Abstract
Purpose
The pharmaceutical industry has been searching for drugs that aim at the prevention, the protection, and the recovery of the skin. Thus, the aim of this study was to evaluate the anti-inflammatory and anti-edematogenic activities of a topical emulsion containing Helianthus annuus oil (5%), glycerin (30%), and vitamin B3 (5%).
Methods
The aim was verified through chronic inflammatory responses and edema that were induced by irritant croton oil in the ears of mice, followed by histological and leukocyte infiltration. The study also affirmed the stability and the cytotoxicity of the emulsion.
Results
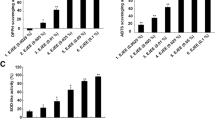
A stable, homogeneous, shiny, slightly-white, and gelatinous emulsion was obtained. The cytotoxicity evaluation allowed for the verification that only in high concentrations were unsatisfactory results presented. The treatment was effective in reversing the inflammatory parameters that were induced by croton oil, such as edema, neutrophil migration, and cell hyperproliferation.
Conclusion
The developed emulsion containing sunflower oil, glycerin, and vitamin B3 had parameters of stability and presented anti-inflammatory activities. The researchers’ findings suggest that the topical use of this formulation is a new and novel strategy for the treatment of inflammatory conditions of the skin.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anon (2006a) ISO 22717:2006 Cosmetic, microbiology, and detection of Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Anon (2006b) ISO 22718:2006 Cosmetic, microbiology, and detection of Staphylococcus aureus.
Araviiskaia E, Dréno B (2016) The role of topical dermocosmetics in acne vulgaris. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol: JEADV 30(6):926–935. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.13579
Bains P, Kaur M, Kaur J, Sharma S (2018) Nicotinamide: mechanism of action and indications in dermatology. Indian J Dermatol Venereol Leprol. 84(2):234–237. https://doi.org/10.4103/ijdvl.IJDVL_286_17
Banerjee K, Thiagarajan N, Thiagarajan P (2019) Formulation and characterization of a Helianthus annuus—alkyl polyglucoside emulsion cream for topical applications. J Cosmet Dermatol 18(2):628–637. https://doi.org/10.1111/jocd.12756
Behm B, Babilas P, Landthaler M, Schremi S (2012) Cytokines, chemokines, and growth factors in wound healing. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 26:812–820. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1468-3083.2011.04415.x
Brazil (2004) Agência Nacional de Vigilância Sanitária (ANVISA) Gerência Geral de cosméticos. Guia de estabilidade de produtos cosméticos [Guide of stability of cosmetics products]. Brasília, 2004. http://bvsms.saude.gov.br/bvs/publicacoes/cosmeticos.pdf
Breternitz M, Kowatzki D, Langenauer M, Elsner P, Fluhr JW (2008) Placebo-controlled, double-blind, randomized, prospective study of a glycerol-based emollient on eczematous skin in atopic dermatitis: biophysical and clinical evaluation. Skin Pharmacol Physiol 21(1):39–45. https://doi.org/10.1159/000111134
Chanamai R, McClements DJ (2000) Dependence of creaming and rheology of monodisperse oil-in-water emulsions on droplet size and concentration. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 172(1–3):79–86
Chen AC, Damian DL (2014) Nicotinamide and the skin. Australas J Dermatol 55(3):169–175. https://doi.org/10.1111/ajd.12163
Christman JC, Fix DK, Lucus SC, Watson D, Desmier E et al (2012) Two randomized, controlled, comparative studies of the stratum corneum integrity benefits of two cosmetic niacinamide/glycerin body moisturizers vs. conventional body moisturizers. J Drugs Dermatol JDD 11(1):22–29
Coelho CS, Gama JAN, Oliveira Junior LAT, Silva BSF, Souza VRC et al (2012) Use of extracts of sunflower-seed oil (Helianthus annuus L.) for the treatment of cutaneous injuries in equine metatarsus: a case report. Revis Bras de Plantas Med [online] 14(1):125–129. http://dx.doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1590/S1516-05722012000100018
Cohen-Letessier A (2008) Actualités cosmétiques dans le vieillissement cutané [Current cosmetics in skin ages]. Ann Dermatol Venereol 135(3S):211–214. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1016/S0151-9638(08)70085-1
Coleman WP III (2010) Skin moisturization. In: Rawlings AA, Leyden JJ (eds) Dermatologic surgery, vol 36, pp 382–382. doi:https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1524-4725.2009.01445.x
