Abstract
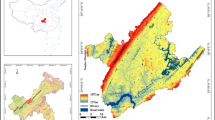
Renewable energy sources are an extremely important component of human life on today's globe. In Ethiopia, 80 percent of the population lives in rural areas with limited access to modern energy. The primary goal of this research was to use a Geographic Information System to identify suitable potential sites for small-scale hydropower in the Fetam Rivers. There were six prospective intake sites discovered using the digital elevation model (30 × 30 m) by converting to contour and identifying head potential along the river, which were coded according to their proximity to town and ease of access. Stream flow data were checked for consistency, outlier testing, and the construction of flow duration curves for ungauged rivers by transferring using the area ratio approach. While the power generated has been approximated, potential sites for implementation have been ranked based on minimum mean monthly stream discharge, net head availability, utility access, and town distance from the grid. The digital elevation model is one of the key driving forces for studying physical processes of surface resources, according to the findings of the study. The findings of the analyses suggest that the examined regions have a maximum and minimum significant potential for small-scale hydropower for use of energy resources of 8,288.48 and 122.52 kW, respectively. Using multi-criteria analysis of eligible locations, it is possible to rank as well as beyond the 6 chosen sites, with site 3 diversions coming in first and site 5 coming in second, according to the specified criteria.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
R.P. Tarife, A.P. Tahud, E.J.G. Gulben et al., Application of geographic information system (GIS) in hydropower resource assessment: a case study in Misamis Occidental, Philippines. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Develop. 8, 507 (2017)
V. Sammartano, L. Liuzzo, G. Freni, Identification of potential locations for run-of-river hydropower plants using a GIS-based procedure. Energies 12, 3446 (2019)
Y. Wada School of graduate studies jimma institute of technology faculty of civil and environmental engineering department of hydraulic and water resources engineering. jimma university. (2018)
S. Hameer, N. Ejigu, A prospective review of renewable energy developments in Ethiopia. AAS Open Res. 3, 64 (2020)
M.K. Ayele, GIS based assessment of hydropower potential (a case study on Gumara river basin). Am. Acad. Sci. Res. J. Eng. Technol. Sci. 69, 26–44 (2020)
P. Punys, A. Dumbrauskas, A. Kvaraciejus et al., Tools for small hydropower plant resource planning and development: a review of technology and applications. Energies 4, 1258–1277 (2011)
Y. Tian, F. Zhang, Z. Yuan et al., Assessment power generation potential of small hydropower plants using GIS software. Energy Rep. 6, 1393–1404 (2020)
A.G. Mulat, S.A. Moges, The impacts of upper Blue Nile Dams construction on agricultural water availability of sudan. Water Pract. Technol. 15, 437–449 (2020)
H. Desalegn, A. Mulu, Mapping flood inundation areas using GIS and HEC-RAS model at Fetam river, upper Abbay basin. Ethiop. Sci. African 12, e00834 (2021)
W.B. Bull, L.D. McFadden, Tectonic geomorphology north and south of the Garlock fault, California, in Geomorphology in arid regions. (Routledge, London, 2020), pp.115–138
M. Fazzini, C. Bisci, P. Billi, The climate of Ethiopia, in Landscapes and landforms of Ethiopia. (Springer, Netherlands, 2015), pp.65–87
A. Tamiru, M. Fakhruldin, A. Mohd Amin, et al. Gas turbines health prognostics: A short review. (2006)
H. Ono, M.D. Basson, H. Ito, P300 inhibition enhances gemcitabine-induced apoptosis of pancreatic cancer. Oncotarget 7, 51301 (2016)
H. Desalegn, A. Mulu, Flood vulnerability assessment using GIS at Fetam watershed, upper Abbay basin. Ethiop. Heliyon 7, e05865 (2021)
M. Dekavalla, D. Argialas, Evaluation of a spatially adaptive approach for land surface classification from digital elevation models. Int. J. Geogr. Inf. Sci. 31, 1978–2000 (2017)
