Abstract
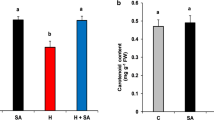
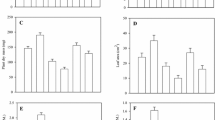
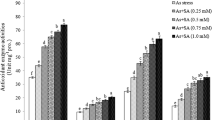
The present study was carried out to examine the effects of salicylic acid (SA) on growth and some physiobiochemical attributes in bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) plants exposed to copper stress. Exposure to copper significantly decreased root and shoot growth, chlorophyll and protein but increased malondialdehyde (MDA), carotenoid and proline. Exogenous application of SA acid was found to alleviate negative effects generated by heavy metals like copper in plant. Salicylic acid significantly increased root and shoot growth, chlorophyll and protein. In addition SA reduced the proline, MDA and carotenoid in copper stressed plants. The data suggest that the useful effect of SA during an earlier growth period could be related to avoidance of damage caused by exposure to copper. In addition, exogenous SA may improve the tolerance of the plant to the copper toxicity.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Prasad R (2012) Micro mineral nutritient deficiencies in humans, animals and plants and their amelioration. Proc Natl Acad Sci, India Sect B 82(2):225–233
Marschner H (1995) Mineral nutrition of higher plants. Academic Press, London
Ouzounidou G (1995) Cu ions mediated changes in growth, chlorophyll and other ion contents in a Cu tolerant Koeleria splendens. Biol Plant 37(1):71–78
Flemming CA, Trevors JT (1989) Cu toxicity and chemistry in the environment: a review. Water Air Soil Pollut 44(1):143–158
Demirevska-Kepova K, Simova-Stoilova L, Stoyanova Z, Holzer R, Feller U (2004) Biochemical changes in barley plants after excessive supply of Cu and Mn. Environ Exp Bot 52:253–266
Hayat Q, Hayata S, Irfan M, Ahmad A (2010) Effect of exogenous SA under changing environment: a review. Environ Exp Bot 68:14–25
Belkhadi A, Hediji H, Abbes Z, Nouairi I, Barhoumi Z, Zarrouk M, Chaïbi W, Djebali W (2010) Effects of exogenous SA pre-treatment on Cd toxicity and leaf lipid content in Linum usitatissimum L. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 73:1004–1011
Mishra A, Choudhuri MA (1999) Effects of SA on heavy metal induced membrane degradation mediated by lipoxygenase in rice. Biol Plant 42:409–415
Khodary SEA (2004) Effect of SA on the growth, photosynthesis and carbohydrate metabolism in salt stressed maize plants. Int J Agr Biol 6:5–8
Strobel NE, Kuc JA (1995) Chemical and biological inducers of systemic resistance to pathogens protect cucumber and tobacco plants from damage caused by paraquat and CuCl2. Phytopathology 85:1306–1310
El-Tayeb MA (2005) Response of barley grains to the interactive efftect of salinity and SA. Plant Growth Regul 45:215–224
Kacar B (1972) Chemical analysis of soil and plant. Ankara University Press, Faculty of Agriculture Publication No. 53, Ankara
Heath RL, Packer L (1968) Photoperoxidation in isolated chloroplasts. I. Kinetics and Stoichiometry of fatty acid peroxidation. Arch Biochem Biophys 125:189–198
Bates LS, Waldren SP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water-stress studies. Plant Soil 39:205–207
Larson LA, Beevers H (1965) Amino acid metabolism in young pea seedlings. Plant Physiol 40:424–432
Lowry OH, Rosebrough NJ, Randall RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–275
Witham FH, Blaydes DF, Dewlin RM (1971) Experiments in Plant Physiology. Von Nostrand Reinhold Company, New York, pp 55–56
Sandoval-Yapiz MR (2004) Reguladores de crecimiento XXIII: efecto del acido salicilico en la biomasa del cempazuchitl (Tagetes erecta). Tesis de Licenciatura, Instituto Tecnologico Agropecuario, Mexico
Gutierrez-Coronado M, Trejo CL, Larque-Saavedra A (1998) Effects of SA on the growth of roots and shoots in soybean. Plant Physiol Biochem 36:563–565
Choudhury S, Panda SK (2004) Role of SA in regulating Cd induced oxidative stress in Oryza sativa L. roots. Bulg J Plant Physiol 30:95–110
Zhou ZS, Guo K, Elbaz AA, Yang ZM (2009) SA alleviates Hg toxicity by preventing oxidative stress in roots of Medicago sativa. Env Exp Bot 65:27–34
Shafio M, Zafar IM, Athar M (2008) Effect of Pb and Cd on germination and seedling growth of Leucaena leucocephal. J Appl Sci Environ Manage 12(2):61–66
Kazemi N, Khavari-Nejad RA, Fahimi H, Saadatmand S, Nejad-Sattari T (2010) Effects of exogenous SA and NO on lipid peroxidation and antioxidant enzyme activities in leaves of B. napus L. under nickel stres. Sci Hort 126:402–407
Hayat S, Fariduddin Q, Ali B, Ahmad A (2005) Effect of SA on growth and enzyme activities of wheat seedlings. Acta Agron Hung 53:433–437
Wang H, Feng T, Peng X, Yan M, Tang X (2009) Up-regulation of chloroplastic antioxidant capacity is involved in alleviation of Ni toxicity of Zea mays L. by exogenous SA. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72:1354–1362
Popova LP, Maslenkova LT, Yordanova RY, Ivanova AP, Krantev AP, Szalai G, Janda T (2009) Exogenous treatment with SA attenuates Cd toxicity in pea seedlings. Plant Physiol Biochem 47:224–231
Young AJ (1991) The photoprotective role of carotenoids in higher plants. Physiol Plant 83:702–708
Moharekar ST, Lokhand SD, Hara T, Tanaka R, Tanaka A, Chavan PD (2003) Effect of salicylic acid on chlorophyll and caroteniods contents of wheat and moong seedlings. Photosynthetica 41:315–317
Matysik J, Alia Bhalu B, Mohanty P (2002) Molecular mechanisms of quenching of reactive oxygen species by proline under stress in plants. Curr Sci 82(5):525–532
Lombardi L, Sebastiani L (2005) Copper toxicity in Prunus cerasifera: growth and antioxidant enzymes responses of in vitro grown plants. Plant Sci 168:797–802
Backor M, Fahselt D, Wu CT (2004) Free proline content is positively correlated with Cu tolerance of the lichen photobiont Trebouxia erici. Plant Sci 167:151–157
Kang G, Wang C, Sun G, Wang Z (2003) SA changes activities of H2O2-metabolizing enzymes and increases the chilling tolerance of banana seedlings. Environ Exp Bot 34:56–59
Guo B, Liang YC, Zhu YG, Zhao FJ (2007) Role of SA in alleviating oxidative damage in rice roots subjected to Cd stress. Environ Pollut 147:743–749
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zengin, F. Exogenous Treatment with Salicylic Acid Alleviating Copper Toxicity in Bean Seedlings. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 84, 749–755 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0285-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0285-4