Abstract
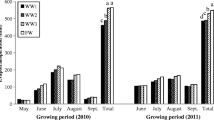
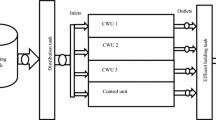
Wastewater (WW) reuse has been identified as an alternative with the potential to reduce the pressure of irrigated agriculture on water resources. However, the limitation of WW reuse in agriculture is its poor quality. Thus, it is recommended to pretreat WW prior to their application. The objective of this study was to evaluate the production and sanitary quality of kales irrigated with effluent from domestic wastewater treated in vertical anaerobic filters. The performance of the wastewater treatment plant (WWTP) was evaluated by analyzing the pH, electrical conductivity (EC), total nitrogen (TN), total phosphorus (TP), potassium (K) and fecal coliforms (Escherichia coli) in the influent and treated wastewater (TWW). Kale cultivation was performed in conventional (CCS) and vertical cultivation systems (VCS) in two cycles. Three treatments were used: T1, 100% TWW; T2, 100% of underground well water (UWW); and T3, 50% TWW and 50% UWW. The number of matured leaves (NML), commercial leaves fresh mass (CLFM) per plant, commercial leaves length (CLL) and sanitary quality of leaves were determined. The WWTP performed satisfactorily, providing TWW with acceptable quality for reuse in crop irrigation, with EC, TN, TP and K significantly below than that observed in influent. The NML, CLFM and CLL per plant were high in the T1 both for CCS and VCS, and significantly different than T2 in the cycle 2. The VCS had highest productivity and irrigation water use efficiency than CCS in both cycles. These observations highlight the positive benefits of application WW in irrigation crops.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
AMBIENTE-CONAMA CNDOM (2005) Resolução CONAMA no357/2005, de 17 de março de 2005: Dispõe sobre a classificação dos corpos de água e diretrizes ambientais para o seu enquadramento, bem como estabelece as condições e padrões de lançamento de efluentes, e dá outras providências. Diário Oficial da União (DOU)
APHA, AWWA, WEF (2012) Standard Methods for examination of water and wastewater. 22nd ed. Washington: American Public Health Association. Standard Methods. ISBN 978–087553–013–0
Abegunrin TP, Awe GO, Idowu DO, Adejumobi MA (2016) Impact of wastewater irrigation on soil physico-chemical properties, growth and water use pattern of two indigenous vegetables in southwest Nigeria. CATENA 139:167–178
Akdaş ZZ, Bakkalbaşı E (2017) Influence of different cooking methods on color, bioactive compounds, and antioxidant activity of kale. Int J Food Prop 20:877–887
Alkhamisi SA, Ahmed M, Al-Wardy M, Prathapar SA, Choudri BS (2017) Effect of reclaimed water irrigation on yield attributes and chemical composition of wheat (Triticum aestivum), cowpea (Vigna sinensis), and maize (Zea mays) in rotation. Irrig Sci 35:87–98
Almuktar SAAAN, Abed SN, Scholz M (2018) Wetlands for wastewater treatment and subsequent recycling of treated effluent: a review. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:23595–23623
Andrade JC de., Cantarella H, Quaggio JA (2001) Análise química para avaliação da fertilidade de solos tropicais. IAC
Ayers RS, Westcot DW (1985) Water quality for agriculture. food and agriculture organization of the United Nations Rome
BRASIL. ANVISA (2001) Resolução no 12, de 2 de janeiro de 2001. Aprova o regulamento técnico sobre padrões microbiológicos para alimentos. Diário Oficial da União, Brasília, DF, 10 jan. Diário Oficial [da] República Federativa do Brasil
Chauhan JS, Kumar S (2020) Wastewater ferti-irrigation: an eco-technology for sustainable agriculture. Sustain Water Resourc Manag 6:1–11
Chen W, Lu S, Jiao W, Wang M, Chang AC (2013) Reclaimed water: a safe irrigation water source? Environ Develop 8:74–83
