Abstract
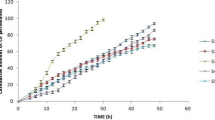
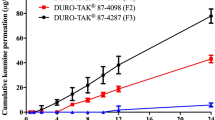
Selegiline transdermal drug delivery system (TDDS) of drug-in-adhesive matrix type was developed using acrylic-rubber hybrid pressure sensitive adhesive (PSA). The permeation rate of selegiline was the highest from silicone, followed by acrylic-rubber hybrid, acrylics. Although the permeation rate of silicone PSA was higher than that of acrylic-rubber hybrid PSA, the cold flow of silicone PSA was unacceptable. When the drug concentration was increased from 3.5 to 8 % w/w of polymer weight, the drug permeation rate also increased proportionally. The correlation coefficient (R2) between selegiline content in the TDDS and the average cumulative amount permeated was 0.999. When the stability study of the TDDS was carried out at the accelerated condition of 40 °C/75 % relative humidity for 12 weeks, no significant changes in both the physical appearance and the drug content were observed. The drug permeation rate from the TDDS was much higher than that from Emsam®. The average cumulative flux of selegiline from the TDDS was 2 times higher than that from Emsam®.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson MC, Hasan F, McCrodden JM, Tipton KF (1993) Monoamine oxidase inhibitors and the cheese effect. Neurochem Res 18:1145–1149
Barrett JS, DiSanto AR, Thomford PJ, Larsen EM, Palazzolo MJ, Morales RJ (1997) Toxicokinetic evaluation of a selegiline transdermal system in the dog. Biopharm Drug Dispos 18:165–184
Birkmayer W (1983) Deprenyl (selegiline) in the treatment of parkinson’s disease. Acta Neurol Scand Suppl 95:103–105
Blackwell B, Marley E, Price J, Taylor D (1967) Hypertensive interactions between monoamine oxidase inhibitors and foodstuffs. Br J Psychiatry 113:349–365
Chen CC, Fang CL, Al-Suwayeh SA, Leu YL, Fang JY (2011) Transdermal delivery of selegiline from alginate–Pluronic composite thermogels. Int J Pharm 415:119–128
Choi HK, Angello JT (1994) The mathematical analysis and optimization of a flow through diffusion cell system. Pharm Res 11:595–599
Ekstedt B, Magyar K, Knoll J (1979) Does the B form selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor lose selectivity by long term treatment? Biochem Pharmacol 28:919–923
Fang JY, Hung CF, Chi CH, Chen CC (2009) Transdermal permeation of selegiline from hydrogel-membrane drug delivery systems. Int J Pharm 380:33–39
Feiger AD, Rickels K, Rynn MA, Zimbroff DL, Robinson DS (2006) Selegiline transdermal system for the treatment of major depressive disorder: an 8-week, double-blind, placebo-controlled, flexible-dose titration trial. J Clin Psychiatry 67:1354–1361
Felner AE, Waldmeier PC (1979) Cumulative effects of irreversible MAO inhibitors in vivo. Biochem Pharmacol 28:995–1002
Glover V, Elsworth JD, Sandler M (1980) Dopamine oxidation and its inhibition by (−)-deprenyl in man. J Neural Transm Suppl 16:163–172
Mann JJ, Aarons SF, Wilner PJ, Keilp JG, Sweeney JA, Pearlstein T, Frances AJ, Kocsis JH, Brown RP (1989) A controlled study of the antidepressant efficacy and side effects of (−)−deprenyl: a selective monoamine oxidase inhibitor. Arch Gen Psychiatry 46:45–50
Mawhinney M, Cole D, Azzaro AJ (2003) Daily transdermal administration of selegiline to guinea-pigs preferentially inhibits monoamine oxidase activity in brain when compared with intestinal and hepatic tissues. J Pharm Pharmacol 55:27–34
McGrath PJ, Stewart JW, Harrison W, Wager S, Nunes EN, Quitkin FM (1989) A placebo-controlled trial of l-deprenyl in atypical depression. Psychopharmacol Bull 25:63–67
Patkar AA, Pae CU, Masand PS (2006) Transdermal selegiline: the new generation of monoamine oxidase inhibitors. CNS Spectr 11:363–375
Riederer P, Youdim MB (1986) Monoamine oxidase activity and monoamine metabolism in brains of parkinsonian patients treated with l-deprenyl. J Neurochem 46:1359–1365
Rohatagi S, Barrett JS, DeWitt KE, Lessard D, Morales RJ (1997) Pharmacokinetic evaluation of a selegiline pulsatile oral delivery system. Biopharm Drug Dispos 18:665–680
Small G, Dubois B (2007) A review of compliance to treatment in Alzheimer’s disease: potential benefits of a transdermal patch. Curr Med Res Opin 23:2705–2713
Sunderland T, Cohen RM, Molchan S, Lawlor BA, Mellow AM, Newhouse PA, Tariot PN, Mueller EA, Murphy DL (1994) High-dose selegiline in treatment-resistant older depressive patients. Arch Gen Psychiatry 51:607–615
Tetrud JW, Langston JW (1989) The effect of deprenyl (selegiline) on the natural history of Parkinson’s disease. Science 245:519–522
Acknowledgments
These authors (E.-Y. Lee, S.-H. Choi, M.-K. Chun, and H.-K. Choi) declare that they have no conflict of interest. This work was supported by a grant of the Korean Health Technology R&D Project, Ministry for Health, Welfare & Family Affairs (A092018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Eun-Young Lee and Seung-Hyuk Choi have contributed equally to this work.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Lee, EY., Choi, SH., Chun, MK. et al. Development of transdermal drug delivery system of selegiline. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 46, 147–152 (2016). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0222-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0222-z