Abstract
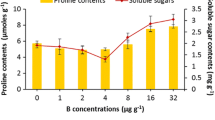
Greenhouse experiments were carried out to study the effect of boron (B) on certain biochemical constituents considering mung bean, Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek as an experimental crop. B as boric acid (H3BO3) was applied at the concentrations of 0, 1, 2, 4, 8, 16 and 32 μg B g−1 soil. Lower applied doses of B up to 4 μg g−1 resulted in an increase in chlorophyll and carotenoid contents and decrease in stress indicators viz. total phenol content and soluble leaf protein content. Maximum increment in chlorophyll and carotenoid contents was observed at 4 μg g−1 B concentrations, while at this concentration (4 μg g−1) maximum decrease in total phenol content and soluble leaf protein content was observed. Reciprocal relationship between total chlorophyll contents and total phenol content was observed. Adverse effect on selected biochemical constituents beyond 4 μg g−1 B concentrations reflected the importance of efficient and appropriate use of boron in agronomic practices for mung bean.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, San Diego
Loomis WD, Durst RW (1992) Chemistry and biology of boron. Biofactors 3:229–239
Nable RO, Bañuelos GS, Paull JG (1997) Boron toxicity. Plant Soil 193:181–198
Bergmann W (1992) Colour atlas: nutritional disorders of plants. Gustav Fischer, New York
Ardıc M, Sekmen AH, Turkan I, Tokur S, Ozdemir F (2009) The effects of boron toxicity on root antioxidant systems of two chickpea (Cicer arietinum L.) cultivars. Plant Soil 314:99–108. doi:10.1007/s11104-008-9709-y
Turan MA, Taban N, Taban S (2009) Effect of calcium on the alleviation of boron toxicity and localization of boron and calcium in cell wall of wheat. Not Bot Hort Agrobot Cluj 37(2):99–103
Blevins DG, Lukaszewski KM (1994) Proposed physiologic functions of boron in plants pertinent to animal and human metabolism. Environ Health Perspect 102(7):31–33
Blevins DG, Lukaszewski KM (1998) Boron in plant structure and function. Annu Rev Plant Physiol Plant Mol Biol 49:481–500. doi:10.1146/annurev.arplant.49.1.481
Arnon DI (1949) Copper enzymes in isolated chloroplasts: polyphenol oxidase in Beta vulgaris. Plant Physiol 24(1):1–15. doi:10.1104/pp.24.1.1
Aery NC (2010) Manual of environmental analysis. CRC Press, Boca Raton
Bradford MM (1976) A rapid and sensitive method for the quantification of microgram quantities of protein utilizing the principle of protein dye binding. Anal Biochem 72:248–254. doi:10.1016/0003-2697(76)90527-3
Mahadevan A, Sridhar R (1982) Methods in physiological plant pathology. Sivakami, Madras
Kastori R, Plesničar M, Panković D, Sakač Z (1995) Photosynthesis, chlorophyll fluorescence, and soluble carbohydrates in sunflower leaves as affected by boron deficiency. J Plant Nutr 18(9):1751–1763. doi:10.1080/01904169509365021
Inbaraj MP, Muthuchelian K (2011) Effect of boron and high irradiance stresses on chlorophyll, protein and starch content in leaves of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata L. Walp. P152). J Biosci Res 2(2):55–61
Yamauchi N, Watada AE (1994) Effectiveness of various phenolic compounds in degradation of chlorophyll by in vitro peroxidase-hydrogen peroxide system. J Jpn Soc Hortic Sci 63(2):439–444
Wang JZ, Tao ST, Qi KJ, Wu J, Wu HQ, Zhang SL (2011) Changes in photosynthetic properties and antioxidative system of pear leaves to boron toxicity. Afr J of Plant Sci 10(85):19693–19700. doi:10.5897/AJB11.2608
Lee CW, Jackson MB, Duysen ME, Freeman TP, Self JR (1996) Induced micronutrient toxicity in ‘Touchdown’ Kentucky Bluegrass. Crop Sci 36(3):705–712. doi:10.2135/cropsci1996.0011183X003600030031x
Landi M, Remorini D, Pardossi A, Guidi L (2013) Boron excess affects photosynthesis and antioxidant apparatus of greenhouse Cucurbita pepo and Cucumis sativus. J Plant Res. doi:10.1007/s10265-013-0575-1
Cervilla LM, Blasco B, Rios JJ, Rosales MA, Rodríguez ES, Rubio-Wilhelmi MM, Romero L, Ruiz JM (2012) Parameters symptomatic for boron toxicity in leaves of tomato plants. J Bot 2012(726206):17. doi:10.1155/2012/726206
