ultrasonic vibration assisted electro-discharge machining of microholes in Nitinol. J. Micromech. Microeng. 13, 693–700 (2003)
S.H. Yeo, L.K. Tan, Effects of ultrasonic vibrations in micro electro-discharge machining of microholes. J. Micromech. Microeng. 9(4), 345–352 (1999)
C. Gao, Z.A. Liu, Study of ultrasonically aided micro-electrical-discharge machining by the application of workpiece vibration. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 139(1–3), 226–228 (2003)
J.C. Hung, J.K. Lin, B.H. Yan, H.S. Liu, P.H. Ho, Using a helical micro-tool in micro-EDM combined with ultrasonic vibration for micro-hole machining. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 2705–2713 (2006)
D.J. Kim, S.M. Yi, Y.S. Lee, C.N. Chu, Straight hole micro-EDM with a cylindrical tool using a variable capacitance method accompanied by ultrasonic vibration. J. Micromech. Microeng. 16, 1092–1097 (2006)
M.S. Murali, B.P. Ganesh, P.R. Kamlakar, A study on process parameters of ultrasonic assisted micro EDM based on Taguchi method. J. Mater. Eng. Perform. 17(2), 210–215 (2008)
R. Garn, A. Schubert, H. Zeidler, Analysis of the effect of vibrations on the micro-EDM process at the workpiece surface. Precis. Eng. 35(2), 364–368 (2011)
G. Puthumana, Analysis of the effect of ultrasonic vibrations on the performance of micro-electrical discharge machining of A2 tool steel. Int. J. Recent Adv. Mech. Eng. 95, 15–22 (2016)
P. Mukhopadhyay, B.R. Sarkar, Advancement in ultrasonic vibration and magnetic field assisted micro-EDM process: an overview. Int. J. Adv. Res. Eng. Technol. (IJARET) 10(2), 362–373 (2019)
Z. Li, J. Tang, J. Bai, A novel micro-EDM method to improve microhole machining performances using ultrasonic circular vibration (UCV) electrode. Int. J. Mech. Sci. 175, 105574 (2020)
G. Singh, P.S. Satsangi, D.R. Prajapati, Effect of rotating magnetic field and ultrasonic vibration on micro-EDM process. Arab. J. Sci. Eng. 45, 1059–1070 (2020)
Q. Xing, Z. Yao, Q. Zhang, Effects of processing parameters on processing performances of ultrasonic vibration-assisted micro-EDM. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 112, 71–86 (2021)
Z. Li, J. Tang, Y. Li, J. Bai, Investigation on surface integrity in novel micro-EDM with two-dimensional ultrasonic circular vibration (UCV) electrode. J. Manuf. Process. 76, 828–840 (2022)
R. Teimouri, H. Baseri, Experimental study of rotary magnetic field-assisted dry EDM with ultrasonic vibration of workpiece. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 67, 1371–1384 (2013)
M.P. Jahan, Y.S. Wong, M. Rahman, Experimental investigations into the influence of major operating parameters during micro-electro discharge drilling of cemented carbide. Mach. Sci. Technol. 16(1), 131–156 (2012)
J. Murray, D. Zdebski, A.T. Clare, Workpiece debris deposition on tool electrodes and secondary discharge phenomena in micro-EDM. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 212, 1537–1547 (2012)
M. Kunieda, T. Kobayashi, Clarifying mechanism of determining tool electrode wear ratio in EDM using spectroscopic measurement of vapor density. J. Mater. Process. Technol. 149, 284–288 (2004)
R. Kumar, O.P. Sahani, M. Vashista, Effect of EDM process parameters on tool wear. J. Basic Appl. Eng. Res. 1(2), 53–56 (2014)
A.B. Pandey, P.K. Brahmankar, A method to predict possibility of arcing in EDM of TiB2p reinforced ferrous matrix composite. Int. J. Adv. Manuf. Technol. 86(9–12), 2837–2849 (2016)
Q. Liu, Q. Zhang, Effect of electrode size on the performances of micro-EDM. Mater. Manuf. Processes 31(4), 391–396 (2016)
R.S. Yadav, V. Yadava, Experimental investigations on electrical discharge diamond face surface grinding (EDDFSG) of hybrid metal matrix composite. Mater. Manuf. Process. 32(2), 135–144 (2017)
D.T. Pham, A. Ivanov, S. Bigot, K. Popov, S. Dimov, A study of micro-electro discharge machining electrode wear. Proc. IMechE Part C J. Mech. Eng. Sci. 221(5), 605–612 (2007)
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The author(s) declared no potential conflicts of interest with respect to the research, authorship, and/or publication of this article.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Singh, P., Yadava, V. & Narayan, A. Machining Performance Characteristics of Ti–6Al–4V Alloy Due to Ultrasonic Assisted Micro-EDM Using Rotating Tool Electrode. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 105, 155–171 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-023-00460-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-023-00460-3