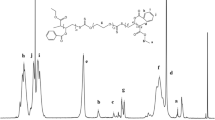
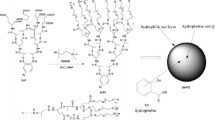
Abstract
In order to increase the bioavailability of hydrophilic unstable drugs, polymersomes from AB3 type tetra block copolymers composing of poly(ethylene glycol)-b-(3) poly(lactic acid) (EO-3LA) as a water-soluble drug delivery carrier have been investigated due to its unique properties such as high stability and high water soluble drug loading efficiency. The sizes of EO-3LA polymersomes determined by dynamic light scattering were ranged in 190–220 nm with monodispersion. Its polymeric layer with 10–20 nm at the outershell was observed by field emission scanning electron microscopy. The polymersomes showed low critical aggregation concentrations (9.2–14.9 ug/ml). Anthocyanin was employed as a model drug for unstable drug in this study. The anthocyanin loading contents of EO-3LA polymersomes are depending on PLLA content in the polymers. The high loading contents (6.6–7.0 wt%) of the polymersomes are due to their tight and rigid polymeric membranes. The polymeric membrane in EO-3LA polymersomes contributed to improve drug stability on various pHs. Moreover, this property induced sustained anthocyanin release pattern from the polymersome. Therefore, the polymersome has potential as a drug carrier for water-soluble and unstable drugs.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmed F, Discher DE (2004) Self-porating polymersomes of PEG-PLA and PEG-PCL: hydrolysis-triggered controlled release vesicles. J Control Release 96:37–53
Allen T, Cleland L (1980) Serum-induced leakage of liposome contents. Biochimt Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 597:418–426
Bangham A (1993) Liposomes: the Babraham connection. Chem Phys Lipids 64:275–285
Bolotin EM, Cohen R, Bar LK, Emanuel N, Ninio S, Barenholz Y, Lasic DD (1994) Ammonium sulfate gradients for efficient and stable remote loading of amphipathic weak bases into liposomes and ligandoliposomes. J Liposome Res 4:455–479
Chiappetta DA, Sosnik A (2007) Poly (ethylene oxide)-poly (propylene oxide) block copolymer micelles as drug delivery agents: Improved hydrosolubility, stability and bioavailability of drugs. Eur J Pharm Biopharm 66:303–317
Cullis P, Mayer L, Bally M, Madden T, Hope M (1989) Generating and loading of liposomal systems for drug-delivery applications. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 3:267–282
Discher DE, Ahmed F (2006) Polymersomes. Annu Rev Biomed Eng 8:323–341
Discher BM, Won YY, Ege DS, Lee J, Bates FS, Discher DE, Hammer DA (1999) Polymersomes: tough vesicles made from diblock copolymers. Science 284:1143
Discher BM, Hammer DA, Bates FS, Discher DE (2000) Polymer vesicles in various media. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 5:125–131
Gregoriadis G (1995) Engineering liposomes for drug delivery: progress and problems. Trends Biotechnol 13:527–537
Harrington KJ, Mohammadtaghi S, Uster PS, Glass D, Peters AM, Vile RG, Stewart JSW (2001) Effective targeting of solid tumors in patients with locally advanced cancers by radiolabeled pegylated liposomes. Clin Cancer Res 7:243–254
Jeong JH, Lim DW, Han DK, Park TG (2000) Synthesis, characterization and protein adsorption behaviors of PLGA/PEG di-block co-polymer blend films. Colloids Surf B 18:371–379
Johnston APR, Such GK, Ng SL, Caruso F (2011) Challenges facing colloidal delivery systems: from synthesis to the clinic. Curr Opin Colloid Interface Sci 16:171–181
Kale AA, Torchilin VP (2007) Enhanced transfection of tumor cells in vivo using “Smart” pH-sensitive TAT-modified pegylated liposomes. J Drug Target 15:538–545
Labhasetwar V, Song C, Levy RJ (1997) Nanoparticle drug delivery system for restenosis. Adv Drug Deliv Rev 24:63–85
Lapidot T, Harel S, Akiri B, Granit R, Kanner J (1999) pH-dependent forms of red wine anthocyanins as antioxidants. J Agric Food Chem 47:67–70
