Abstract
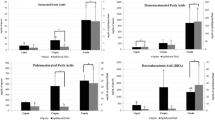
To study the molecular composition of epididymis and its contents, protein and lipid concentration and their profile in its three segments; caput, corpus and cauda was analyzed. The amounts of proteins, lipids and phospholipids was highest in the tissues of caput epididymis as compared to corpus and cauda as well as protein content was higher in caput fluid too. However, their concentration in spermatozoa was highest in those from cauda as compared to other regions. The SDS-PAGE profile of epididymal tissue, its fluid and spermatozoa separately collected from these regions revealed the presence of high (205 and >205 kDa), medium (66, 70, 90, 97.4, 100, 125, 151 kDa) and low (3, 6.5, 8.6, 14.3, 16, 17, 20, 32.5, 43, 54 kDa) molecular weight proteins. A protein of molecular weight 16/17 kDa was present in tissue and fluid of caput only but in spermatozoa from all the three regions which shows its origin from secretory activity of caput and incorporation as such in spermatozoa. However, 100 and 125 kDa proteins were present in tissues of all epididymal regions and appeared as an altered (90/97.4 kDa) protein in spermatozoa from all the three regions. Thin Layer Chromatographic studies of phospholipids in epididymal tissues and its contents in three regions revealed the presence of phosphatidyl choline, phosphatidyl serine, phosphatidyl inositol, sphingomyelin, phosphatidyl glycerol, phosphatidyl ethanolamine and cardiolipin.

Similar content being viewed by others
References
Lowry DH, Rosenbrough NJ, Farr AL, Randal RJ (1951) Protein measurement with Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem 193:265–267
Laemmli UK (1970) Cleavage of structural proteins during the assembly of the head of bacteriophage T4. Nature 15:680–685
Folch J, Lees M, Sloane-Stanley GH (1957) A simple method for isolation and purification of total lipids from animal tissue. J Biol Chem 226:497
Ames BN (1966) In: Newfold EF, Griessburg V (eds) Assay of inorganic phosphate and phosphatases. Academic Press, New York, pp 115
Work TS, Work E (1972) Laboratory techniques in biochemistry and molecular biology, 3rd edn. American Elsevier Publishing Co. Inc, New York, p 551
Dhanju CK, Kaur N (2011) Histomorphological and biochemical composition of epididymis and spermatozoa of the house rat, Rattus rattus L. Int J Innov Biol Chem Sci 2:6–9
Yanagimachi R (1994) In: Knobil E, Neill JD (eds) Mammalian fertilization, 2nd edn. Raven press, New York. pp 189–317
Dacheux JL, Druart X, Syntin P, Gatti JL, Guerin Y, Dacheux E (1995) Secretions and roles of epididymal proteins. Front Endocrinol 11:14–33
Clulow J, Hansen LA, Jones RC (1996) In vivo microperfusion of the ductuli efferentes testis of the rat: flow dependence of fluid reabsorption. Exp Physiol 81:633–644
Syntin P, Dacheux F, Druart X, Gatti JL, Okamura N, Dacheux JL (1996) Characterization and identification of proteins secreted in different regions of the adult boar epididymis. Biol Reprod 55:956–974
Frenette G, Lessard C, Sullivan R (2002) Selected proteins of prostasome-like particles from epididymal caput spermatozoa in bull. Biol Reprod 67:308–313
Blobel CP, Myles DG, Primakoff P, White JH (1990) Proteolytic processing of a protein involved in sperm-egg fusion correlates with the acquisition of fertilization competence. J Cell Biol 111:69–78
Phelps BM, Myles DG (1987) The guinea pig sperm plasma membrane protein PH-20, reaches the surface via two transport pathways and become localized to a domain after an initial uniform distribution. Dev Biol 123:63–72
Myles DG, Primakoff P (1984) Localized surface antigens of guinea pig sperm migrate to new regions prior to fertilization. J Cell Biol 99:1631–1641
Petruszak JAM, Nehme CL, Bartles JR (1991) Endoproteolytic cleavage in the extracellular domain of the integral plasma membrane protein CE9 precedes its redistribution from the posterior to the anterior tail of the rat spermatozoa during epididymal maturation. J Cell Biol 114:917–921
Scully NF, Shafer JH, Shur BD (1987) Spatial and temporal of cell surface galactosyltransferase during mouse spermatogenesis and epididymal maturation. Dev Biol 124:111–124
Jones R, Shalgi R, Hoyland J, Phillips, Phillips DM (1990) Topographical rearrangement of a plasma membrane antigen during capacitation of rat spermatozoa in vitro. Dev Biol 139:349–362
Rankin TL, Tsuruta KJ, Holland MK, Griswold MD, Orgebin-Crist MC (1992) Isolation, immunolocalization and sperm-association of three proteins of 18, 25 and 29 kilodaltons secreted by the mouse epididymis. Biol Reprod 46:747–766
Brooks DE, Tiver K (1983) Localization of epididymal secretory proteins on rat spermatozoa. J Reprod Fertil 69:651–657
Dacheux JL, Dacheux F, Paquignon M (1989) Changes in sperm membrane and luminal proteins fluid during epididymal transit in the boar. Biol Reprod 40:635–651
Okamura N, Dacheux F, Venien A, Onoe S, Huet JC, Dacheux J (1992) Localization of a maturation-dependent epididymal sperm surface antigen recognized by a monoclonal antibody raised against a 135-kilodalton protein in porcine epididymal fluid. Biol Reprod 47:1040–1052
Voglmayr JK, Fairbanks G, Lewis RG (1983) Surface glycoprotein changes in ram spermatozoa during epididymal maturation. Biol Reprod 29:767–775
Pickett BW, Komarek RJ, Gebauer MR, Benson RW, Gibson EW (1967) Lipid and dry weight of ejaculated, epididymal and post-castrate semen from boars. J Anim Sci 26:792–798
Rejraji H, Sion B, Pensier G, Carrenas M, Motta C, Frenoux JM, Vericel E, Grizard G, Vernet P, Drevet JR (2006) Lipid remodelling of murine epididymosomes and spermatozoa during epididymal maturation. Biol Reprod 74:1104–1113
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanju, C.K., Kaur, N. & Cheema, R.S. Protein and Lipid Profile of Different Epididymal Regions and Their Contents in Rattus rattus L.. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. B Biol. Sci. 82, 299–305 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0039-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40011-012-0039-8