Abstract
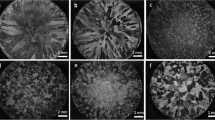
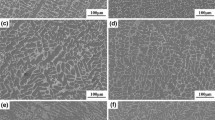
The current work is focused to ascertain the impact on the mechanical and morphological characteristics of hypoeutectic alloy Al–Ni with a range of solution treatment temperatures. Al, Ni, Si, and Mg of necessary weight percentages were melted in a crucible (make–clay graphite) and were cast. The cast alloys were then solutionised for 8 h from 450 to 550 °C, quenched and was aged for 12 h at 170 °C. The fractography, intermediate phase and the elementary composition of alloy was determined. It was observed from the investigation that a rise in solutionising temperature caused grain refinement in the developed hypoeutectic alloys. A surge in the value of hardness was observed with respect to the rise in solutionising temperature. It was also noticed from the analysis that the value of tensile strength, yield strength, ductility and impact resistance of the hypoeutectic alloys enhanced with temperature rise from 480 to 510 °C and then declined from 510 to 550 °C.






















Similar content being viewed by others
References
T.B. Sercombe, G.B. Schaffer, Rapid manufacturing of aluminium components. Science 80, 51 (2003). https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1086989
J.R. Davis, Light metals and alloys-aluminium and aluminium alloys. Alloy. Underst. Basics. (2001). https://doi.org/10.1361/autb2001p351
L.Y. Zhang, Y.H. Jiang, Z. Ma, S.F. Shan, Y.Z. Jia, C.Z. Fan, W.K. Wang, Effect of cooling rate on solidified microstructure and mechanical properties of aluminium-A356 alloy. J. Mater. Process. Technol. (2008). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2007.12.059
J. Ding, P. Zhang, X. Li, L. Wang, W. Liao, L. Huang, X. Xia, Microstructure and thermal stability evolution behaviour of Sc-containing A356.2 aluminium alloy under cyclic thermal exposure conditions. Mater. Sci. Eng. A. (2018). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2018.03.002
M. Zhu, Z. Jian, G. Yang, Y. Zhou, Effects of T6 heat treatment on the microstructure, tensile properties, and fracture behavior of the modified A356 alloys. Des Mater (2012). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.11.018
L. Yu, X. Liu, Z. Wang, X. Bian, Grain refinement of A356 alloy by AlTiC/AlTiB master alloys. J. Mater. Sci. (2005). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-005-2893-8
R. Chen, Q. Xu, Z. Jia, B. Liu, Precipitation behaviour and hardening effects of Si-containing dispersoids in Al–7Si–Mg alloy during solution treatment. Des. Mater. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2015.11.069
J.H. Peng, X.L. Tang, J.T. He, D.Y. Xu, Effect of heat treatment on microstructure and tensile properties of A356 alloys. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(11)60955-2
S. Menargues, E. Martín, M.T. Baile, J.A. Picas, New short T6 heat treatments for aluminium silicon alloys obtained by semisolid forming. Sci. Eng. A Mater. (2015). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2014.10.078
K. Sekar, K. Allesu, M.A. Joseph, Effect of T6 heat treatment in the microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 reinforced with nano Al2O3 particles by combination effect of stir and squeeze casting. Sci. Procedia Mater. (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mspro.2014.07.287
B. Li, Q.L. Pan, Y.J. Shi, C. Li, Z.M. Yin, Microstructural evolution of Al–Zn–Mg–Zr alloy with trace amount of Sc during homogenization treatment. Trans. Nonferrous Met. Soc. China (2013). https://doi.org/10.1016/S1003-6326(13)62902-7
Q.G. Wang, C.J. Davidson, Solidification and precipitation behaviour of Al–Si–Mg casting alloys. J. Mater. Sci. (2001). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1004801327556
B. Dang, Y.B. Li, F. Liu, Q. Zuo, M.C. Liu, Effect of T4 heat treatment on microstructure and hardness of A356 alloy refined by Ga+In+Sn mixed alloy. Des. Mater. 5, 10 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.12.022
A. Mukund, A.S. Nair, S. Nived, R. Raagavendran, A. Premkumar, A.N. Raj, K.V. Shankar, Impact of solutionising temperature on the microstructure, hardness and tensile strength of Al–6.6Si–0.3Mg–3Ni alloys. Mater. Today Proc. 5, 10 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.04.725
A. Nidhin Raj, R. Sellamuthu, Determination of hardness, mechanical and wear properties of cast Al–Mg–Si alloy with varying Ni addition. ARPN J. Eng. Appl. Sci. 11, 5946–5952 (2016)
