Abstract
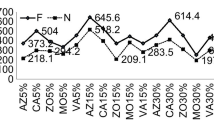
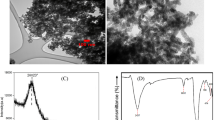
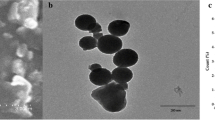
Assessment of effect of nanoparticles on plant growth is essential before adopting nanotechnology in agricultural sector. Four types of metal/metal oxide nanoparticles (NPs) viz. Zinc oxide (ZnO), Titanium oxide (TiO2), Copper oxide (CuO) and Silver (Ag) were studied for their effect on seed germination, vigour and yield in fodder crops, oat and berseem. Nanoparticles were synthesized and characterized before seed treatment. Seeds were treated with NPs at 750 mg (D1), 1000 mg (D2) and 1250 mg/kg of seed (D3). The effect of nanoparticles on seed germination and vigour was studied in the laboratory and seedling emergence rate, tiller number and seed yield were studied in the field. Nanoparticles (except TiO2 and CuO in berseem) enhanced germination at lower dose (D1), but reduction in root and shoot length was noticed at higher doses (D2 and D3). All four types of nanoparticles (NPs) in oat and only Ag in case of berseem enhanced germination to 100 % at lowest dose (D1). Substantial changes were noticed in field observations due to nanoparticle treatments regarding seedling emergence rate, tiller number and seed yield. Among the different NPs, TiO2 produced maximum seed yield at highest dose. No significant effect of nanoparticles on soil microbial populations was noticed during the field study. The experiment confirmed the dose-specific effect of nanoparticles on seed germination, crop growth and seed yield in oat and berseem crops.









Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tarafdar JC (2012) Perspectives of nanotechnological applications for crop production. NAAS News 12:8–11
Pramanik P, Maity A (2013) Nanopollution—a growing issue. Natl Environ Sci Acad Newsl 16(7):2
Subramanian KS, Tarafdar JC (2011) Prospects of nanotechnology in Indian farming. Indian J Agric Sci 81:887–893
Yang L, Watts DJ (2005) Particle surface characteristics may play an important role in phytotoxicity of alumina nanoparticles. Toxicol Lett 158:122–132
Lee WM, An YJ, Yoon H, Kwbon HS (2008) Toxicity and bioavailability of copper nanoparticles to the terrestrial plants mung bean (Phaseolus radiatus) and wheat (Triticum aestivum): plant agar test for water-insoluble nanoparticles. Environ Toxic Chem 27:1915–1921
Khodakovskaya M, Dervishi E, Mahmood M, Xu Y, Li Z, Watanabe F, Biris AS (2009) Carbon nanotubes are able to penetrate plant seed coat and dramatically affect seed germination and plant growth. ACS Nano 3(10):3221–3227
Prasad TN, Sudhakar P, Sreenivasulu Y, Latha P, Munaswamy V, Reddy KR, Sreeprasad TS, Sajanlal PR, Pradeep T (2012) Effect of nanoscale zinc oxide particles on the germination, growth and yield of peanut. J Plant Nutr 35(6):905–927
Lu CM, Zhang CY, Wen JQ, Wu GR, Tao MX (2002) Research of the effect of nanometer materials on germination and growth enhancement of Glycine max and its mechanism. Soybean Sci 21:168–172
Zhang L, Hong F, Lu S, Liu C (2005) Effect of nano-TiO2 on strength of naturally aged seeds and growth of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 106:279–297
Hong F, Zhou J, Liu C, Yang F, Wu C, Zheng L, Yang P (2005) Effects of nano-TiO2 on photochemical reaction of chloroplasts of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 105:269–279
Hong F, Yang F, Liu C, Gao Q, Wan Z, Gu F, Wu C, Ma Z, Zhou J, Yang P (2005) Influence of nano-TiO2 on the chloroplast aging of spinach under light. Biol Trace Elem Res 104:249–260
Yang F, Liu C, Gao F, Su M, Wu X, Zheng L, Hong F, Yang P (2007) The improvement of spinach growth by nano-anatase TiO2 treatment is related to nitrogen photoreduction. Biol Trace Elem Res 119:77–88
Gao F, Hong F, Liu C, Zheng L, Su M, Wu X, Yang F, Wu C, Yang P (2006) Mechanism of nano-anatase TiO2 on promoting photosynthetic carbon reaction of spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 111:239–253
Moghaddam AB, Nazari T, Badraghi J, Kazemzad M (2009) Synthesis of ZnO nanoparticles and electrodeposition of polypyrrole/ZnO nanocomposite film. Int J Electrochem Sci 4:247–257
Lee PC, Meisel D (1982) Adsorption and surface—enhanced Raman of dyes on silver and gold sols. J Phys Chem 86:3391–3395
Wongpisutpaisan N, Charoonsuk P, Vittayakorn N, Pecharapa W (2011) Sonochemical synthesis and characterization of copper oxide nanoparticles. Energy Proced 9:404–409
Arami H, Mazloumi M, Khalifehzadeh R, Sadmezhaad SK (2007) Sonochemical preparation of TiO2 nanoparticles. Mater Lett 61:4559–4561
Braca A, Tommasi ND, Bari LD, Pizza C, Politi M, Morelli I (2001) Antioxidant principles from Bauhinia t arapotensis. J Nat Prod 64:892–895
