Abstract
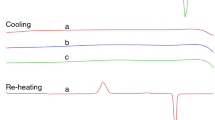
Chrysophyllum mucilage obtained from the fruit of Chrysophyllum albidum (Family Sapotaceae) has been characterised and evaluated as a binding agent in comparison with methylcellulose in paracetamol tablet formulations. Chrysophyllum mucilage was characterised using elemental and proximate analyses as well as material properties. The Heckel and Kawakita plots were used to assess the compressional properties and the tablet properties were evaluated using tensile strength, friability, disintegration and dissolution times. The results showed the presence of calcium, magnesium, potassium, sodium, manganese, iron, copper, zinc and absence of heavy metals from the mucilage. The mucilage exhibited excellent flow and swelling properties, but poor water solubility. The viscosity of chrysophyllum mucilage increased with decrease in temperature in a similar manner with methylcellulose. C. albidum mucilage when used as a binder in paracetamol tablet formulation induced faster onset of plastic deformation and higher amount of total plastic deformation than methylcellulose. The results of the tablet properties showed that the tensile strength, disintegration and dissolution times, increased with increase in binder concentration while friability decreased. Tablets containing chrysophyllum mucilage as binder also had lower tensile strength, disintegration and dissolution times but higher friability values than those containing methylcellulose. However, tablets containing chrysophyllum mucilage at low concentrations conformed to pharmacopeial standard on disintegration indicating its potential usefulness as binder for immediate release tablets. Thus, C. albidum mucilage could be used as an alternative binding agent in pharmaceutical tablets.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adenuga YA, Odeku OA, Adegboye TA, Itiola OA (2008) Comparative evaluation of the binding properties of two species of Khaya gum polymer in a paracetamol tablet formulation. Pharm Dev Technol 13(6):473–480
Adepoju OT, Adeniji PO (2012) Nutrient composition and micronutrient potential of three wildly grown varieties of African star apple (Chrysophylum albidum) from Nigeria. Afr J Food Sci 6(12):344–351. doi:10.5897/AJFS12.045
Akin-Ajani OD, Itiola OA, Odeku OA (2014) Effect of acid modification on the material and compaction properties of fonio and sweet potato starches. Starch/Starke 66:749–759. doi:10.1002/star.201300280
AOAC (Association of Official Analytical Chemists) International (2000). Official methods of analysis of AOAC international, 17th edition
Ayorinde JO, Itiola OA (2010) Individual and interacting effects of formulation variables on the tensile strength and microbial survival in diclofenac tablets. Arch Pharm Res 33(3):395–403
Bamiro OA, Sinha VR, Kumar R, Odeku OA (2010) Characterization and evaluation of Terminalia randii gum as a binder in carvedilol tablet formulation. Acta Pharm Sci 52:254–262
British Pharmacopoeia (2012) Vols. I and II. Her Majesty’s Stationery Office, London
Carr RL (1965) Evaluating flow properties of solids. Chem Eng 72:163–168
Colorcon (2009) Methocel™ product information. www.colorcon.com/literarure/marketing/mr/Extended%20Release/METHOCEL/English/pi_methocel_prep_aq.pdf
Dare K, Akin-Ajani DO, Odeku OA, Itiola OA, Odusote OM (2006) Effects of pigeon pea and plantain starches on the compressional, mechanical and disintegration properties of paracetamol tablets. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 32:357–365
Fuentes-gonzÁlez KI, Villafuerte-robles L (2014) Powder flowability as a functionality parameter of the excipient galeniq 720. Int J Pharm Pharm Sci 6(9):66
Hausner HH (1967) Friction conditions in a mass of metal powder. Int J Powder Metall 3:7–13
Ige MM, Gbadamosi SO (2007) Chemical composition and physical properties of African star apple (Chrysophylum albidum). ASSET Series A 7(1):37–42
Itiola OA, Pilpel N (1986) Studies on metronidazole tablet formulations. J Pharm Pharmacol 38:81–86
Kamba AS, Hassan LG (2011) Phytochemical screening and antimicrobial activities of African star apple (Chrysophyllumalbidum) leaves, stem against some pathogenic microorganism. Int J Pharm Front 1(2):119–129
Kawakita K, Ludde KH (1970/71) Some considerations on powder compression equations. Powder Technol 4:61–68
Kitazawa S, Johno I, Ito Y, Temura S, Okada J (1975) Effects of hardness on disintegration times and dissolution rate of uncoated caffeine tablets. J Pharm Pharmacol 27:765–770
Muazu J, Alpha A, Mohammed GT (2014) Isolation and release retardant properties of a plant gum obtained from ayoyo. Caribb J Sci Technol 2:301–313
Nigeria: Country report to the FAO International Technical Conference on plant genetic resources. Leipzig (1996)
Noyes AA, Whitney WR (1897) The rate of solution of solid substances in their own solutions. J Am Chem Soc 19:930–934
Odeku OA (2013) Potentials of tropical starches as pharmaceutical excipients: a review. Starch/Stärke 65(1/2):89–106
Odeku OA, Patani BO (2005) Evaluation of dika nut mucilage (Irvingia gabonensis) as binding agent in metronidazole tablet formulations. Pharm Dev Technol 10:439–446
Odeku OA, Okunlola A, Lamprecht A (2013) Microbead design for sustained drug release using four natural gums. Int J Biol Macromol 58:113–120
Okafor IS, Chukwu A, Udeala OK (2001) Some physicochemical properties of grewia gum. Nigeria J Polym Sci Technol 2(1):161–168
Okoli BJ, Okere OS (2010) Antimicrobial activity of the phytochemical constituents of Chrysophyllum albidum G. Don_Holl. (African Star apple) plant. J Res Nat Dev 8(1): www.transcampus.org/JORINDV8Jun2010/JournalsV8No1Jun201035.html. Accessed 14 Dec 2015
Okunlola A, Odeku OA (2009) Compressional characteristics and tableting properties of starches obtained from four dioscorea species. Farmacia 57(6):756–770
Onyeka CA, Aligwekwe AU, Olawuyi TS, Nwakanma AA, Kalu EC, Oyeyemi AW (2012) Antifertility effects of ethanolic root bark extract of Chrysophyllumalbidumin male Albino rats. Int J Appl Res Nat Prod 5(1):12–17
Shailendra P, Shikha A, Singh BL (2012) Natural binding agents in tablet formulation. Int J Pharm Biol Arch 3(3):466–473
Ugwu JA, Umeh VC (2015) Assessment of African star apple (Chrysophyllum albidum) fruit damage due to insect pests in Ibadan, Southwest Nigeria. Res J For 9:87–92. doi:10.3923/rjf.2015.87.92
Williams PA, Phillips GO (2004) Gums and stabilizers for the food Industry 12. Royal Society of Chemistry, Cambridge. ISBN 0-85404-891-X
Acknowledgments
The authors gratefully acknowledge the German Research Foundation and The World Academy of Science for a TWAS-DFG visit awarded O. D. Akin-Ajani which enabled her to do some of the characterization. T. O. Ajala, O. D. Akin-Ajani, C. Ihuoma-Chidi and O. A. Odeku declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ajala, T.O., Akin-Ajani, O.D., Ihuoma-Chidi, C. et al. Chrysophyllum albidum mucilage as a binding agent in paracetamol tablet formulations. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 46, 565–573 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0266-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-016-0266-8