Abstract
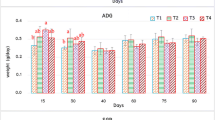
To evaluate the dietary effect of ethanolic extract of Pedalium murex (Bada Gokshru) on growth and haemato-immunological parameters of an Indian major carp, Labeo rohita fingerlings, a 45 days study was conducted. Fishes were fed with diets containing six graded levels (0.0, 0.1, 0.3, 0.7, 1.1 and 1.5 g/100 g diet) of ethanolic extract of P. murex. There was significant variation (p < 0.05) in growth parameters [i.e. net weight gain and specific growth rate (SGR)] and food conversion ratio. The highest weight gain and SGR were recorded as 0.1 g/100 g with P. murex supplemented diet. However, the inclusion of higher levels (1.5 g/100 g diet) of P. murex did not show any significant increase in the growth of fish. Further, the haematological parameters such as packed cell volume, haemoglobin concentration and red blood cells were not significantly different in P. murex supplemented diets as compared to control. A significant (p < 0.05) proliferation of the white blood cells, improvement in respiratory burst activity and lysozyme, lower level of the blood glucose at dietary level of 0.1 g/100 g were observed. The results of present study explain the role of ethanolic extract of P. murex in growth and immune defence mechanism of fish.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Mukherjee PK (2002) Quality control of herbal drugs: an approach to evaluation of botanicals. Business Horizons Pharmaceutical, New Delhi, p 800
Shukla VN, Khanuja SPS (2004) Pharmacology and botanical studies on Pedalium murex. J Med Aromat Plant Sci 26:64–69
Shelke TT, Kothai R, Adkar PP, Bhaskar VH, Juvale KC, Kamble BB (2009) Nephroprotective activity of ethanolic extract of dried fruits of Pedalium murex linn. J cell tissue Res 9:1687–1690
Vibhuti D, Tripathi AK (2009) Herbaceous remedial plants of district Haridwar, Uttarakhand (India). Adv Plant Sci 22:589–594
Upadhayay B, Singh KP, Kumar A (2011) Ethno-veterinary uses and informants consensus factor of medicinal plants of Sariska region, Rajasthan, India. J Ethnopharmacol 133:14–25
Balasubramanian MN, Muralidharan P, Balamurugan G (2008) Antihyperlipidemic activity of Pedalium murex (Linn.) fruits on high fat diet fed rats. Int J Pharmacol 4:310–313
Soosairaj S, Natarajan D, Nagamurugan N, Radha B (2008) Aspergillosidal effect of Pongamia glabra and Pedalium murex- a comparative study. J Phytol Res 21:221–224
Balamurugan G, Murlidharan P, Polapala S (2010) Aphrodisiac activity and curative effect of Pedalium murex (L.) against ethanol induced infertility in male rats. Turkish J Biol 34:153–163
Srinivas P, Venkateshwarlu L, Kumar ACH (2011) Antioxidant activity of Pedalium murex fruits in carbon tetrachloride- induced hepatopathy in rats. Int J Pharm Biosci 2:622–628
Anon (2004) The ayurvedic pharmacopoeia of India, p. 232
Puri HS (2003) Rasayana-ayurvedic herbs for longevity and Rejuvination. Taylor and Francies, London, p 263
Venkatarathina KT, Muthusamy VA, Ramanathan S (2005) Evaluation of the petroleum ether extracts of Pedalium murex against Japanese encephalitis vector culex Tritaenlorhynchus. Antiseptic 102:335–336
Muralidharan P, Balamurugan G (2008) Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of aqueous extract of Pedalium murex Linn. Biomedicine 28:84–87
Subramanian SS, Nair AGR (1972) Flavonoids of the leaves of Pedalium murex Linn. Phytochemistry 11:464–465
Prasad TNV, Sastry KV (1998) A note on the chemical examination of Pedalium murex Linn. leaves. Indian Drugs 25:84–85
Shukla YN, Thakur RS (1983) Heptatriacontan-4-one, Tetratriacontanyl octacosanoate and other constituents from Pedalium murex Linn. Phytochemistry 22:973–974
Harvey SK (1967) A brief comparative pharmacognostic study of certain indigenous drugs. Nat Med J 9:519
