Abstract
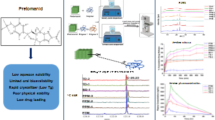
The aim of this study was to compare physicochemical properties of solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) made from different lipids. To make small, stable, uniform and highly encapsulated SLNs, many factors such as the components (lipid, stabilizer) and preparation condition (sonication time, power) can be considered. Out of those, we selected solid lipid as lipid matrix to investigate an effect on SLNs. The SLNs were characterized by particle size, zeta potential, solubility and in vitro release study. In this study, SLNs showed different physicochemical properties and release profiles according to used solid lipid. In case of particle size, M-SLN showed biggest particle size (412.5 ± 29.4 nm) and highest encapsulation efficiency (61.2 ± 4.8 %). And, B-SLN showed highest cumulative drug percentage (85.0 ± 1.7 %, 24 h) in release study. These results suggest that lipids type affect physicochemical properties and release profile of SLN.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Anderson M, Ormi A (2004) The effect of different lipid components on the in vitro stability and release kinetics of liposome formulations. Drug Deliv 11(1):33–39
Carbone C, Tomasello B, Ruozi B, Renis M, Pulglisi G (2012) Preparation and optimization of PIT solid lipid nanoparticles via statistical factorial design. Eur J Med Chem 49:110–117
Ghadiri M, Fatemi S, Vatanara A, Doroud D, Najafabadi AR, Darabi M, Rahimi AA (2012) Loading hydrophilic drug in solid lipid media as nanoparticles : statistical modeling of entrapment efficiency and particle size. Int J Pharm 424(1–2):128–137
HuFQ JiangSP, Du YZ (2005) Preparation and characterization of stearic acid nanostructured lipid carriers by solvent diffusion method in an aqueous system. Colloids Surf B Biointerfaces 45:167–173
Hurst SJ, Lytton-Jean AK, Mirkin CA (2006) Maximizing DNA loading on a range of gold nanoparticle sizes. Anal Chem 78(24):13–18
Joseph S, Bunjes H (2012) Preparation of nanoemulsions an solid lipid nanoparticles by premix membrane emulsification. J Pharm Sci 101(7):2479–2489
Kheradmandnia S, Vasheghani-Farahani E, Nosrati M, Atyabi F (2010) Preparation and characterization of ketoprofen-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles made from beeswax and carnauba wax. Nanomedicine 6(6):753–759
Kumar VV, Chandrasekar D, Ramakrishna S, Kishan V, Rao YM, Diwan PV (2007) Development and evaluation of nitrendipine loaded solid lipid nanoparticles: influence of wax and glyceride lipids on plasma pharmacokinetics. Int J Pharm 335(1–2):167–175
Lee MK, Lim SJ, Kim CK (2007) Preparation, characterization and in vitro cytotoxicity of paclitaxel loaded sterically stabilized solid lipid nanoparticles. Biomaterials 28:2137–2146
Marengo E, Cavalli R, Caputo O, Rodriguez L, Gasco M (2000) Scale-up of preparation process of solid lipid nanospheres. Part I. Int J Pharm 205(1–2):3–13
Mahnert W, Mader K (2001) Solid lipid nanoparticles: production, characterization and applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 47(2–3):165–196
Mukherjee S, Ray S, Thakur RS (2009) Solid lipid nanoparticles: a modern formulation approach in drug delivery system. Indian J Pharm Sci 71(4):349–358
Muller RH, Heinemann S (1992) Fat emulsions for parenteral nutrition. I. Evaluation of microscopic and laser light scattering methods for the determination of the physical stability. Clin Nutr 11:223–272
Muller RH, Mader K, Gohla S (2000) Solid lipid nanoparticles (SLN) for controlled drug delivery—a review of the state of the art. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 50(1):161–177
Nesseem D (2011) Formulation of sunscreens with enhancement sun protection factor response based on solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Cosmet Sci 33(1):70–79
Noack A, Hause G, Mader K (2012) Physicochemical characterization of curcuminoid-loaded solid lipid nanoparticles. Int J Pharm 423(2):440–451
Padois K, Cantieni C, Bertholle V, Bardel C, Pirot F, Falson F (2011) Solid lipid nanoparticles suspension versus commercial solutions for dermal delivery of minoxidil. Int J Pharm 416(1):300–304
Shenoy VS, Gude RP, Murthy RS (2009) Paclitaxel-loaded glyceryl palmitostearate nanoparticles: in vitro release and cytotoxici activity. J Drug Target 17(4):304–310
Sievens-Figueroa L, Bhakay A, Jerez-Rozo JI, Pandya N, Romanach RJ, Michniak-Kohn B, Iqbal Z, Bilgili E, Dave RN (2012) Preparation and characterization of hydroxypropyl methyl cellulose films containing stable BCS Class II drug nanoparticles for pharmaceutical applications. Int J Pharm 423(2):496–508
Song X, Zhao Y, Hou S, Xu F, Zhao R, He J, Cai Z, Li Y, Chen Q (2008) Dual agents loaded PLGA nanoparticles: systematic study of particle size and drug entrapment efficiency. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 69(2):445–453
Spada G, Gavini E, Cossu M, Rassu G, Giunchedi P (2012) Solid lipid nanoparticles with and without hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin: a comparative study of nanoparticles designed for colonic drug delivery. Nanotechnology 23(9):095101
Wissing SA, Kayser O, Muller RH (2004) Solid lipid nanoparticles for parenteral drug delivery. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 56:1257–1272
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Basic Science Research Program (2012R1A1B5003358) through the National Research Foundation of Korea (NRF) funded by the Ministry of Education, Science and Technology.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Baek, JS., Shin, SC. & Cho, CW. Effect of lipid on physicochemical properties of solid lipid nanoparticle of paclitaxel. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 42, 279–283 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0038-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0038-z