Abstract
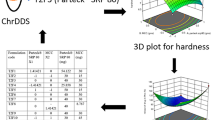
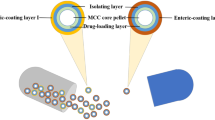
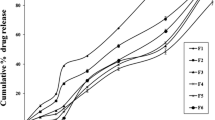
The objective of present work was to develop a “tablets in capsule” system for facilitating both immediate and pulsatile drug deliveries of theophylline to mimic the circadian rhythm of nocturnal asthma. The system comprised of capsule filled with two tablets, first pulse and second pulse tablet prepared by wet granulation method. First pulse tablet was not coated and was responsible for providing loading dose whereas; second pulse tablet was coated with Eudragit L100 and Eudragit S100 to release drug in colon after specific lag time. Two independent variables, amount of polymers and coating thickness, were optimized by 32 full factorial design. The optimum formulation consisted of Eudragit L100: Eudragit S100 in 1:1.5 ratio and coating thickness of 20 % (w/w). In vitro drug release of “tablets in capsule” system in three different media (pH 1.2, pH 6.8, and pH 7.4) revealed immediate and pulsatile release patterns.








Similar content being viewed by others
References
Amin PD, Gupta SS, Prabhu NB, Wadhwani AR (2005) Fast disintegrating dosage form of ofloxacin and metronidazole benzoate. Investig Drug 42:614–617
Ashford M, Fell T (1994) Targeting drugs to the colon: delivery systems for oral administration. J Drug Target 2:241–258
Ashford M, Fell JT, Attwood D, Wood head PJ (1993) An in vitro investigation into the suitability of pH-dependent polymers for colon targeting. Int J Pharm 91:241–245
Botti B (2004) Chronopharmaceutics gimmick or clinically relevant approach to drug delivery-a review. J Control Release 98:337–353
Bjorn L (1996) The clinical relevance of chronopharmacology in therapeutics. Pharmacol Res 33:107–115
Chauhan CS, Naruka PS, Rathore RS, Badadwal V (2010) Formulation and evaluation of prednisolone tablet for colon targeted drug delivery system. J Chem Pharm Res 2:993–998
Chourasia MK, Jain SK (2003) Pharmaceutical approaches to colon targeted drug delivery systems. J Pharm Pharm Sci 6:33–66
Degussa (2009) Specifications and test methods for Eudragit® L100 and Eudragit® S100.http://www.solimide.eu/de/pharmapolymers/eudragit/quality/spezifikationen_neu.Par.0001.TRow.0006.TCell.0002.File.tmp/7.1.03_INFO7.3e_L100_S100_200409.pdf. Accessed 23 March 2011
Gibaldi M, Feldman S (1967) Establishment of sink conditions in dissolution rate determinations. Theoretical considerations and application to nondisintegrating dosage forms. J Pharm Sci 56:1238–1242
Gupta VK, Beckert TE, Price JC (2001) A novel pH- and time-based multi-unit potential colonic drug delivery system I. Development. Int J Pharm 213:83–91
Gupta VK, Gnanarajan G, Kothiyal P (2012) A review article on colonic targeted drug delivery system. Pharma Innov 1(7):14–24
Kinget R, Kalala W, Vervoort L, Vanden G (1998) Colonic targeting. J Drug Target 6:129–149
Korsmeyer RW, Gurney R, Dueler EM, Bury P, Peppas NA (1983) Mechanism of solute release from porous hydrophilic polymers. Int J Pharm 15:25–35
Kothari CR (2004) Methods and techniques. Reaserach methodology, 2nd edn. New age international publishers, New Delhi, pp 47–52
Kulkarni AR, Soppimath KS, Aminabhavi TM, Rudzinski WE (2001) Invitro release kinetics of cefadroxil-loaded sodium alginate interpenetrating network beads. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 51:127–133
Libo Y, James SC, Joseph AF (2002) Colon specific drug delivery: new approaches and in vitro/in vivo evaluation—review. Int J Pharm 235:1–15
Marvola M, Nykanen P, Rautio S, Isonen N, Autere AM (1999) Enteric polymers as binders and coating materials in multiple unit site-specific drug delivery systems. Eur J Pharm Sci 7:259–267
Mastiholimath V, Dandagi P, Jain SS, Gadad A, Kulkarni A (2007) Time and pH dependent colon specific, pulsatile delivery of theophylline for nocturnal asthma. Int J Pharm 328:49–56
Richard JM, Susan BS (1998) Chronobiology of asthma. Am J Respir Crit Care Med 158:1002–1007
Sarasija S, Stutie P (2005) Chronotherapeutics: emerging role of biorhythms in optimizing drug therapy. Ind J Phrm Sci 67:135–140
Shah R, Patel S, Patel H, Pandey S, Shah S, Shah D (2011) Formulation development of carvedilol compression coated tablet. Pharm Dev Technol 5:1–10
Shivakumar HN, Sarasija S, Desai BG (2007) Design and evaluation of ph sensitive minitablets for chronotherapeutic delivery of theophylline. Ind J Pharm Sci 69(1):73–79
USP 28-NF 23 (2005) The official Compendia of Standards, Asian Edition. United States Pharmacopoeial Convention Inc., Washington, D.C, pp 626–627
Wagner JG (1969) Interpretation of percent dissolved-time plots derived from in vitro testing of conventional tablets and capsules. J Pharm Sci 58:1253–1257
Watts PJ, Illum L (1997) Colonic drug delivery. Drug Dev Ind Pharm 23:893–913
Acknowledgments
This article dose not contain any studies with human and animal subjects performed by any of the authors. All authors (S. Pandey, P. Mehta, H. Patel, R. Shah, A. Gupta, and A. Mishra) declare that they have no conflict of interest. The authors wish to acknowledge Sidmak Pharmaceuticals, Valsad, India for providing theophylline as gift sample and Dr. Renu Chauhan for sparing her valuable time for correcting language and grammatical errors of the manuscript.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pandey, S., Mehta, P., Patel, H. et al. Novel time and site specific “tablets in capsule” system for nocturnal asthma treatment. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 44, 381–390 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0133-4
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-014-0133-4