Mangle MS, Jolley CI (1998) HPTLC studies on Tribulus terrestris (Chhota gokhru) and Pedalium murex (Bada gokhru). Indian Drugs 35:189–194
Bhakuni RS, Shukla YN, Thakur RS (1992) Flavonoids and other constituents from Pedalium murex Linn. Phytochemistry 31:2917–2918
Rastogi JN, Sharma OD, Loiwal SD (1982) Amino acids in certain medicinal plants. Bull Pure Appl Sci 1:11–12
Kavitha K, Sharma LL (1996) Use of herb (Asparagus recemous Wild) supplemented diet for promoting growth in the fry of Labeo rohita. The fourth Indian Fisheries Forum, Kochi, p 136
Rajendra KR (1990) Prevention and control of fish diseases by herbal medicine. Fish Health Sect News 3:3–4
Dierekbusarakom S (2004) Application of medicinal herbs to aquaculture in Asia. Walailak J Sci Technol 1(1):7–14
Harborne JB (1973) Phytochemical methods. In: A guide to modern techniques of analysis. Chapman and Hall, London
Jobling M (1983) A short critique of methodology used in fish growth and nutrition studies. J Fish Biol 23:685–703
AOAC (1995) Official methods of analysis of AOAC international vol. 1 agriculture chemicals; contaminants, drugs, 16th edn. AOAC International, Arlington
Nelson-Somogyi, 1944, 1945, cited by Oser Bl (1965) ln: Hawk’s physiological Chemistry, 14th edn. McGraw Hill, New York
Secombes CJ (1990) Isolation of salmonid macrophage and analysis of their killing activity. ln: Stolen JSTC, Fletcher DP, Anderson BS, WB Van, M Winkel (Eds) Techniques in fish immunology. SOS Publication, New Jersey
Stasiack AS, Bauman CP (1996) Neutrophil activity as a potent indicator for concomitant analysis. Fish Shellfish Immunol 37:539
Kaleeswaran B, Ilavenil S, Ravikumar S (2011) Growth response, Feed conversion ratio and Antiprotease activity of Cynodon dactylon (L.) Mixed diet in Catla catla (Ham.). J Animal Veterinary Adv 10(4):517–518
Prasad G, Mukhthiraj S (2011) Effect of methanolic extract of Andrographis paniculata (Nees) on growth and haematology of Oreochromis mossambicus (Peters). World J Fish Marine Sci 3(6):473–479
Sanchez JAO, Flores AC, Hernandez JRO (2009) The effect of herbal growth promoter feed additive on Shrimp performance. Res J Biol Sci 4(9):1022–1024
Kour D, Sharma LL, Sharma BK (2004) Use of Bala (Sida cordifolia Linn.) as growth promoter in the supplementary feed of Cirrhinus mrigala (Ham.). Indian J Fish 51(4):501–504
Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2001) Preliminary nutritional evaluation of Mucuna seed meal (Mucuna pruriens var.utilis) in common carp (Cyprinus carpio L.): an assessment by growth performance and feed utilization. Aquaculture 196:105–123
Siddhuraju P, Becker K (2003) Comparative nutritional evaluation of differentially processed mucuna seeds (Mucuna pruriens (L.) DC var. utilis (Wallex Wight) Baker ex Burck) on growth performance, feed utilization and body composition in Nile tilapia (Oreochromis niloticus L.). Aquac Res 34:487–500
Adeyemo OK (2005) Haematological and histopathological effects of cassava mill effluent in Clarias gariepinus. Afr J Biomed Res 8(3):179–183
Omoniyi I, Agbon AO, Sodunke SA (2002) Effect of lethal and sublethal concentrations of tobacco (Nicotiana tobaccum) leaf dust extract on weight and hematological changes in Clarias gariepinus (Burch.). J Appl Sci Environ Manage 6(2):37–41
Gabriel UU, Obomanu FG, Edori OS (2009) Haematology, Plasma enzymes and organ indices of Clarias gariepinus after intramuscular injection with aqueous leaves extracts of Lepidagathis alopecuroides. Afr J Biochem Res 3(9):312–316
Sahu S, Das BK, Pradhan J, Mohapatra BC, Mishra BK, Sarangi NN (2007) Effect of Mangifera indica kernel as feed additive on immunity and resistance to Aeromonas hydrophila in Labeo rohita fingerlings. Fish Shellfish Immunol 23:109–118
