Abstract
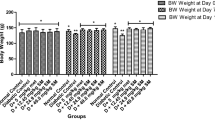
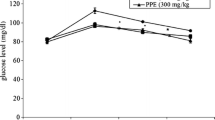
Marsilea quadrifolia is an indigenous medicinal plant and it has a folk reputation in central and southern India as hypoglycemic agent. The present study was aimed to evaluate the effect of methanolic leaf and stem extracts of Marsilea quadrifolia on carbohydrate metabolic enzymes in alloxan induced diabetic rats. In this study, the blood glucose level was increased in alloxan induced diabetic rats when compared to normal control rats. The decreased level of blood glucose was observed in diabetic rats treated with leaf and stem of M. quadrifolia. The activities of hexokinase, pyruvate kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, glucose-6-phosphatase, fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase in liver and kidney and glycogen content, glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase in liver were analysed. Glibenclamide was used as a reference drug in the present investigation. The activities of hexokinase, pyruvate kinase and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase were significantly decreased and the activities of lactate dehydrogenase, glucose-6-phosphatase and fructose 1,6-bisphosphatase were significantly increased in liver and kidney of alloxan induced diabetic rats when compared to normal control rats. Oral administration of methanolic leaf and stem extracts of M. quadrifolia (300 mg/kg bw) to diabetic rats for 45 days showed significantly reverted levels of above mentioned enzymes. The levels of glycogen and glycogen synthase in liver were significantly decreased and the glycogen phosphorylase activity was significantly increased in diabetic rats when compared to normal control rats. The diabetic rats treated with leaf and stem extracts of M. quadrifolia reverted the levels of glycogen, glycogen synthase and glycogen phosphorylase to near normal. The present study clearly indicates that the methanolic leaf and stem extracts of M. quadrifolia possesses potent antidiabetic activity.
Similar content being viewed by others
References
Al-Shamaony L, Al-khazrajoi SM, Twaij HAA (1994) Hypoglycaemic effect of Artemisia herba alba. II. Effect of a valuable extract on some blood parameters in diabetic animals. J Ethnopharmacol 43:167–171
Anderson JW, Stowring L (1973) Glycolytic and gluconeogenic enzyme activities in renal cortex of diabetic rats. Am J Physiol 224:930–936
Awaji Y, Hastimoto H, Matsui Y, Kawaguchi K, Okumura K, Lto T, Stake T (1990) Isoenzyme profiles of creatine kinase, lactate dehydropgenase and aspartate aminotransferase in diabetic heart: comparison with hereditary and catecholamine cardiomyopathies. Cardivasc Res 24:547–554
Bergmeyer HU (1984) Glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase. In: Bergmeyer HU (ed), Methods of enzymatic analysis, vol 2, Academic Press, New York, pp 222–223
Brandstrup N, Kirk JE, Brunic C (1957) The hexokinase and phosphoglucoisomerase activities of aortic and pulmonary artery tissue in individuals of various ages. J Gerontol 12:166–171
Carette C, Dubois-Laforgue D, Gautier JF, Timsit J (2011) Diabetes mellitus and glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency: from one crisis to another. Diabetes Metab 37:79–82
Cornblath M, Randle PJ, Parmeggiani M, Morgan HE (1963) Regulation of glycogenolysis in muscle. J Biol Chem 238:1952
Ding Z, Lu Y, Lu Z, Lv F, Wang Y, Bie Y et al (2010) Hypoglycaemic effect of comatin, an antidiabetic substance separated from Coprinus comatus broth, on alloxan-induced-diabetic rats. Food Chem 121:39–43
Dongare SS, Maske AP, Patil SM, Umbare RP, Mate GS (2009) Antidiabetic Activity of Marsilea quadrifolia linn in alloxan-diabetic rats. Res J Pharm Phytochem 1(1):15–17
Farswan M, Mazumder PM, Percha V (2009) Protective effect of Cassia glauca Linn on the serum glucose and hepatic enzymes level in streptozotocin induced NIDDM in rats. Indian J Pharmacol 41:19–22
Feshani AM, Kouhsari SM, Mohammadi S (2011) Vaccinium arctostaphylos a common herbal medicine in Iran: molecular and biochemical study of its antidiabetic effects on alloxan-diabetic Wistar rats. J Ethnopharmacol 133:67–74
Gancedo JM, Gancedo C (1971) Fructose 1,6-bisphophatase, phosphofructokinase and glucose 6-phosphate dehydrogenase from fermenting yeast and non-fermenting yeast. Arch Microbiol 76:132–138
Ghule S, Prakash T, Kotresha D, Karki R, Surendra V, Goli D (2010) Anti: diabetic activity of Celosia argentea root in streptozotocin-induced diabetic rats. Int J Green Pharm 4:206–210
Gilman AG, Rall TW, Nles AS, Tayer P (eds) (1990) Goodman and Gilman’s: the pharmacological basis of therapeutics, 8th edn. Pergamen Press, New York, pp 1317–1322, 1463–1495
Gupta SK, Srinivasan AK, Singh PK, Tuli R (1997) In vitro proliferation of shoots and regeneration of cotton. Plant Cell Tiss Org Cult 51: 149–152.