Cosmetic Ingredient Review Expert Panel (2005) Final report of the safety assessment of niacinamide and niacin. Int J Toxicol 24(Suppl 5):1–31. https://doi.org/10.1080/10915810500434183
Eimpunth S, Wanitphadeedecha R, Manuskiatti W (2012) A focused review on acne-induced and aesthetic procedure-related postinflammatory hyperpigmentation in Asians. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 27(1S):7–18. https://doi.org/10.1111/jdv.12050
Fluhr JW, Darlenski R, Surber C (2008) Glycerol and the skin: a holistic approach to its origin and functions. Br J Dermatol 159(1):23–34. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-2133.2008.08643.x
Forbat E, Al-Niaimi F, Ali FR (2017) Use of nicotinamide in dermatology. Clin Exp Dermatol 42(2):137–144. https://doi.org/10.1111/ced.13021
Guo S, Ge Y, Na Jom K (2017) A review of phytochemistry, metabolite changes, and medicinal uses of the common sunflower seed and sprouts (Helianthus annuus L.). Chem Cent J 11(1):95. https://doi.org/10.1186/s13065-017-0328-7
Hecker E, Schmidt R (1974) Phorbol esters—the irritants and cocarcinogens of Croton tiglium L. In: Herz W, Grisebach H, Kirby GW (eds) Fortschritte der Chemie Organischer Naturstoffe/progress in the chemistry of organic natural products. Vienna, Springer, vol 31, pp 377–467. https://doi.org/https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-7091-7094-6
Homayoonfal M, Khodaiyan F, Mousavi SM (2014) Walnut oil nanoemulsion: optimization of the emulsion capacity, cloudiness, density, and surface tension. J Dispers Sci Technol 35(5):725–733. https://doi.org/10.1080/01932691.2013.807742
Huang J, Hitchins AD, Tran TT, McCarron JE (2017) BAM: bacteriological analytical manual. Chapter 23: microbiological methods for cosmetics. http://wayback.archive-it.org/7993/20170722052148/https://www.fda.gov/Food/FoodScienceResearch/LaboratoryMethods/ucm073598.htm
Korponyai C, Szél E, Behány Z, Varga E, Mohos G et al (2017) Effects of locally applied glycerol and xylitol on the hydration, barrier function and morphological parameters of the skin. Acta Dermato-Venereologicae 97(2):182–187. https://doi.org/10.2340/00015555-2493
Lania BG, Morari J, Almeida AR, Silva M, Vieira-Damiani G et al (2019) Topical essential fatty acid oil on wounds: local and systemic effects. PLoS ONE 14(1):e0210059. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0210059
Lin TK, Zhong L, Santiago JL (2018) Anti-inflammatory and skin barrier repair effects of topical application of some plant oils. Int J Mol Sci 19(1):70. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms19010070
Manela-Azulay M, Bagatin E (2009) Cosmeceuticals vitamins. Clin Dermatol 27(5):469–474. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2009.05.010
Manhezi AC, Bachion MM, Pereira AL (2008) Utilização de ácidos graxos essenciais no tratamento de feridas [The use of essential fatty acids in the wound treatment]. Rev Bras de Enfermagem [online] 61(5):620–628. https://doi.org/10.1590/S0034-71672008000500015
McCusker MM, Grant-Kels JM (2010) Healing fats of the skin: the structural and immunologic roles of the omega-6 and omega-3 fatty acids. Clin Dermatol 28(4):440–451. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clindermatol.2010.03.020
Mendes DB, Serra JCV (2012) Glicerina: uma abordagem sobre a produção e o tratamento [Gliceryn: an approach about the production and the treatment]. Rev Liberato 13:59–67
Mesquita Júnior D, Araújo JAP, Catelan TTT, Souza AWS, Silva NP et al (2010) Aspectos celulares e moleculares da inflamação [Molecular and celular aspects of inflammation]. Sinopse de Reumatol 8(3):66–81. http://www.moreirajr.com.br/revistas.asp?fase=r003&id_materia=4053/
Moyma P, Heizen H (2010) Lípidos: química y productos naturales que los contienen, [Lipids: chemistry and natural products that content them]. In: Simões CMO et al (ed) Farmacognosia: da planta ao medicamento, 6 ed., UFRGS Ed., Porto Alegre, 435–466
Mullany LC, Darmstadt GL, Khatry SK, Tielsch JM (2005) Traditional massage of newborns in Nepal: implications for trials of improved practice. J Trop Pediatr 51(2):82–86. https://doi.org/10.1093/tropej/fmh083
Okan G, Rendon MI (2011) The effects of a high glycerin content hydrogel pre-molded mask dressing on post-laser resurfacing wounds. J Cosmet Laser Ther 13(4):162–165. https://doi.org/10.3109/14764172.2011.594063