Pikovskaya RI (1948) Mobilization of phosphorus in soil in connection with vital activity of some microbial species. Mikrobiologiya 17:362–370
Omeliansky WL (1902) Ueber die Garung der Cellulose. Proc Indiana Acad Sci Cent F Bakt II 8:225–231
Subba Rao NS (1999) In soil microbiology, 4th edn. Oxford and IBH Pub. Co Pvt. Ltd., New Delhi
Navarro E, Baun A, Behra R, Hartmann NB, Filser J, Miao A, Quigg A, Santschi PH, Sigg L (2008) Environmental behaviour and ecotoxicity of engineered nanoparticles to algae, plants, and fungi. Ecotoxicology 17:372–386
Wierzbicka M, Obidzin´SKA J (1998) The effect of lead on seed imbibition and germination in different plant species. Plant Sci 137:155–171
Sresty TVS, Rao KVM (1999) Ultrastructural alterations in response to zinc and nickel stress in the root cells of pigeonpea. Environ Exp Bot 41:3–13
Lin D, Xing B (2007) Phytotoxicity of nanoparticles: inhibition of seed germination and root growth. Environ Pollut 150:243–250
Xuming W, Fengqing G, Linglan M, Jie L, Sitao Y, Ping Y, Fashui H (2008) Effects of nano-anatase on Ribulose-1, 5-bisphophate carboxylase/oxygenase mRNA expression in spinach. Biol Trace Elem Res 126:280–289
Riahi-Madvar A, Rezaee F, Jalali V (2012) Effects of alumina nanoparticles on morphological properties and antioxidant system of Triticum aestivum. Iran J Plant Physiol 3(1):595–603
Mahmoodzadeh H, Nabavi M, Kashefi H (2013) Effect of nanoscale titanium dioxide particles on the germination and growth of canola (Brassica napus). J Ornam Plants 3(1):25–32
Shah V, Belozerova I (2009) Influence of metal nanoparticles on the soil microbial community and germination of lettuce seeds. Water Air Soil Pollut 197:143–148
Corredor E, Testillano PS, Coronado MJ, González-Melendi P, Fernández-Pacheco R, Marquina C, Ibarra MR, de la Fuente JM, Rubiales D, Pérez-De-luque A, Risueño MC (2009) Nanoparticle penetration and transport in living pumpkin plants: in situ subcellular identification. BMC Plant Biol 9:45–54
Rico C, Majumdar S, Duarte-Gardea M, Peralta JR, Gardea-Torresdey JL (2011) Interaction of nanoparticles with edible plants and their possible implications in the food chain. J Agric Food Chem 59:485–498
Adhikari T, Kundu S, Biswas AK, Tarafdar J, Subba Rao A (2012) Effect of copper oxide nano particle on seed germination of selected crops. J Agric Sci Technol A 2:815–823
Roghayyeh SMS, Mehdi TS, Rauf SS (2010) Effects of nano-iron oxide particles on agronomic traits of soybean. Not Sci Biol 2:112–113
Musante C, White JC (2010) Toxicity of silver and copper to Cucurbita pepo: differential effects of nano and bulk-size particles. Environ Toxic. doi:10.1002/tox.20667
Miao AJ, Quigg A, Schwehr K, Xu C, Santschi P (2007) Engineered silver nanoparticles (ESNs) in coastal marine environments: bioavailability and toxic effects to the phytoplankton Thalassiosira weissflogii. In: Second international conference on the environmental effects of nanoparticles and nanomaterials, 24–25th sep, London UK
Tong Z, Bischoffff M, Nies L, Apppplegate B, Turco RF (2007) Impact of fullerene (C60) on a soil microbial community. Environ Sci Technol 51:2985–2991
Nyberg L, Turco RF, Nies L (2008) Assensing the impact of nanomaterial on anaerobic microbial communities. Environ Sci Technol 42:1938–1943
Brunnnner TI, Wick P, Manser P, Spohn P, Grass RN, Limbach LK, Bruinink A, Stark WJ (2006) In vitro cytotoxicity of oxide nanoparticles: comparison to asbestos, silica, and effect of particle solubility. Environ Sci Technol 40:4374–4381
Murashov V (2006) Comments on ‘‘particle surface characteristics may play an important role in phytotoxicity of alumina nanoparticles’’ by Yang L, Watts DJ, Toxicology Letters, 2005, 158, 122–132. Toxicol Lett 164:185–187
Acknowledgments
The authors duly acknowledge the facilities provided by Department of Nanoscience and Technology, Tamil Nadu Agriculture University, Coimbatore and Innovation Centre, Bundelkhand University, Jhansi to conduct the laboratory experiment and Indian Grassland and Fodder Research Institute, Jhansi to conduct rest of the study. To the best of the knowledge there is no conflict of interest involved in the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Maity, A., Natarajan, N., Vijay, D. et al. Influence of Metal Nanoparticles (NPs) on Germination and Yield of Oat (Avena sativa) and Berseem (Trifolium alexandrinum). Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 88, 595–607 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-016-0796-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-016-0796-x