Abstract
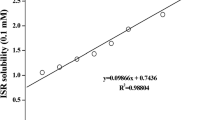
A lot of polymeric oral dosage forms have been invented for suitable drug delivery and compliance of patient. Oral dissolving film (ODF) offers a comfortable way to enable drug administration. The purpose of this study was to develop an ODF using lidocaine, with moderate mechanical strength and thickness, fast disintegration time and local anesthetic effect. Hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose, sodium alginate, glycerin, sodium lauryl sulfate, polyvinylpyrrolidone and citric acid were used to build the polymeric film base of the ODF. The optimal composition was determined by changing the ratio of individual excipients. The thickness was insignificantly varied in the range of 0.04 ± 0.01 to 0.06 ± 0.01 mm. On the other hand, the tensile strength was 1.23 ± 0.20 to 1.83 ± 0.30 N/cm2. Drug content in the films was evaluated and the values were 16 mg of lidocaine per each ODF (40 mg/strip). Lidocaine ODF formulation showed the release of 91.7% of lidocaine within 1 min and 96.3% of lidocaine in 5 min. These results suggested that lidocaine ODF was well prepared and showed the fast release of lidocaine.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelbary A, Bendas ER, Ramadan AA, Mostafa DA (2014) Pharmaceutical and pharmacokinetic evaluation of a novel fast dissolving film formulation of flupentixol dihydrochloride. AAPS Pharm Sci Tech 15:1603–1610
Acharjya SK, Panda P, Mallick P, Kumar KR, Narendra A, Sravani Y, Annapurna SMM (2010) Spectrophotometric methods for simultaneous estimation of flupentixol dihydrochloride and melitracen hydrochloride in combined tablet dosage form. J Chem Pharm Res 2:158–171
Bala R, Pawar P, Khanna S, Arora S (2013) Orally dissolving strips: a new approach to oral drug delivery system. Int J Pharm Investig 3:67–76
Cilurzo F, Cupone IE, Minghetti P, Selmin F, Montanari L (2008) Fast dissolving films made of maltodextrins. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 70:895–900
Gowacka K, Orzechowska-Juzwenko K, Bieniek A, WielaHojeñska A, Hurkacz M (2009) Optimization of lidocaine application in tumescent local anesthesia. Pharmacol Rep 61:641–653
Hansen DL, Tulinius D, Hansen EH (2008) Adolescents’ struggles with swallowing tablets: barriers, strategies and learning. Pharm World Sci 30:65–69.
Nagendrakumar D, Keshavshetti GG, Mogale P, Swami S, Swami H (2015) Formulation and evaluation of fast dissolving oral films of metoprolol succinate. Int J Eng App Sci 6:28–38
Nissen LM, Haywood A, Steadman KJ (2009) Solid medication dosage form modification at the bedside and in the pharmacy of Queensland Hospitals. J Pharm Prac Res 39:129–134.
Padula C, Colombo G, Nicoli S, Catellani PL, Massimo G, Santi P (2003) Bioadhesive film for the transdermal delivery of lidocaine: in vitro and in vivo behavior. J Control Release 88:277–285
Pathare YS, Hastak VS, Bajaj AN (2013) Polymers used for fast disintegrating oral films: A review. Int J Pharm Sci Rev Res 21:169–178
Preis M, Woertz C, Schneider K, Kukawka J, Broscheit J, Roewer N, Breitkreutz J (2014) Design and evaluation of bilayered buccal film preparations for local administration of lidocaine hydrochloride. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 86:552–561
Roh JY, Han MR, Kim KN, Kim KM (2016) The in vitro and in vivo effects of a fast-dissolving mucoadhesive bi-layered strip as topical anesthetics. Dental Materials J 35:601–605
Rozanski R, Prirnosch RE, Courts FJ (1988) Clinical efficacy of I and 2% solutions of lidocaine. Pediatr Dent 10:287–290
Siddiqui N, Garg G, Sharma P (2011) A short review on “a novel approach in oral fast dissolving drug delivery system and their patents”. Adv Bio Res 5:291–303.
Stecker SS, Swift JQ, Hodges JS, Erickson PR (2002) Should a mucoadhesive patch (DentiPatch) be used for gingival anesthesia in children? Anesth Prog 49:3–8
Stegemann S, Gosch M, Breitkreutz J (2012) Swallowing dysfunction and dysphagia is an unrecognized challenge for oral drug therapy. Int J Pharm 430:197–206
Varun R, Senthil V, Lavanya K, Ritu H (2011) A brief review on oral film technology. Int J Res in Ayurveda Pharm 2:1138–1147
Acknowledgements
All authors (B.S. Kim, G.T. Park, M.H. Park, Y.G. Shin, C.W. Cho) declare that they have no conflict of interest. This study was supported by Chungnam National University.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Kim, BS., Park, GT., Park, MH. et al. Preparation and evaluation of oral dissolving film containing local anesthetic agent, lidocaine. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 47, 575–581 (2017). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0298-0
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0298-0