Abstract
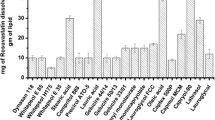
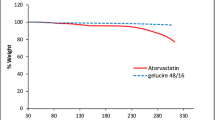
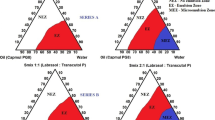
The objective of present investigation was to enhance solubility, dissolution rate and bioavailability of poorly water soluble drug atorvastatin using solid lipid glycerol monostearate and surfactant poloxamer-407. Oral pastilles of glycerol monostearate and poloxamer were formulated by pastillation technique and optimized by central composite design. Hemispherical pastilles were evaluated for drug content, saturation solubility study, thermal properties and in vitro, ex vivo and in vivo drug release study. Formulation F4 at high level of glycerol monostearate (1000 mg) and poloxamer-407 (400 mg) showed 25-fold and 3-fold increased in solubility and dissolution rate, respectively. X-Ray diffraction and scanning electron microscopic study proved the decrease in crystallinity of atorvastatin and confirmed the conversion of crystalline to amorphous form, respectively. Ex vivo study revealed that maximum amount of released drug was absorbed through the everted intestine. In vivo study in rats showed higher HMG CoA to mevalonate ratio of pastilles than plain drug. This indicated better bioavailability and hyperlipidemic activity of pastilles than atorvastatin. Thus, the solubility, dissolution rate and bioavailability of atorvastatin were enhanced successfully using lipid carrier system.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anwar M, Warsi M, Mallick N, Akhter S, Gahoi S (2011) Enhanced bioavailability of nano-sized chitosan–atorvastatin conjugate after oral administration to rats. Eur J Pharm Sci 44:241–249
Cespi M, Bonacucina G, Misici-Falzi M, Golzi R, Boltri L, Palmieri G (2007) Stress relaxation test for the characterization of the viscoelasticity of pellets. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 67:476–484
Chakraborty S, Shukla D, Mishra B, Singh S (2009) Lipid—an emerging platform for oral delivery of drugs with poor bioavailability. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 73:1–15
Eloy J, Maldonado JM (2014) Solid dispersions containing ursolic acid in Poloxamer 407 and PEG 6000: a comparative study of fusion and solvent methods. Powder Technol 253:98–106
Ibric S, Kolasinac N, Kachrimanis K, Homsek I, Grujic B, Duricb Z (2012) Solubility enhancement of desloratadine by solid dispersion in poloxamers. Int J Pharm 436:161–170
Jain P, Patil S, Haswani N, Girase M, Surana S (2010) Hypolipidemic activity of Moringa oleifera Lam., Moringaceae, on high fat diet induced hyperlipidemia in albino rats. Rev Bras Farmacogn 20:969–973. doi:10.1590/S0102-695X2010005000038
Kalepu S, Mohanvarma Manthina M, Padavala V (2013) Oral lipid-based drug delivery systems—an overview. Acta Pharm Sin B 3(6):361–372
Kim J, Ulrich J (2003) Prediction of degree of deformation and crystallization time of molten droplets in pastillation process. Int J Pharm 257:205–215
Kim M, Jin S, Kim J, Park H, Song H, Neubert R, Hwang S (2008) Preparation, characterization and in vivo evaluation of amorphous atorvastatin calcium nano particles using supercritical antisolvent (SAS) process. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 69:454–465
Kleinebudde P, Witzleb R, Mullertz A, Kanikanti V, Hamann H (2012) Dissolution of solid lipid extrudates in biorelevant media. Int J Pharm 422:116–124
Pandit AP, Tekade AR, Devkar TB, Divase GT, Rodde MS, (Patent filed 2012) An apparatus for conducting ex vivo studies on tissues, Indian Patent. 2363-MUM: 2012
Pandit AP, Divase GT, Chavan TT, Khandelwal KR (2014) Oral lipid based multiparticulate pastilles: design and effect of pore former. J Pharm Invest volume 44-4:40005-014-0141-4
Partani P, Verma S, Gurule S, Khuroo A, Monif T (2014) Simultaneous equation of atorvastatin and its two active metabolites in human plasma by liquid chromatography/electrospray tandem mass spectrometry. J Pharm Anal 4(1):26–36
Porter CJ, Charman WN (2001) In vitro assessment of oral lipid based formulations. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 50:127–147
Prabhu S, Ortega M, Ma C (2005) Novel lipid-based formulations enhancing the in vitro dissolution and permeability characteristics of a poorly water-soluble model drug piroxicam. Int J Pharm 301:209–216
Pushp RN, Han Hyo-Kyung, Choi Hoo-Kyun (2010) Enhancement of solubility and dissolution of Coenzyme Q10 using solid dispersion formulation. Int J Pharm 383:147–153
Venugopal Rao A, Ramakrishanan S (1975) Indirect assessment of hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase (NADPH) activity in liver tissue. Clin Chem 21:1523–1525
Zakir F, Choudharya A, Ranaa A, Aggarwal G, Kumara V (2012) Development and characterization of an atorvastatin solid dispersion formulation using skimmed milk for improved oral bioavailability. Acta Pharm Sin B 2:421–428
Acknowledgments
All authors (A. P. Pandit, T. T. Chavan, K. R. Khandelwal) declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandit, A.P., Chavan, T.T. & Khandelwal, K.R. Enhancement of solubility, dissolution rate and bioavailability of atorvastatin using solid lipid: in vitro and in vivo characterization. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 45, 503–513 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0199-7
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0199-7