Abstract
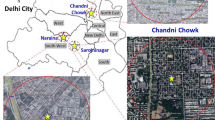
The fate of air pollution at any location calls for a critical knowledge of sources, its land-use attributes, and the prevailing meteorology. The accountability of all these ultimately enables air quality managers in sound decision making process for air quality assessment and management. The aim of this study is to assess the status of a critical pollutant (PM2.5) at selected locations in Delhi city and the subsequent formulation of source-specific control measures considering the surrounding local activities. The study analyzed a robust three years dataset of PM2.5 of seven stations located at institutional, residential, commercial and kerbside land-use types. Annual, seasonal, monthly and daily variations have been ascertained to determine variations in the activity profiles in terms of the activity types and their levels. The variations have been correlated with the likely sources found during field investigation. Further, a comparative analysis has been done by analyzing lockdown period data to evaluate the impact of restricted activities/sources. The study concludes by focusing on the need of development of source-specific interventions for effective air quality improvement.





Similar content being viewed by others

Data availability
Data sharing not applicable to this article as no datasets were generated or analyzed during the current study. This is a review article and data were compiled from secondary literature.
References
World Health Organization (WHO) (2022). Billions of people still breathe unhealthy air: new WHO data. https://www.who.int/news/item/04-04-2022-billions-of-people-still-breathe-unhealthy-air-new-who-data. Accessed April 2022
Lancet Planet Health (2022) Pollution and health: a progress update. https://doi.org/10.1016/S2542-5196(22)00090-0
H. Guo, S.H. Kota, S.K. Sahu, J. Hu, Q. Ying, A. Gao, H. Zhang, Source apportionment of PM2.5 in North India using source-oriented air quality models. Environ. Pollut. 231, 426–436 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2017.08.016
P. Goyal, S. Gulia, S.K. Goyal, Review of land use specific source contributions in PM 2.5 concentration in urban areas in India. Air Qual. Atmos. Health 14, 1–14 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11869-020-00972-x
S. Sharma, M. Khare, S.H. Kota, Action plans to reduce PM2.5 concentrations in hotspots of Delhi-NCR using a one-way coupled modeling approach. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 22, 210377 (2022)
P. Kumar, S. Jain, B.R. Gurjar, L. Morawska, New directions: can a “blue sky: return to Indian megacities?” Atmos. Environ. 71, 198–201 (2013)
S.M. Hama, P. Kumar, R.M. Harrison, W.J. Bloss, M. Khare, S. Mishra, A. Namdeo, R. Sokhi, P. Goodman, C. Sharma, Four-year assessment of ambient particulate matter and trace gases in the Delhi-NCR region of India. Sustain. Cities Soc. 54, 102003 (2020)
A.K. Gorai, P.B. Tchounwou, S.S. Biswal, F. Tuluri, Spatio-temporal variation of particulate matter (PM2.5) concentrations and its health impacts in a mega city. Delhi India Environ Health Insights 12, 1178630218792861 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1177/1178630218792861
Sharma, M., Dikshit, O. (2016). Comprehensive study on air pollution and greenhouse gases (GHGs) in Delhi. Final report, prepared by IIT Kanpur, sponsored by Delhi pollution control committee, New Delhi. 298
S. Gokhale, Traffic flow pattern and meteorology at two distinct urban junctions with impacts on air quality. Atmos. Environ. 45(10), 1830–1840 (2011). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.atmosenv.2011.01.015
Automotive Research Association of India (ARAI). The Energy Resources Institute (TERI) (2018). Source apportionment of PM2.5 and PM10 of Delhi NCR for identification of major sources. 560 https://www.teriin.org/sites/default/files/2018-08/Report_SA_AQM-Delhi-NCR_0.pdf
C. Perrino, S. Tiwari, M. Catrambone, S. Dalla Torre, E. Rantica, S. Canepari, Chemical characterization of atmospheric PM in Delhi, India, during different periods of the year including Diwali festival. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2(4), 418–427 (2011). https://doi.org/10.5094/APR.2011.048
S.K. Guttikunda, B.R. Gurjar, Role of meteorology in seasonality of air pollution in megacity Delhi. India Environ. monit. assess. 184(5), 3199–3211 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-011-2182-8
S. Gulia, S.M.S. Nagendra, M. Khare, Extreme events of reactive ambient air pollutants and their distribution pattern at urban hotspots. Aerosol Air Qual. Res. 17(2), 394–405 (2016). https://doi.org/10.4209/aaqr.2016.06.0273
Census, Population Census (2011), https://www.census2011.co.in/. Accessed 12 January 2023
S. Gulia, I. Khanna, K. Shukla, M. Khare, Ambient air pollutant monitoring and analysis protocol for low and middle income countries: an element of comprehensive urban air quality management framework. Atmos. Environ. 222, 117120 (2020)
S. Gulia, P. Prasad, S.K. Goyal, R. Kumar, Sensor-based wireless air quality monitoring network (SWAQMN): a smart tool for urban air quality management. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 11(9), 1588–1597 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apr.2020.06.016
Central Control Room for Air Quality Management: all India. https://app.cpcbccr.com/ccr/#/caaqm-dashboard-all/caaqm-landing/data. Accessed 20 November 2022
S. Gulia, P. Goyal, M. Prakash, S.K. Goyal, R. Kumar, Policy interventions and their impact on air quality in Delhi City: an analysis of 17 years of data. Water Air Soil Pollut. 232(11), 1–13 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05402-x
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AKJ contributed to Literature Review, Original Writing and Design of Paper, S contributed to Supervision, Conceptualization, Critical Review and Re-write SKM contributed to Conceptualization and Critical Review.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Jha, A.K., Suman & Mishra, S.K. Critical Analysis of PM2.5 in Delhi Region to Strategize Effective Air Pollution Management Plan. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 105, 49–59 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-023-00777-y
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-023-00777-y