Gupta D, Raju J, Baquer NZ (1999) Modulation of some gluconeogenic enzyme activities in diabetic rat liver and kidney: effect of antidiabetic compoumds. Indian J Exp Biol 37:196–199
Kamboj VP (2000) Herbal medicine. Curr Sci 78(1): 35–39
King J (1965) In practical clinical enzymology. D. Van Nostrand Co., London, pp. 83–93
Kletzien RF, Harris PK, Foellmi LA (1994) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase: a “housekeeping” enzyme subject to tissue-specific regulation by hormones, nutrients, and oxidant stress. FASEB J 8:174–181
Koide H, Oda T (1959) Pathological occurrence of glucose 6-phosphatase in serum in liver diseases. Clin Chim Acta 4:554–561
Laakso M, Malkki M, Deeb SS (1995) Amini acid substituents in hexokinase II among patients with NIDDM. Diabetes 44:330–334
Leloir LF, Goldemberg SH (1960) Sybthesis of glycogen from uridine diphosphatate glucose in liver. J Biol Chem 235(4):919–923
Meenakshi P, Bhuvaneshwari R, Rathi MA, Thirumoorthi L, Guravaiah DC, Jiji MJ et al (2010) Antidiabetic activity of ethanolic extract of Zaleya decandra in alloxan-induced diabetic rats. Appl Biochem Biotechnol 162:1153–1159
Mohammad Ali E, Razeih Y (2004) Hypoglycemic effect of Teucrium polium studies with rat pancreatic islets. J Ethanopharmacol 95:27–30
Morales MA, Jabbagy AJ, Terenzi HP (1975) Mutations affecting accumulation of glycogen. Neurospora News Lett 20:24–25
Murray RK, Granner DK, Mayes PA, Rodwell VW (2000) Harper’s biochemistry, vol 25, Appleton and Lange, Stanford, pp 610–617
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (2001) The OECD 423 guideline for testing of chemicals acute oral toxicity acute toxic class method. OECD, Paris
Pareek H, Sharma S, Khajja BS, Jain K, Jain GC (2010) Evaluation of hypoglycemic and anti hyperglycemic potential of Tridax procumbens (Linn.). BMC Complement Altern Med 9:48
Patel SS, Goyal RK (2011) Prevention of diabetes-induced myocardial dysfunction in rats using the juice of the Emblica officinalis fruit. Exp Clincardiol 16:87–91
Pinna A, Contini EL, Carru C, Solinas G (2013) Glucose-6-phosphate dehydrogenase deficiency and diabetes mellitus with severe retinal complications in a sardinian population, Italy. Int J Med Sci 10(13):1907–1913
Rajendran K, Vijayabharathi R (2005) Anti-hyperglycemic activity of ethanol leaf extract of Marsilea quadrifolia Linn. Hamdard Med 48(4):17–20.
