Abstract
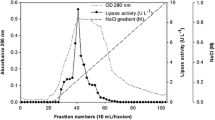
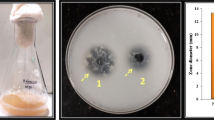
An extracellular lipase produced by marine fish intestinal isolate Halobacillus sp. AP-MSU 8 was purified and characterized. The lipase was purified to homogeneity using ammonium sulphate precipitation, DEAE-Sepharose anion exchange chromatography and Sephadex G-75 gel filtration chromatography. The overall purification protocols resulted in 25 % yield of lipase with 10.6-fold. The SDS-PAGE (12 %) analysis of purified lipase resulted in the molecular mass of the purified lipase as 25-kDa. The optimum pH and temperature required for maximum activity of purified lipase was 9.0 and 40 °C respectively. Also, this lipase is halo tolerant and requires 2.5 M NaCl for maximum activity. The activity of the purified lipase was more in the presence of BaCl2 and MgSO4, and in contrast the enzyme activity was totally inhibited in the presence of ZnSO4 and ZnCl2. The surfactants such as polyethylene glycol and Tween 20 enhanced the lipase activity. Likewise 10 % concentration of organic solvents such as benzene and acetone stimulated the lipase activity, whereas at 20 % concentration all the tested solvents inhibited the lipase activity.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Castro-Ochoa LD, Gomez CR, Alfaro GV, Ros RO (2005) Screening, purification and characterization of the thermoalkalophilic lipase produced by Bacillus thermoleovorans CCR11. Enzym Microb Technol 37:648–654
Liu Z, Chi Z, Wang L, Li J (2008) Production, purification and characterization of an extracellular lipase from Aureobasidium pullulans HN2.3 with potential application for the hydrolysis of edible oils. Biochem Eng J 40:445–451
Chen S, Qian L, Shi B (2007) Purification and properties of enantioselective lipase from a newly isolated Bacillus cereus C71. Process Biochem 42:988–994
Kanjanavas P, Khuchareontaworn S, Khawsak P, Pakpitcharoen A, Pothivejkul K, Santiwatanakul S, Matsui K, Kajiwara T, Chansiri K (2010) Purification and characterization of organic solvent and detergent tolerant lipase from thermotolerant Bacillus sp. RN2. Int J Mol Sci 11:3783–3792
Kumar S, Kikon K, Upadhyay A, Kanwar SS, Gupta R (2005) Production, purification, and characterization of lipase from thermophilic and alkaliphilic Bacillus coagulans BTS-3. Protein Expr Purif 41(1):38–44
Lianghua T, Liming X (2005) Purification and partial characterization of a lipase from Bacillus coagulans ZJU318. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 125:139–146
Madan B, Mishra P (2009) Overexpression, purification and characterization of organic solvent stable lipase from Bacillus licheniformis RSP-09. J Mol Microb Biotechnol 17:118–123
Debashish G, Malay S, Barindra S, Joydeep M (2005) Marine Enzymes. Adv Biochem Eng Biotechnol 96:189–218
Rohban R, Amoozegar MA, Ventosa A (2009) Screening and isolation of halophilic bacteria producing extracellular hydrolyses from Howz Soltan lake. Iran J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:333–340
Li X, Yu HY, Lin YF (2012) Purification and characterization of an extracellular esterase from a moderately halophilic bacterium, Halobacillus sp. strain LY5. Afr J Biotechnol 11(23):6327–6334
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantitation of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein-dye binding. Ann Biochem 72(1–2):248–254
Zibaee A, Sadeghi-Sefidmazgib A, Fazeli-Dinan M (2011) Properties of a lipase produced by Beauveria bassiana: purification and biochemical studies. Biocontrol Sci Technol 21(3):317–331
Zhang J, Guan R, Tan Z, Yu Y, Hou Z, Qi Z, Wang S (2005) Purification and properties of lipases/esterases from a Bacillus strain for enantioselective resolution of (S)-ketoprofen. Artif Cells Blood Substit Biotechnol 33:435–445
Lee KW, Bae HA, Shin GS, Lee YH (2006) Purification and catalytic properties of novel enantioselective lipase from Acinetobacter sp. ES-1 for hydrolysis of (S)-ketoprofen ethyl ester. Enzym Microb Technol 38:443–448
