Abstract
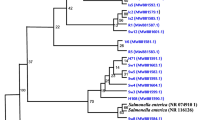
Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) including non-O157 strains have been linked to outbreaks and sporadic cases of illness worldwide. A total of 647 milk samples were collected at different levels of collection and processing (udder, milking utensils, milk collection centres and receiving dock) within West Coast region of India. The milk samples were screened for the presence of E. coli and further tested for the Shiga-toxin (stx) genes by PCR. The isolates were characterized for their serogroups and XbaI digestion patterns of total DNA separated by pulsed-field gel electrophoresis (PFGE). A total of 77 (11.90 %) isolates were confirmed as having E. coli. The serogroups reported were O4, O60, O112, O56, O159, O120, O2, O83, O88, O95, O141, O21, O25, O80, O140, O97, O24, O166, O146, O51, O169, O147, O103, O18, O100, O15, O69, O43, O7, O3, O45, O124, O110, O84, and O114. Out of the 77 E. coli isolates, 25 (32.46 %) could be classified as Shiga-toxigenic based on PCR results. Of these 11, 3 and 11 isolates were positive for stx1, stx2, and both stx1 and stx2, respectively. PFGE profiles indicated genetic diversity of E. coli strains. Much variation was observed among isolates recovered at different levels of collection. Further research is needed to uncover unique characteristics and resistance of non-O157 STEC strains.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Oliver SP, Jayarao BM, Almeida RA (2005) Foodborne pathogens in milk and the dairy farm environment: food safety and public health implications. Foodborne Pathog Dis 2:115–129
Bonfoh B, Wasem A, Traore AN, Fane A, Spillmann H, Simb CF, Alfaroukh IO, Nicolet J, Farah Z, Zinsstag J (2003) Microbiological quality of cow’s milk taken at different intervals from the udder to the selling point in Bamako (Mali). Food Control 14:495–500
Hayes MC, Ralyea RD, Murphy SC, Carey NR, Scarlett JM, Boor KJ (2001) Identification and characterization of elevated microbial counts in bulk tank raw milk. J Dairy Sci 84:292–298
Ryser ET (1998) Public health concerns. In: Marth EH, Steele JL (eds) Applied dairy microbiology. Marcel Dekker Inc., New York, pp 263–403
Fairbrother JM, Nadeau E (2006) Escherichia coli: on-farm contamination of animals. Rev Sci Tech 25:555–569
Kaper JB, Nataro JP, Mobley HLT (2004) Pathogenic Escherichia coli. Nat Rev Microbiol 2:123–140
Solomakos N, Govaris A, Angelidis AS, Pournaras S, Burriel AR, Kritas SK, Papageorgiou DK (2009) Occurrence, virulence genes and antibiotic resistance of Escherichia coli O157 isolated from raw bovine, caprine and ovine milk in Greece. Food Microbiol 26:865–871
European Food Safety Authority (EFSA) (2007) The community summary report on trends and sources of zoonoses, zoonotic agents, antimicrobial resistance and foodborne outbreaks in the European Union in 2006. EFSA J 130:1–352
Holko I, Bisova T, Holkova Z, Kmet V (2006) Virulence markers of Escherichia coli strains isolated from traditional cheeses made from unpasteurised sheep milk in Slovakia. Food Control 17:393–396
Jayarao BM, Henning DR (2001) Prevalence of foodborne pathogens in bulk tank milk. J Dairy Sci 84:2157–2162
Paneto BR, Schocken-Iturrino RP, Macedo C, Santo E, Marin JM (2007) Occurrence of toxigenic Escherichia coli in raw milk cheese in Brazil. Arquivo Brasileiro de Medicina Vet Zootec 59:508–512
WHO (2011) The enterohaemorrhagic Escherichia coli (EHEC) outbreak. http://www.euro.who.int/en/what-we-do/health-topics/emergencies/international-health-regulations/ehec-outbreak-in-germany. Accessed 10 June 2012
Schaffzin JK, Coronado F, Dumas NB, Root TP, Halse TA, Schoonmaker-Bopp DJ, Lurie MM, Nicholas D, Gerzonich B, Johnson GS, Wallace BJ, Musser KA (2011) Public health approach to detection of non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli: summary of two outbreaks and laboratory procedures. Epidemiol Infect 140:283–289
