Abstract
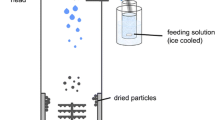
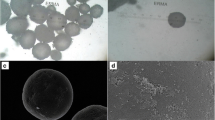
The aim of the present study was to investigate the effect of processing and formulation variables on polymeric microparticles, intended to be used for sustaining drug delivery of ibuprofen. Ibuprofen, polycaprolactone, dichloromethane (DCM), water, stirring speed and polyvinyl alcohol were selected as independent variables during the microparticles preparation. The independent variables influencing encapsulation efficiency (E.E.) and physical characteristics were assessed. The resultant microparticles were characterized for their E.E., surface morphology, and in vitro drug release. Ibuprofen loaded polymeric microparticles were characterized by FESEM, FTIR, DSC, and XRPD analysis. Graphical and mathematical analysis of the design showed that ibuprofen, polycaprolactone and DCM were significant effect on the E.E. of the microparticles. The low magnitudes of error and the significant values of R2 in the present investigation prove the high prognostic ability of the design. The microparticles showed high E.E. (76.11 ± 0.06–104.9 ± 0.46 %) with average particle size of 5–100 μm. The microparticles were found to be discrete, spherical with smooth surface. The FTIR analysis confirmed the compatibility of ibuprofen with the polymers. The XRPD and DSC study revealed the dispersion of drug within microparticles formulation. In vitro study showed sustain drug release over 12 h, thus prolong the drug action to treat the musculoskeletal disorder.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Agnihotri S, Aminabhavi T (2004) Controlled release of clozapine through chitosan microparticles prepared by a novel method. J Control Release 96:245–259
Ahuja M, Yadav M, Kumar S (2010) Application of response surface methodology to formulation of ionotropically gelled gum cordia/gellan beads. Carbohydr Polym 80:161–167
Alberto L, Rodriguez G (1997) Nonsteroidal antiinflammatory drugs, ulcers and risk: a collaborative meta-analysis. Semin Arthritis Rheum 6:16–20
Bas D (2007) Modeling and optimization I: usability of response surface methodology. J Food Eng 78:836–845
Chang J, Huang Y, Hou S, Wang R (2007) Formulation optimization of meloxicam sodium gel using response surface methodology. Int J Pharm 338:48–54
Chopra S, Patil G, Motwani S (2007) Release modulating hydrophilic matrix systems of losartan potassium: optimization of formulation using statistical experimental design. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 66:73–82
Current Good Manufacturing Practices for Drugs (2004) Reports, guidances and additional information—pharmaceutical cGMPs for the 21st century—a risk-based approach. Centre for Drug Evaluation and Research, pp 20–26
Deshmukh RK, Naik JB (2013) Diclofenac sodium-loaded Eudragit® microspheres optimization using statistical experimental design. J Pharm Innov 8:276–287
Deshmukh RK, Naik JB (2014) Aceclofenac microspheres: quality by design approach. Mater Sci Eng C 36:320–328
Dillen K, Vandervoort J, Van den Mooter G, Verheyden L, Ludwig A (2004) Factorial design, physicochemical characterisation and activity of ciprofloxacin-PLGA nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 275:171–187
Dillen K, Vandervoort J, Van Den Mooter G, Ludwig A (2006) Evaluation of ciprofloxacin-loaded Eudragit® RS100 or RL100/PLGA nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 314:72–82
Dong Y, Feng S (2007) Poly ((d, l-lactide-co-glycolide) (PLGA) nanoparticles prepared by high pressure homogenization for paclitaxel chemotherapy. Int J Pharm 342:208–214
Freitas S, Merkle HP, Gander B (2005) Microencapsulation by solvent extraction/evaporation: reviewing the state of the art of microsphere preparation process technology. J Control Release 102:313–332
Howard PA, Delafontaine P (2004) Nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs and cardiovascular risk. J Am Coll Cardiol 43:519–525
Indian Pharmacopoeia Commission (2007) Ministry of Health & Family Welfare Govt. of India, Ghaziabad, Indian Pharmacopoeia 2007, p 480
Liu R, Tang Y (2010) Tuber melanosporum fermentation medium optimization by Plackett–Burman design coupled with Draper–Lin small composite design and desirability function. Bioresour Technol 101:3139–3146
McGinity J, O’Donnell P (1997) Preparation of microspheres by the solvent evaporation technique. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 28:25–42
Mennini N, Furlanetto S, Cirri M, Mura P (2012) Quality by design approach for developing chitosan-Ca-alginate microspheres for colon delivery of celecoxibhydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin–PVP complex. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 80:67–75
Naik J, Lokhande A, Mishra S, Kulkarni R (2012) Development of sustained release micro/nanoparticles using different solvent emulsification technique. Int J Pharm Biol Sci 3:573–590
Pilotto A, Sancarlo D, Addante F, Scarcelli C, Franceschi M (2010) Non-steroidal antiinflammatory drug use in the elderly. Surg Oncol 19:167–172
Plackett RL, Burman JP (1946) The design of optimum multifactorial experiments. Biometrika 33:305–325
Ragonese R, Macka M, Hughes J, Petocz P (2007) The use of the Box–Behnken experimental design in the optimisation and robustness testing of a capillary electrophoresis method for the analysis of ethambutol hydrochloride in a pharmaceutical formulation. J Pharm Biomed Anal 27:995–1007
Rhee Y, Chang S, Park C, Chi S, Park E (2008) Optimization of ibuprofen gel formulations using experimental design technique for enhanced transdermal penetration. Int J Pharm 364:14–20
Sastry SV, Khan MA (1998) Aqueous based polymeric dispersion: Plackett–Burman design for screening of formulation variables of atenolol gastrointestinal therapeutic system. Pharm Acta Helv 73(2):105–112
Shah PP, Mashru RC, Rane YM, Thakkar A (2008) Design and optimization of mefloquine hydrochloride microparticles for bitter taste masking. Pharm Sci Tech 9:377–389
Sostres C, Gargallo C, Arroyo M, Lanas A (2010) Adverse effects of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs, aspirin and coxibs) on upper gastrointestinal tract. Best Pract Res Clin Gastroenterol 24:121–132
Wang P, Wang Z, Wu Z (2012) Insights into the effect of preparation variables on morphology and performance of polyacrylonitrile membranes using Plackett–Burman design experiments. Chem Eng J Lausanne 193–194:50–58
Yang YY, Chung TS, Ng NP (2001) Morphology, drug distribution, and in vitro release profiles of biodegradable polymeric microspheres containing protein fabricated by double emulsion solvent extraction/evaporation method. Biomaterials 22:231–241
Acknowledgments
All authors (A. S. Gawali, R. K. Deshmukh, J. B. Naik) declare that they have no conflict of interest. This article does not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors. The authors want to express their sincere thanks to Technical Education Quality Improvement Program (TEQIP II), MHRD New Delhi, India for financial support. Authors are very much thankful to Natco Pharma Limited (Hyderabad, India), for providing the gift sample of Ibuprofen.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Gawali, A.S., Deshmukh, R.K. & Naik, J.B. Development and optimization of sustained release polymeric microparticles by screening design. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 45, 349–358 (2015). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0181-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-015-0181-4