Yu M, Qin S, Tan T (2007) Purification and characterization of the extracellular lipase Lip2 from Yarrowia lipolytica. Process Biochem 42:384–391
Bharti MK, Khokhar D, Pandey AK, Gaur AK (2013) Purification and characterization of lipase from Aspergillus japonicas: a potent enzyme for biodiesel production. Natl Acad Sci Lett 36(2):151–156
Burg B (2003) Extremophiles as a source for novel enzymes. Curr Opin Microbiol 6:213–218
Boutaiba S, Bhatnagar T, Hacene H, Mitchell DA, Baratti JC (2006) Preliminary characterisation of a lipolytic activity from an extremely halophilic archaeon, Natronococcus sp. J Mol Catal B 41:21–26
Ozcan B, Ozyilmaz G, Cokmus C, Caliskan M (2009) Characterization of extracellular esterase and lipase activities from five halophilic archaeal strains. J Ind Microbiol Biotechnol 36:105–110
Gopinath SCB, Hilda A, priya TL, Annadurai G (2002) Purification of lipase from Cunninghamella verticillata and optimization of enzyme activity using response surface methodology. World J Microbiol Biotechnol 18:449–458
Rubingh DN (1996) The influence of surfactants on enzyme activity. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 1:598–603
Zacchigna M, Di Luca G, Lassiani L, Varnavas A, Boccù E (1998) Properties of methoxy (polyethylene glycol)-lipase from Candida rugosa in organic solvents. II Farmaco 53(12):758–763
Mine Y, Fukunaga K, Yoshimoto M, Nakao K, Sugimura Y (2001) Modification of lipases with polyethylene glycol and polyoxyethylene detergents and their catalytic activities in organic solvents. J Biosci Bioeng 92(6):539–543
Ruiz B, Farrés A, Langley E, Masso F, Sánchez S (2001) Purification and characterization of an extracellular lipase from Penicillium candidum. Lipids 36:283–289
Wang HK, Shao J, Wei YJ, Zhang J, Qi W (2011) A novel low-temperature alkaline lipase from Acinetobacter johnsonii LP28 suitable for detergent formulation. Food Technol Biotechnol 49(1):96–102
Talukder MMR, Zaman MM, Hayashi Y, Wu JC, Kawanishi T (2005) Pretreatment of Chromobacterium viscosum lipase with acetone increases its activity in sodium bis-(2-ethylhexyl) sulfosuccinate (AOT) reverse micelles. J Chem Technol Biotechnol 80:1166–1169
Seghal Kiran G, Shanmughapriya S, Jayalakshmi J, Selvin J, Gandhimathi R, Sivaramakrishnan S, Arunkumar M, Thangavelu T, Natarajaseenivasan K (2008) Optimization of extracellular psychrophilic alkaline lipase produced by marine Pseudomonas sp. (MSI057). Bioprocess Biosyst Eng 31:483–492
Ahmed EH, Raghavendra T, Madamwar D (2010) An alkaline lipase from organic solvent tolerant Acinetobacter sp. EH28: Application for ethyl caprylate synthesis. Bioresour Technol 101:3628–3634
Li S, Pang H, Lin K, Xu J, Zhao J, Fan L (2011) Refolding, purification and characterization of an organic solvent-tolerant lipase from Serratia marcescens ECU1010. J Mol Catal B 71:171–176
Nawani N, Dosanjh NS, Kaur J (1998) A novel thermostable lipase from a thermophilic Bacillus sp.: characterization and esterification studies. Biotechol Lett 20:997–1000
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the financial assistance extended in the form of a Senior Research Fellowship by the Council of Scientific and Industrial Research (CSIR), Ministry of Human Resource Development, Government of India to P. Esakkiraj. Also, they thank Dr. Georgina Sandoval (Industrial Biotechnology Department, CIATEJ, Guadalajara, Mexico) for her valuable suggestions, support and constant encouragement.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Esakkiraj, P., Prabakaran, G., Maruthiah, T. et al. Purification and Characterization of Halophilic Alkaline Lipase from Halobacillus sp.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 86, 309–314 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0437-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-014-0437-1