Stefan G (1997) Food safety issues affecting the dairy beef industry. J Dairy Sci 80:3458–3462
Valeeva NI, Meuwissen MP, Lansink AG, Huirne RB (2005) Improving food safety within the dairy chain: an application of conjoint analysis. J Dairy Sci 88:1601–1612
Pal A, Ghosh S, Ramamurthy T, Yamasaki S, Tsukamoto T, Bhattacharya SK, Nair GB, Takeda Y (1999) Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli from healthy cattle in a semi urban community in Calcutta, India. Indian J Med Res 110:83–85
Bhat MA, Nishikawa Y, Wani SA (2008) Prevalence and virulence gene profiles of Shiga toxin—producing Escherichia coli and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli from diarrhoeic and healthy lambs in India. Small Rumin Res 75:65–70
Sanath Kumar H, Otta SK, Karunasagar I, Karunasagar I (2001) Detection of Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC) in fresh seafood and meat marketed in Mangalore, India by PCR. Lett Appl Microbiol 33:334–338
Khan A, Yamasaki S, Sato T, Ramamurthy T, Pal A, Datta S, Chowdhury NR, Das SC, Sikdar A, Tsukamoto T, Bhattacharya SK, Takeda Y, Nair GB (2002) Prevalence and genetic profiling of virulence determinants of non-O157 Shiga-toxin producing Escherichia coli isolated from cattle, beef and humans, Calcutta, India. Emerg Infect Dis 8:54–62
Chattopadhayay UK, Dutta S, Deb A, Pal D (2001) Verotoxin producing Escherichia coli—an environment induced emerging zoonosis in and around Calcutta. Int J Environ Health Res 1:107–112
Cebula TA, Payne WL, Feng P (1995) Simultaneous identification of strains of Escherichia coli serotype O157:H7 and their shiga-like toxin type by mismatch amplification mutation assay-multiplex PCR. J Clin Microbiol 33:248–250
Fremaux B, Raynaud S, Beutin L, Rozand CV (2006) Dissemination and persistence of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) strains on French dairy farms. Vet Microbiol 117:180–191
Altalhi AD, Hassan SA (2009) Bacterial quality of raw milk investigated by Escherichia coli and isolates analysis for specific virulence-gene markers. Food Control 20:913–917
Soomro AH, Arain MA, Khaskheli M, Bhutto B (2002) Isolation of Escherichia coli from milk and milk products in relation to public health sold under market conditions at Tandojam. Pak J Nutr 1:151–152
Wani SA, Samanta I, Bhat MA, Nishikawa Y (2004) Investigation of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in avian species in India. Lett Appl Microbiol 39:389–394
Mishra A, Sharda R, Chhabra D, Moghe MN (2002) Escherichia coli isolates from domestic poultry. Indian J Anim Sci 72:727–729
DebRoy C, Roberts E, Valadez AM, Dudley EG, Cutter CN (2011) Detection of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli O26, O45, O103, O111, O113, O121, O145, and O157 serogroups by multiplex polymerase chain reaction of the wzx gene of the O-antigen gene cluster. Foodborne Pathog Dis 8:651–652
Zweifel C, Giezendanner N, Corti S, Krause G, Beutin L, Danuser J, Stephan R (2010) Characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli isolated from Swiss raw milk cheese within a 3-year monitoring program. J Food Prot 73:88–91
Osman KM, Mustafa AM, Aly MA, AbdElhamed GS (2012) Serotypes, virulence genes, and intimin types of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli isolated from mastitic milk relevant to human health in Egypt. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis 12:297–305
Padola NL, Sanz ME, Blanco JE, Blanco M, Blanco J, Etcheverria AI, Arroyo GH, Usera MA, Parma AE (2004) Serotypes and virulence genes of bovine Shiga-toxigenic Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from a feedlot in Argentina. Vet Microbiol 100:3–9