Cherfouh R, Lucas Y, Derridj A, Merdy P (2018) Long-term, low technicality sewage sludge amendment and irrigation with treated wastewater under Mediterranean climate: impact on agronomical soil quality. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:35571–35581
Cirelli GL, Consoli S, Licciardello F, Aiello R, Giuffrida F, Leonardi C (2012) Treated municipal wastewater reuse in vegetable production. Agric Water Manag 104:163–170
da Cunha AR, Martins D (2009) Climatic classification for the districts of Botucatu and São Manuel, SP. Irriga 14:1–11
Demir AD, Sahin U (2017) Effects of different irrigation practices using treated wastewater on tomato yields, quality, water productivity, and soil and fruit mineral contents. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:24856–24879
El-hendawy SE, El-lattief EAA, Ahmed MS (2008) Irrigation rate and plant density effects on yield and water use efficiency of drip-irrigated corn. 95:836–844
Emin M, Kusman N, Caliskan S (2009) Field Crops Research Effects of plant density on the yield and yield components of true potato seed ( TPS ) hybrids in early and main crop potato production systems. 114:223–232
Eustáquio Júnior V, de Matos AT, Lo Monaco PAV, de Campos LC, Borges AC (2012) Efficiency of constructed wetland systems cultivated with black oats treatment of domestic sewage. Acta Scientiarum Tech 34:391–398
Fadigas JC, dos Santos AMP, de Jesus RM, Lima DC, Fragoso WD, David JM, Ferreira SLC (2010) Use of multivariate analysis techniques for the characterization of analytical results for the determination of the mineral composition of kale. Microchem J 96:352–356
Ferreira DF (2019) Sisvar: a computer analysis system to fixed effects split plot type designs. Revista Brasileira De Biometria 37:529
da Fonseca AF, Herpin U, de Paula AM, Victória RL, Melfi AJ (2007) Agricultural use of treated sewage effluents: agronomic and environmental implications and perspectives for Brazil. Scientia Agricola 64:194–209
Gatta G, Libutti A, Gagliardi A, Beneduce L, Brusetti L, Borruso L, Disciglio G, Tarantino E (2015) Treated agro-industrial wastewater irrigation of tomato crop: effects on qualitative/quantitative characteristics of production and microbiological properties of the soil. Agric Water Manag 149:33–43
Grossi B, Homem C, Barroca O, Neto DA, Condé MS, Silva MD, Ferreira IM (2014) Efeito do uso prolongado de água residuária da suinocultura sobre as propriedades químicas e físicas de um Latossolo Vermelho-Amarelo Effect of prolonged use of swine wastewater on soil properties. 299–309
Hespanhol I (2008) Um novo paradigma para a gestão de recursos hídricos. Estudos Avancados 22:131–158
Hussar G, Paradela AL, Bastos MC, Reis TKB, Jonas eles C, Serra W, Gomes JP (2005) Efeito do efluente de reator anaeróbio compartimentado na fertirrigação da beterraba. Engenharia Ambiental—Espirito Santo do Pinhal 2:35–45
Jaramillo MF, Restrepo I (2017) Wastewater reuse in agriculture: a review about its limitations and benefits. Sustainability (Switzerland). https://doi.org/10.3390/su9101734
Jeong H, Seong C, Jang T, Park S (2016) Classification of wastewater reuse for agriculture: a case study in South Korea. Irrig Drain 65:76–85
Kaboosi K (2017) The assessment of treated wastewater quality and the effects of mid-term irrigation on soil physical and chemical properties (case study: Bandargaz-treated wastewater). Appl Water Sci 7:2385–2396
Le THX, Mosley L, Nguyen DT, Marschner P (2020) Effect of short-term irrigation of wastewater on wheat growth and nitrogen and phosphorus in soil. J Soil Sci Plant Nutr. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42729-019-00122-y
Libutti A, Gatta G, Gagliardi A, Vergine P, Pollice A, Beneduce L, Disciglio G, Tarantino E (2018) Agro-industrial wastewater reuse for irrigation of a vegetable crop succession under Mediterranean conditions. Agric Water Manag 196:1–14
Marouelli W (2017) Irrigação no cultivo de Brássicas.
