Abstract
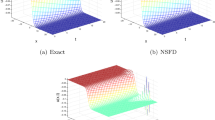
In this paper, a fully implicit finite difference method is presented to solve the generalized equal width equation. This implicit method allows to handle any values of p. Since the equation is nonlinear the scheme leads to a system of nonlinear equations. At each time step, Newton’s method is used to solve this nonlinear system. The linear stability analysis of the proposed method is investigated using von Neumann approach and at the end of this investigation is seen that the method is unconditionally stable. The results are comparisons with analytical and other numerical values clearly show that results obtained using the fully implicit finite difference scheme are precise and reliable.










Similar content being viewed by others
References
Evans DC, Raslan KR (2005) Solitary waves for the generalized equal width (GEW) equation. Int J Comput Math 82:445–455
Morrison PJ, Meiss JD, Carey JR (1984) Scattering of regularized-long-wave solitary waves. Physica D 11:324–336
Gardner LRT, Gardner GA (1992) Solitary waves of the equal width wave equation. J Comput Phys 101:218–223
Gardner LRT, Gardner GA, Ayoub FA, Amein NK (1997) Simulations of the EW undular bore. Commun Numer Meth En 13:583–592
Khalifa AK, Raslan KR (1999) Finite difference methods for the equal width wave equation. J Egypt Math Soc 7:239–249
Khalifa AK, Ali AH, Raslan KR (1999) Numerical study for the equal width wave (EWE) equation. Mem Fac Sci Kochi Univ 20:47–55
Zaki SI (2000) A least-squares finite element scheme for the EW equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 189:587–594
Zaki SI (2001) Solitary waves induced by the boundary forced EW equation. Comput Methods Appl Mech Eng 190:4881–4887
Dag I, Saka B (2004) A cubic B-spline collocation method for the EW equation. Math Comput Appl 9:381–392
Raslan KR (2004) A computational method for the equal width equation. Int J Comput Math 81:63–72
Esen A (2005) A numerical solution of the equal width wave equation by a lumped Galerkin method. Appl Math Comput 168:270–282
Dogan A (2005) Application of Galerkin’s method to equal width wave equation. Appl Math Comput 160:65–76
Raslan KR (2005) Collocation method using quartic B-spline for the equal width (EW) equation. Appl Math Comput 168:795–805
Saka B (2006) A finite element method for equal width equation. Appl Math Comput 175:730–747
Esen A, Kutluay S (2006) A linerized implicit finite-difference method for solving the equal width wave equation. Int J Comput Math 83:319–330
Ramos JI (2006) Explicit finite difference methods for the EW and RLW equations. Appl Math Comput 179:622–638
Ramos JI (2007) Solitary waves of the EW and RLW equations. Chaos Solitons Fractals 34:1498–1518
Saka B, Dag I, Dereli Y, Korkmaz A (2008) Three different methods for numerical solution of the EW equation. Eng Anal Bound Elem 32:556–566
Ali AHA (2008) Spectral method for solving the equal width equation based on Chebyshev polynomials. Nonlinear Dyn 51:59–70
İnan B, Bahadır AR (2014) A numerical solution of the equal width wave equation using a fully implicit finite difference method. Turk J Math Comput Sci 2:1–14
Zaki SI (2000) Solitary waves interactions for the modified equal width equation. Comput Phys Commun 126:219–231
Esen A (2006) A lumped Galerkin method for the numerical solution of the modified equal-width wave equation using quadratic B-splines. Int J Comput Math 83:449–459
Wazwaz AM (2006) The tanh and the sine-cosine methods for a reliable treatment of the modified equal width equation and its variants. Commun Nonlinear Sci 1:148–160
Esen A, Kutluay S (2008) Solitary wave solutions of the modified equal width wave equation. Commun Nonlinear Sci 13:1538–1546
Mohyud-Din ST, Yildirim A, Berberler ME, Hosseini MM (2010) Numerical solution of modified equal width wave equation. World Appl Sci J 8:792–798
Raslan KR (2006) Collocation method using cubic B-spline for the generalised equal width equation. Int J Simul Process Modell 2:37–44
Roshan T (2011) A Petrow-Galerkin method for solving the generalized equal width (GEW) equation. J Comput Appl Math 235:1641–1652
Fan H (2012) The classification of the single traveling wave solutions to the generalized equal width equation. Appl Math Comput 219:748–754
Panahipour H (2012) Numerical simulation of GEW equation using RBF collocation method. Commun Numer Anal. https://doi.org/10.5899/2012/cna-00059
Bahadır AR (1999) Numerical solution for one-dimensional Burgers’ equation using a fully implicit finite-difference method. Int J Appl Math 1:897–909
Bahadır AR (2003) A fully implicit finite-difference scheme for two-dimensional Burgers’ equations. Appl Math Comput 137:131–137
Karakoç SBG, Zeybek H (2016) A septic B-spline collocation method for solving the generalized equal width wave equation. Kuwait J Sci 43:20–31
Karakoç SBG, Zeybek H (2016) A cubic B-spline Galerkin approach for the numerical simulation of the GEW equation. Stat Optim Inf Comput 4:30–41
Abo Essa YM (2017) Multigrid method for solving the generalized equal width wave equation. Int J Math Arch 8:56–62
Acknowledgements
The authors thank the anonymous referees and editor for their valuable time, effort and extensive comments which help to improve the quality of this paper.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Inan, B., Bahadir, A.R. A Fully Implicit Finite Difference Approach for Numerical Solution of the Generalized Equal Width (GEW) Equation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci., India, Sect. A Phys. Sci. 90, 299–308 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-019-00594-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40010-019-00594-8