Lee JS, Zhou W, Meng F, Zhang D, Otto C, Feijen J (2010) Thermosensitive hydrogel-containing polymersomes for controlled drug delivery. J Control Release 146:400–408
Leson A, Filiz V, Förster S, Mayer C (2007) Water permeation through block-copolymer vesicle membranes. Chem Phys Lett 444:268–272
Li S, Byrne B, Welsh JE, Palmer AF (2007) Self assembled poly (butadiene)-b-poly (ethylene oxide) polymersomes as paclitaxel carriers. Biotechnol Prog 23:278–285
Lian T, Ho RJY (2001) Trends and developments in liposome drug delivery systems. J Pharm Sci 90:667–680
Liu D, Liu F, Song YK (1995) Recognition and clearance of liposomes containing phosphatidylserine are mediated by serum opsonin. Biochim Biophys Acta (BBA) Biomembr 1235:140–146
Meng F, Hiemstra C, Engbers GHM, Feijen J (2003) Biodegradable polymersomes. Macromolecules 36:3004–3006
Moghimi S, Szebeni J (2003) Stealth liposomes and long circulating nanoparticles: critical issues in pharmacokinetics, opsonization and protein-binding properties. Prog Lipid Res 42:463–478
Musumeci T, Ventura C, Giannone I, Ruozi B, Montenegro L, Pignatello R, Puglisi G (2006) PLA/PLGA nanoparticles for sustained release of docetaxel. Int J Pharm 325:172–179
Na K, Park KM, Jo EA, Lee KS (2006) Self-organized pullulan/deoxycholic acid nanogels: physicochemical characterization and anti-cancer drug-releasing behavior. Biotechnol Bioprocess Eng 11:262–267
Nakaoka R, Tabata Y, Yamaoka T, Ikada Y (1997) Prolongation of the serum half-life period of superoxide dismutase by poly (ethylene glycol) modification. J Control Release 46:253–261
Orton CG (1995) Width of the therapeutic window: What is the optimal dose-per-fraction for high dose rate cervix cancer brachytherapy? Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 31:1011
Panyam J, Williams D, Dash A, Leslie-Pelecky D, Labhasetwar V (2004) Solid-state solubility influences encapsulation and release of hydrophobic drugs from PLGA/PLA nanoparticles. J Pharm Sci 93:1804–1814
Paula S, Volkov A, Van Hoek A, Haines T, Deamer DW (1996) Permeation of protons, potassium ions, and small polar molecules through phospholipid bilayers as a function of membrane thickness. Biophys J 70:339–348
Ruan G, Feng SS (2003) Preparation and characterization of poly (lactic acid)-poly (ethylene glycol)-poly (lactic acid) (PLA-PEG-PLA) microspheres for controlled release of paclitaxel. Biomaterials 24:5037–5044
Sahoo SK, Dilnawaz F, Krishnakumar S (2008) Nanotechnology in ocular drug delivery. Drug Discov Today 13:144–151
Singh R, Lillard JW Jr (2009) Nanoparticle-based targeted drug delivery. Exp Mol Pathol 86:215–223
Torchilin VP, Lukyanov AN (2003) Peptide and protein drug delivery to and into tumors: challenges and solutions. Drug Discov Today 8:259–266
Uhrich KE, Cannizzaro SM, Langer RS, Shakesheff KM (1999) Polymeric systems for controlled drug release. Chem Rev Columb 99:3181–3198
Westesen K, Bunjes H, Koch M (1997) Physicochemical characterization of lipid nanoparticles and evaluation of their drug loading capacity and sustained release potential. J Control Release 48:223–236
Yin H, Kang SW, Bae YH (2009) Polymersome formation from AB2 type 3-miktoarm star copolymers. Macromolecules 42:7456–7464
Zheng XL, Kan B, Gou ML, Fu SZ, Zhang J, Men K, Chen LJ, Luo F, Zhao YL, Zhao X (2010) Preparation of MPEG-PLA nanoparticle for honokiol delivery in vitro. Int J Pharm 386:262–267
Acknowledgments
This research was financially supported by the Next-Generation BioGreen 21 program (PJ007186201002).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Jeong, D., Seo, S. & Na, K. Drug stabilization and controlled release from AB3 type tetra block copolymer based polymersome. Journal of Pharmaceutical Investigation 42, 101–108 (2012). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0016-5
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40005-012-0016-5