Rivas M, Miliwebsky E, Chinen I, Roldán CD, Balbi L, García B, Fiorilli G, Sosa-Estani S, Kincaid J, Rangel J, Griffin PM, Case-Control Study Group (2006) The case-control study group 2006 characterization and epidemiologic subtyping of Shiga toxing producing Escherichia coli strains isolated from hemolytic uremic syndrome and diarrhea cases in Argentina. Foodborne Pathog Dis 3:88–96
Irino K, Kato MA, Vaz TM, Ramos II, Souza MA, Cruz AS, Gomes TA, Vieira MA, Guth BE (2005) Serotypes and virulence markers of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli (STEC) isolated from dairy cattle in Sao Paulo State. Braz Vet Microbiol 105:29–36
Rasooly R, Do PM (2010) Shiga toxin Stx2 is heat stable and not inactivated by pasteurization. Int J Food Microbiol 136:290–294
Xia X, Meng J, McDermott PF, Ayers S, Blickenstaff K, Tran TT, Abbott J, Zheng J, Zhao S (2010) Presence and characterization of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli and other potentially diarrheagenic E. coli strains in retail meats. Appl Environ Microbiol 76:1709–1717
Carneiro LA, Lins MC, Garcia FR, Silva AP, Mauller PM, Alves GB, Rosa AC, Andrade JR, Freitas-Almeida AC, Queiroz ML (2006) Phenotypic and genotypic characterization of Escherichia coli strains serogrouped as enteropathogenic E. coli (EPEC) isolated from pasteurised milk. Int J Food Microbiol 108:15–21
Montenegro MA, Ite MB, Trumpf T, Aleksic S, Reuter G, Bulling E, Helmuth R (1990) Detection and characterization of fecal verotoxin-producing Escherichia coli from healthy cattle. J Clin Microbiol 28:1417–1421
Bettelheim KA (2007) The non-O157 Shiga-toxigenic (verocytotoxigenic) Escherichia coli: under-rated pathogens. Crit Rev Microbiol 33:67–87
Brooks JT, Sowers EG, Wells JG, Greene KD, Griffin PM, Hoekstra RM, Strockbine NA (2005) Non-O157 Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli infections in the United States, 1983–2002. J Infect Dis 192:1422–1429
Meng J, Doyle MP, Zhao T, Zhao S (2007) Enterohemorrhagic Escherichia coli. In: Doyle MP, Beuchat LR (eds) Food microbiology: fundamentals and frontiers, 3rd edn. ASM Press, Washington, DC
Caro I, Garcia-Armesto MR (2007) Occurrence of Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli in a Spanish raw ewe’s milk cheese. Int J Food Microbiol 116:410–413
Stephan R, Schumacher S, Corti S, Krause G, Danuser J, Beutin L (2008) Prevalence and characteristics of Shiga toxin-producing Escherichia coli in Swiss raw milk cheeses collected at producer level. J Dairy Sci 91:2561–2565
Paton AW, Paton JC (1998) Detection and characterization of shiga toxigenic Escherichia coli by using multiplex PCR assays for stx1, stx2, eaeA, enterohaemorrhagic E. coli hlyA, rfbO111 and rfbO157. J Clin Microbiol 36:598–602
Narato JP, Kaper JB (1998) Diarrheagenic Escherichia coli. Clin Microbiol Rev 11:142–201
Farooq S, Hussain I, Mir MA, Bhat MA, Wani SA (2009) Isolation of atypical enteropathogenic Escherichia coli and Shiga toxin1 and 2f-producing Escherichia coli from avian species in India. Lett Appl Microbiol 48:692–697
Dutta TK, Roychoudhury P, Bandyopadhyay S, Wani SA, Hussain I (2011) Detection and characterization of Shiga toxin producing Escherichia coli (STEC) and enteropathogenic Escherichia coli (EPEC) in poultry birds with diarrhoea. Indian J Med Res 133:541–545
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to the Director, ICAR Research Complex for Goa, Old Goa for providing necessary facilities. DD is working under Faculty Improvement Programme of University Grants Commission, New Delhi.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
D’Costa, D., Bhosle, S.N., Dhuri, R.B. et al. Prevalence, Serogroups, Shiga-toxin Genes and Pulsed Field Gel Electrophoresis Analyses of Escherichia coli Isolated from Bovine Milk. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 83, 423–429 (2013). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0145-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0145-7