Abstract
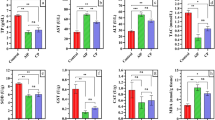
In the present investigation, detailed oral subacute toxicity study of fipronil, a phenylpyrazole insecticide, was undertaken in male buffalo calves. In oral subacute toxicity study, fipronil was administrated to male buffalo calves at repeated oral dose of 0.5 mg kg−1 day−1 for 21 consecutive days. Fipronil produced varying degree of mild to moderate toxic signs in buffalo calves. Fipronil produced toxic signs of salivation, lachrymal discharge, dullness, depression, decreased body weight gain, alopecia and sunken eyes. All the fipronil-exposed animals recovered within 7 days after insecticidal treatment was stopped. Repeated oral administration of fipronil at the dose rate of 0.5 mg kg−1 day−1 for 21 consecutive days produced significant elevation of whole blood cholinesterase to the extent of 45.17 %. Fipronil on repeated oral administration produced significant increase in the plasma levels of lactate dehydrogenase (7.08 %), aspartate aminotransferase (43.55 %) and acid phosphatase (11.647), but no significant effect on the plasma levels of alanine aminotransferase and alkaline phosphatase in male buffalo calves. Subacute oral administration of fipronil elevated the levels of gamma-glutamyl transferase (25.53 %), total plasma proteins (20.59 %) and blood glucose (40.75 %). However, no significant alteration in the levels of blood urea nitrogen, plasma creatinine and cholesterol was seen following daily oral administration of fipronil in the buffalo calves.



Similar content being viewed by others
References
Tingle CC, Rother JA, Dewhurst CF, Lauer S, King WJ (2003) Fipronil: environmental fate, ecotoxicology and human health concerns. Rev Environ Contam Toxicol 176:1–66
Gunasekara AS, Truong T, Goh KS, Spurlock F, Tjeerdema RS (2007) Environmental fate and toxicology of fipronil. J Pesticide Sci 32(3):189–199
Tomlin CDS (2006) The pesticide manual, a world compendium, 14th edn. British Crop Protection Council, Hampshire, pp 462–464
Moffat AS (1993) New chemicals seek to outwit insect pests. Science 261:550–551
Le Faouder J, Bichon E, Brunschwig P, Landelle R, Andre F, Le Bizec B (2007) Transfer assessment of fipronil residues from feed to cow milk. Talanta 73:710–717
Clasen B, Loro VL, Cattaneo R, Moraes B, Lópes T, de Avila LA, Zanella R, Reimche GB, Baldisserotto B (2012) Effects of the commercial formulation containing fipronil on the non-target organism Cyprinus carpio: implications for rice-fish cultivation. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf. doi:10.1016/j.ecoenv.2011.10.001
Leghait J, Gayrard V, Toutain PL, Picard-Hagen N, Viguié C (2010) Is the mechanisms of fipronil-induced thyroid disruption specific of the rat: re-evaluation of fipronil thyroid toxicity in sheep? Toxicol Lett 194:51–57
EFSA (2012) Reasoned opinion on the modification of the existing MRL for fipronil in poultry fat. Eur Food Safety Auth J 10(5):2707 [32 p]. doi:10.2903/j.efsa.2012.2707
Mohamed F, Senarathna L, Percy A, Abeyewardene M, Eaglesham G, Cheng R, Azher S, Hittarage A, Dissanayake W, Sheriff MHR, Davies W, Buckley N, Eddleston M (2004) Acute human self-poisoning with the N-phenylpyrazole insecticide Fipronil—a GABAA-gated chloride channel blocker. J Toxicol 42:955–963
Upadhyay RK, Jaiswal G, Ahmad S (2010) Biochemical and enzymatic alterations after application of fipronil, thiomethoxam and malathion to Odontotermes obesus (Isoptera: Termitidae). Acta Univ Sapientiae Agri Environ 2:58–79
WHO (1997) Pesticide residues in food. Fipronil; International Programme on Chemical Safety, World Health Organization, Lyon
Jennings KA, Keller RJ, Doss RB (2002) Human exposure to fipronil from dogs treated with frontline. Controv Toxicol 44:301–303