Raju J, Gupta D, Rao AR, Pramod K, Baquer NYZ (2001) Trigonella foenum graecum (fenugreek) seed powder improves glucose homeostasis in alloxan diabetic rat tissues by reversing the altered glycolytic, gluconeogenic and lipogenic enzymes. Mol Cell Biochem 224:45–51
Ramachandran B, kandaswamy M, Narayanan V, Subramanian S (2003) Insulin mimetic effects of macrocyclic binuclear oxovanadium complexes on streptozotocin-induced experimental diabetes in rats. Diabetes Obes Metab 5:455–461
Ripa FA, Nahar L, Haque M, Islam MM (2009) Antibacterial, cytotoxic and antioxidant activity of crude extract of Marsilea Quadrifolia. Eur J Sci Res 33(1):123–129
Sasaki T, Masty S, Sonae A (1972) Effect of acetic acid concentration on the colour reaction in the Otoluidine boric acid method for blood glucose estimation. Rinshbo Kagaku 1:346–353
Shull KH, Ashmore J, Mayer J (1956) Hexokinase, glucose-6-phosphatase and phosphorylase levels in hereditarily obese-hyperglycemic mice. Arch Biochem Biophys 62:210–216
Sochor M, Baquer NZ, McLean P (1982) Regulation of pathways of glucose metabolism in kidney. The effect of the pentose phosphate pathway and glucorunate-xylulose pathway. Arch Biochem Biophys 198:632–646
Sochor M, Baquer NZ, McLean P (1985) Glucose over- and under-utilization in diabetes: comparative studies on the change in activities of enzymes of glucose metabolism in rat kidney and liver. Mol Physiol 7:51–68
Tiwari AK, Madhusudana RJ (2002) Diabetes mellitus and multiple therapeutic approaches of phytochemicals: present status and future prospects. Curr Sci 83:30–38
Trinder P (1969) Determination of glucose in blood using glucose oxidase with an alternative oxygen acceptor. Ann Clin Biochem 6:24–27
Valentine WN, Tanaka KR (1966) Pyruvate kinase: clinical aspects. Methods Enzymol 9:468–473
Venkatesh S, Madhava Reddy B, Dayanand Reddy G, Mullangi R, Lakshman M (2010) Antihyperglycemic and hypolipidemic effects of Helicteres isora roots in alloxan-induced diabetic rats: a possible mechanism of action. J Nat Med 64:295–304
Warjeet Singh L (2011) Traditional medicinal plants of Manipur as anti-diabetics. J Med Plants Res 5:677–687
Weber A, Marie J, Cottreau D, Simon MP, Besmond C, Dreyfus JC, Kahn A (1984) Dietary control of aldolase B and L-type pyruvate kinase mRNAs in rat. Study of translational activity and hybridization with cloned cDNA probes. J Biol Chem 259:1798–1802
World Health Organization Expert committee (1980). Diabetes mellitus. 2nd report. World Health Organization Technical Reports Series, Geneva
Yoon JW, Ray UR (1985) Perspectives on the role of viruses in insulin dependent diabetes. Diabetes Care 1:39–44
Acknowledgements
This research work was financially supported by the University Grants Commission [UGCMRP-F. No. 42–638/2013 (SR)], New Delhi, India. The authors are also thankful to Dr. P. Mariappan, Assistant Professor and Head, Department of Zoology. Rajah Serfoji Government College, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India, for statistical analysis.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors have declared that there are no conflict of interest exits.
Ethical approval
Animal studies were carried out in Central Animal Facility (CAF) at SASTRA University, Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India. All applicable international, national, and/or institutional guidelines for the care and use of animals were followed. All procedures performed in studies involving animals were in accordance with the Institutional Animal Ethics Committee (IAEC), SASTRA University. Thanjavur, Tamil Nadu, India.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Karikalan, G., Rajangam, U. Effect of Marsilea quadrifolia (L.) on carbohydrate metabolic enzymes in alloxan induced diabetic rats. J. Pharm. Investig. 48, 477–486 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0347-3
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-017-0347-3