Murador DC, Mercadante AZ, De Rosso VV (2016) Cooking techniques improve the levels of bioactive compounds and antioxidant activity in kale and red cabbage. Food Chem 196:1101–1107
Novo M, do C, de S, Prela-Pantano A, Trani PE, Blat SF (2010) Desenvolvimento e produção de genótipos de couve manteiga. Hortic Bras 28:321–325
Obayomi O, Edelstein M, Safi J, Mihiret M, Ghazaryan L, Vonshak A, Bernstein N, Gillor O (2020) The combined effects of treated wastewater irrigation and plastic mulch cover on soil and crop microbial communities. Biol Fertil Soils 56:729–742
Rahman MZ, Riesbeck F, Dupree S (2018) The Opportunity Versus Risks in Wastewater Irrigation. Safe Use of Wastewater in Agriculture. Springer International Publishing, Cham, pp 13–25
Salgot M, Folch M, Unit SS (2018) Wastewater treatment and water reuse. Current Opinion Environ Sci Health 2:64–74
Shakir E, Zahraw Z, Al-Obaidy AHMJ (2017) Environmental and health risks associated with reuse of wastewater for irrigation. Egypt J Pet 26:95–102
Shin S, Lee J, Son B, Kim J, Kim SG, Kim M, Kim S, Baek S, Woo M, Bae HH (2014) Effect of Plant Density on Growth and Yield of Extremely Late-Planted Korean Sweet Corn Hybrids ( Zea mays L .) for Fresh Market. 289–295
Sousa VF de, Coelho EF, Pinto JM, Nogueira LC, Coelho MA, Araújo AR de (2011) Manejo da fertirrigação em fruteiras e hortaliças. Irrigação e fertilização em fruteiras e hortaliças 319–337
Souza CF, Bastos RG, de Gomes MP, Pulschen AA (2015) Eficiência de estação de tratamento de esgoto doméstico visando reuso agr{\’\i}cola. Revista Ambiente & Água 10:587–597
Thavarajah D, Siva N, Johnson N, McGee R, Thavarajah P (2019) Effect of cover crops on the yield and nutrient concentration of organic kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala). Sci Rep 9:1–8
Thavarajah D, Thavarajah P, Abare A, Basnagala S, Lacher C, Smith P, Combs GF (2016) Mineral micronutrient and prebiotic carbohydrate profiles of USA-grown kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala). J Food Compos Anal 52:9–15
Trani Espíndola P et al (2014) Couve de folha: do plantio à pós-colheita. Igarss 2014:1–5
Tunc T, Sahin U (2016) Red cabbage yield, heavy metal content, water use and soil chemical characteristics under wastewater irrigation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:6264–6276
US Environmental Protection Agency (2012) Guidelines for water reuse. Development. EPA16251R-921004
Ucker FE, Almeida RA, Kemerich PDC (2012) Remoção de nitrogênio e fósforo do esgoto sanitário em um sistema de alagados construídos utilizando o capim vetiver Ambiente e Agua—an interdisciplinary. J Appl Sci 7:87–98
Urbano VR, Mendonça TG (2015). Physical-chemical effects of irrigation with treated wastewater on Dusky Red Latosol soil Efeitos físico-químicos da irrigação com água de reúso em um Latossolo Vermelho distrófico. https://doi.org/10.4136/1980-993X
Urbano VR, Mendonça TG, Bastos RG, Souza CF (2017) Effects of treated wastewater irrigation on soil properties and lettuce yield. Agric Water Manag 181:108–115
Ventura KM (2017) Eficiência do uso da água em um sistema vertical sob irrigação localizada. