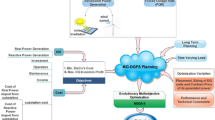
Abstract
A new indicator-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm (MOEA) using the objective discretization method is proposed for the meter placement problem (MPP) in active distribution system. Because MPP is a combinatorial optimization, a combination of measurement sets produces a discrete objective space. Therefore, the objective discretization method has been adopted to enhance the performance of MOEA. The proposed MOEA is an indicator-based method using an inverted generational distance indicator with noncontributing solution detection (IGD-NS) and with an adaptive reference point method (IB-MOEA-AR). The advantage of the IGD-NS indicator is that it measures the diversity and convergence of the solution set as well as identifies the solutions, which does not contribute to the indicator. As the performance of MOEA mostly depends on the Pareto front shape, the proposed method employs an adaptive reference point approach to follow the shape of the Pareto front. Moreover, the effect of distributed generation is investigated on distribution system state estimation performance for different measurement uncertainties as well as for various distributed renewable generations. The MPP is modeled as a multi-objective problem with the objectives consisting of minimization of total meter cost and state estimation errors. The versatility of the proposed method is demonstrated on Indian Practical 85-bus distribution system and UKGDS 95-bus distribution system. The results obtained are compared to existing MOEAs in the literature, to demonstrate the superiority of the proposed method over other methods.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.Z. Fanucchi, M. Bessani, M.H.M. Camillo, A.S. da Soares, B.A. João, Stochastic indexes for power distribution systems resilience analysis. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 13(12), 2507–2516 (2019)
V.A. Evangelopoulos, P.S. Georgilakis, N.D. Hatziargyriou, Optimal operation of smart distribution networks: a review of models, methods and future research. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 14(12), 95–106 (2016)
A. Angioni, T. Schlsser, F. Ponci, A. Monti, Impact of pseudo measurements from new power profiles on state estimation in low voltage grids. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 65(1), 70–77 (2016)
R.A. Jabr, B.C. Pal, R. Singh, Choice of estimator for distribution system state estimation. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 3(7), 666–678 (2009)
M.E. Baran, J. Zhu, A.W. Kelley, Meter placement for real-time monitoring of distribution feeders. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 11(1), 332–337 (1996)
C. Muscas, F. Pilo, G. Pisano, S. Sara, Optimal allocation of multichannel measurement devices for distribution state estimation. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 58(6), 1929–1937 (2009)
P.A. Pegoraro, S. Sulis, Robustness-oriented meter placement for distribution system state estimation in presence of network parameter uncertainty. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 62(5), 954–962 (2013)
R. Sing, B.C. Pal, R.A. Jabr, B. Richard, Vinter, meter placement for distribution system state estimation: an ordinal optimization approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 26(4), 2328–2335 (2011)
K. Chauhan, R. Sodhi, Placement of distribution-level phasor measurements for topological observability and monitoring of active distribution networks. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. (2019). https://doi.org/10.1109/TIM.2019.2939951
M.G. Damavandi, V. Krishnamurthy, J.R. Marti, Robust meter placement for state estimation in active distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 6(4), 1972–1982 (2015)
R. Sing, B.C. Pal, R.B. Vinter, Measurement placement in distribution system state estimation. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 24(2), 668–675 (2009)
K. Dehghanpour, Z. Wang, J. Wang, Y. Yuan, Bu. Fankun, A survey on state estimation techniques and challenges in smart distribution systems. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 10(2), 2312–2322 (2019)
F. Ahmad, A. Rasool, S. Emre Ozsoy, A.S. Rajasekar, M. Elitas, Distribution system state estimation-a step towards smart grid. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 81(1), 2659–2671 (2018)
A. Zhou et al., Multi-objective evolutionary algorithms: a survey of the state of the art. Swarm E Comput. 1(1), 32–49 (2011)
J. Liu, F. Ponci, A. Monti, C. Muscas, P.A. Pegoraro, S. Sulis, Optimal meter placement for robust measurement systems in active distribution grids. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 63(5), 1096–1105 (2014)
A. Shafiu, N. Jenkins, G. Strbac, Measurement location for state estimation of distribution networks with generation. IEEE Proc. Gener. Transm. Distrib. 152(2), 240–246 (2005)
J. Liu, J. Tang, F. Ponci, A. Monti, C. Muscas, P.A. Pegoraro, Trade-offs in PMU deployment for state estimation in active distribution grids. IEEE Trans. Smart Grid 3(2), 915–924 (2012)
M. Pau, P.A. Pegoraro, S. Sulis, Efficient branch-current-based distribution system state estimation including synchronized measurement. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 62(9), 2419–2429 (2013)