Lee SJ, Mulay P, Brown BD, Lackovic MJ, Mehler LN, Beckman J, Waltz J, Prado JB, Yvette A, Mitchell YA, Higgins SA, Schwartz A, Calvert GM (2010) Acute illnesses associated with exposure to fipronil surveillance data from 11 states in the United States, 2001–2007. Clin Toxicol 48:737–744
Cardinet GH (1997) Skeletal muscle function. In: Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML (eds) Clinical biochemistry of animals, 5th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 407–440
Ranjan R, Uppal SK, Chand N, Dhaliwal PS, Dumka VK (2010) Clinico-haematobiochemical profile in organophosphate/carbamate compound poisoned bovine. Ind Vet J 87(2):178–179
Chaidee A, Wongchai C, Pfeiffer W (2008) Extracellular alkaline phosphatase is a sensitive marker for cellular stimulation and exocytosis in heterotroph cell cultures of Chenopodium ruburm. J Plant Physiol 165(16):1655–1666
Ranjan B, Dumka VK, Ola AK, Rampal S (2012) Effect of oral subacute exposure of acetamiprid on some biochemical parameters in buffalo calves. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci. doi:10.1007/s40011-012-0085-2
Kramer JW, Hoffman WE (1997) Clinical enzymology. In: Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML (eds) Clinical biochemistry of animals, 5th edn. Academic press, San Diego, pp 303–326
Tennant BC (1997) Hepatic function. In: Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML (eds) Clinical biochemistry of domestic animals, 5th edn. Academic Press, San Diego, pp 327–352
Jaffrezic-Renault N (2001) New trends in biosensors for organophosphorus. Pest Sens 1:60–74
Luskova V, Svoboda M, Kolaova J (2002) The effect of diazinon on blood plasma biochemistry in carp (Cyprinus carpio L.). Acta Vet Brun 71:117–123
Rosol TJ, Capen CC (1997) Calcium regulating hormones and diseases of abnormal mineral (calcium, phosphorus and magnesium) metabolism. In: Kaneko JJ, Harvey JW, Bruss ML (eds) Clinical biochemistry of animals, 5th edn. Academic press, San Diego, pp 619–702
Khan AM, Sultana M, Raina R, Dubey N, Verma PK (2013) Effect of sub-acute oral exposure of bifenthrin on biochemical parameters in crossbred goats. Proc Natl Acad Sci India Sect B Biol Sci. doi:10.1007/s40011-012-0150-x
Radostits MO, Gay CC, Blood CD, Hinchcliff W (ed) (2000) Vetrinary medicine. A textbook of the diseases of cattle, sheep, pigs, goats and horses, 9th edn. WB Saunders, New York, pp 353–354
USEPA (1996) Office of prevention, pesticides and toxic substances. Fipronil: environmental assessment, current for the turf registration. Memo from D. Farrar, Environmental Fate and Effects Division, to R. Keigwin, Registration Division. Washington, DC, April 26
Servaljevic L, Bogojevic D, Poznanovic G, Matic S (1990) Toxic response to paraoxon is accompanied by an increased rate of acute-phase protein synthesis. Pestic Biochem Physiol 38:216–222
Welch WJ (1993) How cells respond to stress. Sci Am 268:56–64
Brar RS, Sandhu HS, Singh A (2000) Veterinary clinical diagnosis by laboratory methods. Kalyani Publishers, Ludhiana, pp 130–131
Shridhar NB (2010) Toxicity of imidacloprid in buffaloes. Ind J Anim Res 44(3):224–225
Yeh IJ, Lin TJ, Hwang DY (2010) Acute multiple organ failure with imidacloprid and alcohol ingestion. Am J Emerg Med 28(2):255.e1–255.e3
Goyal S, Sandhu HS (2009) Toxic effects of sub-chronic oral exposure of indoxacarb on biochemical parameters in buffalo calves. Toxicol Int 16(2):141–146
Acknowledgments
The authors acknowledge the facilities and funding provided by Guru Angad Dev Veterinary and Animal Sciences University for conducting the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ola, A.K., Sandhu, H.S., Ranjan, B. et al. Fipronil-Induced Biochemical Alterations During Oral Subacute Toxicity in Buffalo Calves. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 83, 539–544 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0167-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-013-0167-9