Keles Y, Öncel I, Yenice N (2004) Relationship between boron content and antioxidant compounds in Citrus leaves taken from fields with different water source. Plant Soil 265:345–353. doi:10.1007/s11104-005-0646-8
Sakihama Y, Cohen MF, Grace SC, Yamasaki H (2002) Plant phenolic antioxidant and prooxidant activities: phenolics-induced oxidative damage mediated by metals in plants. Toxicology 177:67–80
Cakmak I, Römheld V (1997) Boron deficiency induced impairment of cellular function in plants. Plant Soil 193:71–83. doi:10.1023/A:1004259808322
Camacho-Cristóbal JJ, Rexach J, González-Fontes A (2008) Boron in plants: deficiency and toxicity. J Integr Plant Biol 50:1247–1255. doi:10.1111/j.1744-7909.2008.00742.x
Ruiz JM, Bretones G, Baghour M, Ragala L, Belakbir A, Romero L (1998) Relationship between boron and phenolic metabolism in tobacco leaves. Phytochemistry 48(2):269–272. doi:10.1016/S0031-9422(97)01132-1
Liakopoulos G, Karabourniotis G (2005) Boron deficiency and concentrations and composition of phenolic compounds in Olea europaea leaves: a combined growth chamber and field study. Tree Physiol 25(3):307–315. doi:10.1093/treephys/25.3.307
Mondy NI, Munshi CB (1993) Effect of boron on enzymatic discoloration and phenolic and ascorbic acid contents of potatoes. J Agric Food Chem 41:554–556. doi:10.1021/jf00028a009
Rivero RM, Ruiz JM, Garćia PC, López-Lefebre LR, Sánchez E, Romero L (2001) Resistance to cold and heat stress: accumulation of phenolic compounds in tomato and watermelon plants. Plant Sci 160:315–321. doi:10.1016/S0168-9452(00)00395-2
Wang W, Vinocur B, Shoseyov O, Altman A (2004) Role of plant heat-shock proteins and molecular chaperones in the abiotic stress response. Trends Plant Sci 9(5):244–252. doi:10.1016/j.tplants.2004.03.006
Bishnoi SK, Kumar B, Rani C, Datta KS, Kumari P, Sheoran IS, Angrish R (2006) Changes in protein profile of pigeonpea genotypes in response to NaCl and boron stress. Biol Plant 50(1):135–137. doi:10.1007/s10535-005-0088-4
Anuradha M, Nageswara RK, Sivaraju K, Krishnamurthy V (2009) Effect of boron stress on growth, soluble protein and enzyme activities in flue-cured tobacco. Indian J Plant Physiol 14(3):315–318
Rana DK, Aery NC (1999) Effect of aluminium stress on the biochemical constituents during early seedling growth of mustard. Bionature 19(2):47–50
Mali M, Aery NC (2009) Effect of silicon on growth, biochemical constituents, and mineral nutrition of cowpea. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 40:1041–1052. doi:10.1080/00103620902753590
Mani D, Sharma B, Kumar C, Balak S (2012) Cadmium and lead bioaccumulation during growth stages alters sugar and vitamin C content in dietary vegetables. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B 82(4):477–488
Kumar A, Aery NC (2012) Effect of tungsten on the growth, dry-matter production, and biochemical constituents of cowpea. Commun Soil Sci Plant Anal 43:1098–1107. doi:10.1080/00103624.2012.656171
Shyam R, Aery NC (2011) Influence of lanthanum on biochemical constituents and peroxidase activity of cowpea (Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.). Afr J Plant Sci 5(2):87–91
Shyam R, Aery NC (2012) Effect of cerium on growth, dry matter production, biochemical constituents and enzymatic activities of cowpea plants [Vigna unguiculata (L.) Walp.]. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr 12(1):1–14. doi:10.4067/S0718-95162012000100001
Kumar A, Aery NC (2011) Effect of tungsten on growth, biochemical constituents, molybdenum and tungsten contents in wheat. Plant Soil Environ 57(11):519–525
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to University Grant Commission, New Delhi for providing financial assistance in the form of meritorious fellowship to Kunal Seth.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Seth, K., Aery, N.C. Effect of Boron on the Contents of Chlorophyll, Carotenoid, Phenol and Soluble Leaf Protein in Mung Bean, Vigna radiata (L.) Wilczek. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 84, 713–719 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0293-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0293-4