X. Chen, J. Lin, C. Wan, Y. Song, S. You, Yi. Zong, W. Guo, Y. Li, Optimal meter placement for distribution network state estimation: a circuit representation-based MILP approach. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 31(6), 4357–4370 (2016)
S. Prasad, D.M. Vinod Kumar, Optimal allocation of measurement devices for distribution state estimation using multi-objective hybrid PSO–krill herd algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 66(8), 2022–2035 (2017)
S. Prasad, D.M. Vinod Kumar, Multi-objective hybrid estimation of distribution algorithm-interior point method-based meter placement for active distribution state estimation. IET Gener. Transm. Distrib. 12(3), 767–779 (2018)
S. Prasad, D.M. Vinod Kumar, Trade-offs in PMU and IED deployment for active distribution state estimation using multi-objective evolutionary algorithm. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 67(6), 1298–1307 (2018)
S. Prasad, D.M. Vinod Kumar, Robust meter placement for active distribution state estimation using a new multi-objective optimization model. IET Sci. Meas. Technol. 12(8), 1047–1057 (2018)
R.C. Purshouse, P.J. Fleming, On the evolutionary optimization of many conflicting objectives. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 11(6), 770–784 (2007)
K. Li, K. Deb, Q. Zhang, S. Kwong, an evolutionary many-objective optimization algorithm based on dominance and decomposition. IEEE Trans. Evolut. Comput. 19(5), 694–716 (2015)
H. Ishibuchi, Y. Setoguchi, H. Masuda, Y. Nojima, Performance of decomposition-based many-objective algorithms strongly depends on Pareto front shapes. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 21(2), 169–190 (2017)
W. Chen, H. Ishibuchi, K. Shang, Effects of discretization of decision and objective spaces on the performance of evolutionary multi- objective optimization algorithms, IEEE Symposium Series on Computational Intelligence (SSCI), (Xiamen, China, 2019)
H. Ishibuchi, M. Yamane, Y. Nojima, Difficulty in evolutionary multiobjective optimization of discrete objective functions with different granularities, Lecture notes in computer science 7811: evolutionary multi-criterion optimization, (Springer, Berlin, 2013), pp.230–245
M. Li, S. Yang, X. Liu, Pareto or non-pareto: Bi-criterion evolution in multiobjective optimization. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 20(5), 645–665 (2016)
H. Wang, N.N. Schulz, A revised branch current-based distribution system state estimation algorithm and meter placement impact. IEEE Trans. Power Syst. 19(1), 207–213 (2004)
M. Pau, P.A. Pegoraro, S. Sulis, Efficient branch-current-based distribution system state estimation including synchronized measurements. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 62(9), 2419–2429 (2013)
Y. Tian, R. Cheng, X. Zhang, F. Cheng, Y. Jin, An indicator-based multi-objective evolutionary algorithm with reference point adaption for better versatility. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 22(4), 609–622 (2018)
L. While, P. Hingston, L. Barone, S. Huband, A faster algorithm for calculating hypervolume. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 10(1), 29–38 (2006)
D. Brockhoff, T. Wagner, H. Trautmann, On the properties of the R2 indicator, in Proc. 14th Annu. Conf. Genet. E Comput., (Philadelphia, PA, USA, 2012) pp. 465–472
A. Zhou, Y. Jin, Q. Zhang, B. Sendhoff, E. Tsang, Combining model-based and genetics-based offspring generation for multi-objective optimization using a convergence criterion, in Proc. IEEE Congr. E Comput., (Vancouver, BC, Canada, 2006) pp. 892–899
I. Das, J.E. Dennis, Normal-boundary intersection: a new method for generating Pareto optimal points in multicriteria optimization problems. SIAM J. Optim. 8(3), 631–657 (1998)
R. Cheng, Y. Jin, M. Olhofer, B. Sendhoff, A reference vector guided evolutionary algorithm for many-objective optimization. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 20(5), 773–791 (2016)
X. Zhang, Y. Tian, R. Cheng, Y. Jin, An efficient approach to nondominated sorting for evolutionary multi-objective optimization. IEEE Trans. E Comput. 19(2), 201–213 (2015)
S. Kayalvizhi, D. M. V. Kumar, Dispatchable DG planning in distribution networks considering costs, in Proc. IEEE Int. Conf. Recent Develop. Control, Autom. Power Eng. (2016)
K. Deb, A. Pratap, S. Agarwal, T. Meyarivan, A fast and elitist multi-objective genetic algorithm: NSGA-II. IEEE Trans. Evol. Comput. 6(2), 182–197 (2002)
D. Das, D.P. Kothari, A. Kalam, Simple and efficient method for load flow solution of radial distribution networks. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 17(5), 335–346 (1995)
Funding
No funding is received for this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no known conflicts of interest associated with this Manuscript and there has been no significant financial support for this work that could have influenced its outcome.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Prasad, C.B., Kumar, D.M.V. Meter Placement in Active Distribution System using Objective Discretization and Indicator-Based Multi-Objective Evolutionary Algorithm with Adaptive Reference Point Method. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. B 103, 887–901 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-021-00703-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40031-021-00703-5