Chukwudi NH, Siemon O, Chinyere AJ (2011) Analysis of some biochemical and Haematological parameters for Mucuna pruriens (DC) seed powder in male rats. Pakistan J Pharm Sci 24(4):523–526
Rajaram N, Janardhanan K (1991) The biochemical composition and nutritional potential of the tribal pulse, Mucuna gigantean (Wildd) DC. Plant Foods Hum Nutr 44:45–51
Coleseh (1986) Veterinary clinical pathology. Saunders, Philadelphia, p 615
Suresh RN, Amolkumar H (2009) Evaluation of Immunomodulatory activity of an extract of Andrographolides from Andrographis paniculata. Thiemee J planta Med 75(8):785–791
Secombes CJ, Fletcher TC (1992) The role of phagocytes in the protective mechanisms of fish. Ann Rev Fish Dis 2:53–71
Sharp GJE, Secombes CJ (1993) The role of reactive oxygen species in the killing of the bacterial fish pathogen Aeromonas salmonicida by rainbow trout macrophages. Fish Shellfish Immunol 3:119–129
Dugenci SK, Arda N, Candan A (2003) Some medicinal plants as immunostimulant for fish. J Ethnopharmacol 88:99–106
Chen X, Wu Z, Yin J, Li L (2003) Effects of four species of herbs on immune function of Carassius auratus gibelio. Journal of Fish Sciences of China 10:36–40 (China)
Neumann NF, Stafford JL, Barreda D, Ainsworth AJ, Belosevic M (2001) Antimicrobial mechanisms of fish phagocytes and their role in host defence. Dev Comp Immunol 25:807–825
Seeley KR, Gillespie PD, Weeks BA (1990) A simple technique for the rapid spectrophotometric determination of phagocytosis by fish macrophages. Marine Environ Res 30:123–128
Ainsworth AJ (1994) A beta-glucan inhibitable zymosan receptor on channel catfish eutrophils. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 41:141–152
Siwicki AK, Anderson DP, Rumsey GL (1994) Dietary intake of immunostimulants by rainbow trout affects non-specific immunity and protection against furunculosis. Vet Immunol Immunopathol 41:125–139
Jeney G, Galeotti M, Volpatti D, Jeney Z, Anderson DP (1997) Prevention of stress in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) fed diets containing different doses of glucan. Aquaculture 154:1–15
Metwally MAA (2009) Effects of garlic (Allium sativum) on some antioxidant activities in tilapia nilotica (Oreochromis niloticus). World J Fish Marine Sci 1(1):56–64
Kumar GR, Reddy KP (1999) Reduced nociceptive responses in mice with alloxan induced hyperglycemia after garlic (Allium sativum Linn.) treatment. Indian J Exp Biol 37:662–666
Thomson M, Ali M (2003) Garlic (Allium sativum): a review of its potential use as an anticancer agent. Curr Cancer Drug Targ 3:67–81
Sheela CG, Augusti KT (1992) Antidiabetic effects of S-allyl cysteine sulphoxide isolated from garlic, Allium sativum Linn. Indian J Exp Biol 30:523
Alexander JB, Ingram GA (1992) Non-cellular non-specific defence mechanisms of fish. Ann Rev Fish Dis 2:249–279
Jian J, Wu Z (2003) Effects of traditional Chinese medicine on nonspecific immunity and disease resistance of large yellow croaker, Pseudosciaena crocea (Richardson). Aquaculture 218:1–9
Jian J, Wu Z (2004) Influences of traditional Chinese medicine on nonspecific immunity of Jian carp (Cyprinus carpio var. Jian). Fish Shellfish Immunol 16:185–191
Acknowledgement
The authors would like to acknowledge the Director, Central Institute of Fisheries Education (CIFE), Mumbai, ICAR, New Delhi, and Vice Chancellor, Maharana Pratap University of Agriculture and Technology Udaipur, Rajasthan, India for providing facilities for the research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ojha, M.L., Chadha, N.K., Saini, V.P. et al. Effect of Ethanolic Extract of Pedalium murex on Growth and Haemato-Immunological Parameters of Labeo rohita . Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 84, 997–1003 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0282-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0282-7