Oliveira SM, Silva CR, Wentz AP, Paim GR, Correa MS et al (2014) Antinociceptive effect of 3-(4-fluorophenyl)-5-trifluoromethyl-1H-1-tosylpyrazole. A Celecoxib structural analog in models of pathological pain. Pharmacol Biochem Behav 124:396–404. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pbb.2014.07.005
Otuki MF, Vieira-Lima F, Malheiros A, Yunes RA, Calixto JB (2005) Topical anti-inflammatory effects of the ether extract from Protium kleinii and alpha-amyrin pentacyclic triterpene. Eur J Pharmacol 507(1–3):253–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2004.11.012
Periz G, Misock J, Huang MJ, Dewan K, Sadrieh N (2018) FDA 2014 survey of eye area cosmetics for microbiological safety. J Appl Microbiol 67(1):32–38. https://doi.org/10.1111/lam.12995
Piana M, Camponogara C, Boligon AA, Machado MM, de Brum TF et al (2016) Topical anti-inflammatory activity of Solanum corymbiform leaves. J Ethnopharmacol 17(179):16–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jep.2015.12.036
Piana M, Camponogara C, Boligon AA, Oliveira SM (2017) Solanum paranense extracts and solanine present anti-inflammatory activity in an acute skin inflammation model in mice. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. https://doi.org/10.1155/2017/4295680
Rignal A (2018) ICH quality guidelines: an implementation guide, first edition. In: Teasdale A, Elder D, Nims RW (eds) John Wiley & Sons, Inc., New Jersey
Scudiero DA, Shoemaker RH, Paull KD, Monks A, Tierney S et al (1988) Evaluation of a soluble tetrazolium/formazan assay for cell growth and drug sensitivity in culture using human and other tumor cell lines. Cancer Res 48:4827
Stanley PL, Steiner S, Havens M, Tramposch KM (1991) Mouse skin inflammation induced by multiple topical applications of 12-O-tetradecanoylphorbol-13-acetate. Skin Pharmacol 4(4):262–271
Tadros T (2004) Application of rheology for assessment and prediction of the long-term physical stability of the emulsion. Adv Colloid Interface Sci 108–9:227–258. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cis.2003.10.025
Vaughn AR, Clark AK, Sivamani RK, Shi VY (2018) Natural oils for skin-barrier repair: ancient compounds now backed by modern science. Am J Clin Dermatol 19(1):103–111. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40257-017-0301-1
Zidan SM, Eleowa SA (2014) Banking and use of glycerol preserved full-thickness skin allograft harvested from body contouring procedures. Burns 40(4):641–647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.burns.2013.08.039
Funding
This research did not receive any specific grant from funding agencies in the public, commercial, or not-for-profit sectors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
AHS and LMF conceived and designed the research. APC, EW, L de MF, AR, MFPF, and GJVA conducted the experiments. FTTA, INR, AHS, ESO, and IG analyzed the data. FTTA, LMF, INR, AHS, and IG wrote the manuscript. All of the authors have read and approved the manuscript for publication.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there are no conflicts of interest.
Statement on the welfare of animals
The study was carried out in accordance with the Institutional Guidelines for the Care and Use of Animals and the Ethical Standards of the Lutheran University of Brazil (ULBRA, Canoas, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil). The procedures were conducted after previous approbation from the Institutional Research Ethics Committee under the protocol 2014-30P.
Ethical approval
All applicable International, National, and/or Institutional Guidelines for the Care and Use of Animals were followed. All of the procedures that were performed in the studies involving the animals were conducted in accordance with the Ethical Standards of the Research Ethics Committee of the Lutheran University of Brazil (ULBRA, Canoas, Rio Grande do Sul, Brazil), and this University is where the studies were administered under protocol 2014-30P.
Availability of data and materials
The authors declare that the data and the material are available on request.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Freitas, L.M., Antunes, F.T.T., Obach, E.S. et al. Anti-inflammatory effects of a topical emulsion containing Helianthus annuus oil, glycerin, and vitamin B3 in mice. J. Pharm. Investig. 51, 223–232 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-020-00508-6
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-020-00508-6