Abstract
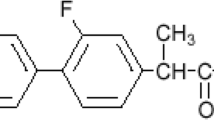
In this study, we aimed to design fast disintegrating tablets (FDT) of ketorolac tromethamine (KT) to reduce gastric side effects of KT by physically associating it with phospholipon 80H (PL) by wet granulation. First preliminary batches were formulated to determine the effect of PL on tablet characteristics and to select best superdisintegrant among sodium starch glycolate and crospovidone. The effect of PL and maltodextrin (MD) concentrations on hardness, disintegration time and % drug release at 4 min was studied for the optimization of FDT. Optimization of FDT was done by employing 32 full factorial design using Design expert 10.1 software. The optimized batch of FDT showed disintegration time and percent release value of 37.33 ± 1.47 s and 42.74 ± 1.53% respectively. It was also found that 91.87% of drug was released within 10 min. Thus, by an appropriate combination of excipients, it was possible to formulate FDT capable of undergoing fast disintegration and having optimum hardness using simple and conventional techniques.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anand B, Romero JJ, Sanduja SK, Lichtenberger LM (1999) Phospholipid association reduces the gastric mucosal toxicity of asprin in human subjects. AJG 94:1818–1822
Badgujar B, Mundada A (2011) The technologies used for developing orally disintegrating tablets: a review. Acta Pharm 61:117–139
Bajwa PS, Bhargava A, Sharma J, Sharma S, Sharma AR, Sharma B (2017) Development and in vitro-in vivo characterization of chronomodulated pulsatile delivery formulation of terbutaline sulphate by Box-Behnken statistical design. AAPS PharmSciTech. https://doi.org/10.1208/s12249-017-0838-6
Banker GS, Anderson NR. Lachman L, Lieberman HA, Kanig JL (1987) Tablets. The theory and practice of industrial pharmacy, 3rd edn. Varghese Publishing House, Mumbai, p 296
Beringer P, Marderosian AD, Felton L, Gelone S, Gennaro AR, Gupta PK, Hoover JE (2005) Oral solid dosage form, 21st edn. vol 1, The Science and Practice of Pharmacy, Remington, pp 917–918
Dobetti L (2012) Fast disintegrating tablet. EP Patent 1058538 B2
Elnaggar YSR, Massik MAE, Abdullah OY, Ebian AER (2010) Maltodextrin: a novel excipient used in sugar-based orally disintegrating tablets and phase transition process. AAPS PharmSciTech 11:645–651
Fini A, Bergamante V, Ceschel GC, Ronchi C, Moraes CAF (2008) Fast dispersible/slow releasing ibuprofen tablets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 69:335–341
Fu Y, Yang S, Jeong SH, Kimura S, Park K (2004) Orally fast disintegrating tablet: developments, technologies, taste-masking and clinical studies. Crit Rev Ther Drug Carrier Syst 21:433–475
Genc L, Jalvand E (2008) Preparation and in vitro evaluation of controlled release hydrophilic matrix tablets of ketorolac tromethamine using factorial design. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 34:903–910
Giraud MN, Motta C, Romero JJ, Bommelaerg G, Lichtenberger LM (1999) Interaction of indomethacin and naproxen with gastric surface-active phospholipids: a possible mechanism for the gastric toxicity of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (nsaids). Biochem Pharmacol 57:247–254
Kurinets A, Lichtenberger LM (1998) Phophatidylcholine-association asprin accelerates healing of gastric ulcers in rats. Dig Dis Sci 43:786–790
Massing T, Brandi AB (2008) Tablet containing hydrogenated phospholipids. US Patent 0187583 A1
Moffat AC, Osselton MD, Widdop B (2011) Clarke’s analysis of drugs and poisons, 4th edn. Pharmaceutical Press, London, pp 1545–1546
Mohapatra A, Parikh RK, Gohel MC (2008) Formulation, development and evaluation of patient friendly dosage forms of metformin, part-1: orally disintegrating tablets. Asian J Pharm 2:167–171
British Pharmacopoeia (2009) Her Majesty’s stationary office, British Pharmacopoeia Commission, London, p A443
Setty CM, Prasad DVK, Gupta VRM, Sa B (2008) Development of fast dispersible aceclofenac tablets: effect of functionality of superdisintegrants. Indian J Pharm Sci 70:180–184
Tripathi KD (2003) Essential of medical pharmacology, 5th edn. Jaypee Brothers Medical Publishers, New Delhi, p 178
United State Pharmacopoeia/NF, 38/33 (2015a) United Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc. Rockville, p 675
United State Pharmacopoeia/NF, 38/33 (2015b) United Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc. Rockville, p 1432
United State Pharmacopoeia/NF, 38/33 (2015c) United Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc. Rockville, p 483
United State Pharmacopoeia/NF, 38/33 (2015d) United Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc. Rockville, p 4012
United State Pharmacopoeia/NF, 38/33 (2015e) United Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc. Rockville, p 486
Acknowledgements
The authors are thankful to MSN Laboratories Ltd. Andhra Pradesh, India for providing gift sample of KT. They also wish to express their gratefulness to the ASBASJSM College of pharmacy for providing necessary facilities for the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Statement of human and animal rights
This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any author.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Raina, B., Sharma, A. & Bajwa, P.S. Formulation evaluation and optimization of fast disintegrating tablets of ketorolac tromethamine. J. Pharm. Investig. 48, 685–695 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0366-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0366-0