S. Moges, E. Anagnostou, D.G. Eshete, et al. (2020) Integration of SWAT and remote sensing techniques to simulate soil moisture in data scarce micro-watersheds: a case of awramba micro-watershed in the upper blue nile basin, ethiopia. In: advances of science and technology: 7th EAI international conference, ICAST 2019, Bahir Dar, Ethiopia, August 2–4, 2019, Proceedings. (Springer Nature, 294)
H. Piégay, F. Arnaud, B. Belletti et al., Remotely sensed rivers in the Anthropocene: State of the art and prospects. Earth Surf. Proc. Land. 45, 157–188 (2020)
D.G. Larentis, W. Collischonn, F. Olivera et al., Gis-based procedures for hydropower potential spotting. Energy 35, 4237–4243 (2010)
F. Dikbas, M. Yasar, Data-driven modeling of flows of antalya basin and reconstruction of missing data. Iran. J. Sci. Technol. Trans. Civ. Eng. 44, 1335–1344 (2020)
C. Jaliu, D. Diaconescu, M. Neagoe et al., The eco-impact of small hydro implementation. Environ. Eng. Manag. J. (EEMJ) 8(4), 837–841 (2009)
M.A. Wegene, N.G. Gejo, D.Y. Bedecha et al., Utilization of preconception care and associated factors in Hosanna Town. Southern Ethiop. PloS one 17, e0261895 (2022)
C.N. Kroll, K.E. Croteau, R.M. Vogel, Hypothesis tests for hydrologic alteration. J. Hydrol. 530, 117–126 (2015)
J.J. Fritz, Small and mini hydropower systems: resource assessment and project feasibility. (1984)
K. Motwani, S. Jain, R. Patel, Cost analysis of pump as turbine for pico hydropower plants–a case study. Proc. Eng. 51, 721–726 (2013)
N. Zelalem Integration of hydropower in the ongoing reservoir studies of lake tana sub-basin. (2008)
C. Kasamba, P.M. Ndomba, S.B. Kucel et al., Analysis of flow estimation methods for small hydropower schemes in Bua River. Energy Power Eng. 7, 55 (2015)
A.R. Inversin Micro-hydropower sourcebook; a practical guide to design and implementation in developing countries. (1986)
Seymore T. Bioaccumulation of metals in barbus marequensis from the olifants river, kruger national park and lethal levels of manganese to juvenile oreochromis mossambicus. University of Johannesburg, South Africa. (2014)
U.G. Wali, Estimating hydropower potential of an ungauged stream. Int. J. Emerg. Technol. Adv. Eng. 3, 592–600 (2013)
K. Lawrence, E. de la Hoz, J. Barker, et al. Principal aquatic scientist. (2017)
S. Otuagoma, E. Ogujor, P. Kuale, Evaluation of the small hydropower potential of river Ethiope using the RETScreen software. Int. J. Eng. Res. 5, 1–5 (2016)
S. Kucukali, K. Baris, Assessment of small hydropower (SHP) development in Turkey: laws, regulations and EU policy perspective. Energy Policy 37, 3872–3879 (2009)
I. Yüksel, Development of hydropower: a case study in developing countries. Energy Sour. Part B 2, 113–121 (2007)
P. Kumar, S. Kunwar, V. Garg, Hydropower sites investigation and sensitivity analysis of assessed potential using geospatial inputs, in Development of water resources in India. (Springer, Cham, 2017), pp.499–522
K. Kumar, R. Saini, A review on operation and maintenance of hydropower plants. Sustain. Energy Technol. Assess. 49, 101704 (2022)
ESHA, Guide on how to develop a small hydropower plant, European Small Hydropower Association-ESHA, Belgium (2004)
C.S. Kaunda, C.Z. Kimambo, and T.K. Nielsen Hydropower in the context of sustainable energy supply: a review of technologies and challenges. Int. Sch. Res. Not. (2012)
G. Choy, O. Khalilzadeh, K.J. Dreyer et al., Current applications and future impact of machine learning in radiology. Radiology 288(2), 318 (2018)
Funding
The authors have not disclosed any funding.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have not disclosed any competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Desalegn, H., Damtew, B., Mulu, A. et al. Identification of Potential Sites for Small-Scale Hydropower Plants Using a Geographical Information System: A Case Study on Fetam River Basin. J. Inst. Eng. India Ser. A 104, 81–94 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-022-00692-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40030-022-00692-8