D.K. Dwivedi, Influence of modifier and grain refiner on solidification behaviour and mechanical properties of cast Al–Si base alloy. J. Inst. Eng. 3, 91 (2002)
D.K. Dwivedi, Sliding temperature and wear behaviour of cast Al–Si–Mg alloys. Sci. Eng. A Mater (2004). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msea.2004.05.014
B.K. Prasad, Structure-property related changes in a hypoeutectic aluminium-silicon alloy induced by solutionising. Trans. JIM Mater (1994). https://doi.org/10.2320/matertrans1989.35.873
L.F. Mondolfo, Al–Mg–Si Aluminium–Magnesium–Silicon system. Aluminium Alloys. (1976). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-408-70932-3.50283-7
P.A. Rometsch, G.B. Schaffer, An age hardening model for Al–7Si–Mg casting alloys. Sci. Eng. A Mater. (2002). https://doi.org/10.1016/S0921-5093(01)01479-4
J. Campbell, Castings practice. Cast. Pract. (2016). https://doi.org/10.1016/b978-0-7506-4791-5.x5000-2
E. Sjölander, S. Seifeddine, Optimisation of solution treatment of cast Al–Si–Cu alloys. Des. Mater. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2009.10.035
H. Möller, G. Govender, W.E. Stumpf, The T6 Heat Treatment of Semi-Solid Metal Processed Alloy A356. Sci. J Open Mater. (2008). https://doi.org/10.2174/1874088x00802010006
E. Sjlander, S. Seifeddine, The heat treatment of Al-Si-Cu-Mg casting alloys. J. Mater. Process. Technol. (2010). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmatprotec.2010.03.020
M. Ishak, A. Amir, A.H. Ahmad, Effect of solution treatment temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of A356 alloy. Int. Rev. Mech. Eng. 8, 289–295 (2014). https://doi.org/10.15866/ireme.v8i1.1273
C.J. Davidson, J.R. Griffiths, A.S. Machin, The effect of solution heat-treatment time on the fatigue properties of an Al–Si–Mg casting alloy. Eng. Mater. Struct Fatigue Fract (2002). https://doi.org/10.1046/j.8756-758x.2001.00490.x
S. Ma, M.D. Maniruzzaman, D.S. Mackenzie, R.D. Sisson, A methodology to predict the effects of quench rates on mechanical properties of cast aluminium alloys. Metall. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. (2007). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-007-9044-3
C.H. Caceres, C.J. Davidson, J.R. Griffiths, Q.G. Wang, The effect of Mg on the microstructure and mechanical behaviour of Al–Si–Mg casting alloys. Mater. Trans. A Phys. Metall. Mater. Sci. 2, 10 (1999). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11661-999-0301-8
R. Sharma, A. Kumar, D.K. Dwivedi, Influence of solution temperature on microstructure and mechanical properties of two cast Al–Si alloys. Mater. Manuf. Process. 21, 309–314 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1080/10426910500464784
C.R.M. Afonso, J.E. Spinelli, C. Bolfarini, W.J. Botta, C.S. Kiminami, A. Garcia, Rapid solidification of an Al–5Ni alloy processed by spray forming. Mater Res. (2012). https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-14392012005000044
M.A. Moustafa, F.H. Samuel, H.W. Doty, Effect of solution heat treatment and additives on the hardness, tensile properties and fracture behaviour of Al–Si (A413.1) automotive alloys. J. Mater. Sci. (2003). https://doi.org/10.1023/A:1027385619114
S. Shivkumar, S. Ricci, C. Keller, D. Apelian, Effect of solution treatment parameters on tensile properties of cast aluminium alloys. J. Heat Treat. (1990). https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02833067
A. Malekan, M. Emamy, J. Rassizadehghani, A.R. Emami, The effect of solution temperature on the microstructure and tensile properties of Al-15%Mg2Si composite. Des. Mater. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2011.01.020
D.A. Lados, D. Apelian, L. Wang, Solution treatment effects on microstructure and mechanical properties of Al-(1 to 13 pct) Si-Mg cast alloys. Mater. Trans. B Process Metall. Mater. Process. Sci. (2011). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11663-010-9437-6
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding authors
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shankar, K.V., Manu, K., Raj, A.N. et al. Solutionising Temperature Influence on the Morphological and Mechanical Characteristics of Al–Si–Mg–Ni Hypoeutectic Alloys. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. D 102, 131–148 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00259-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40033-021-00259-0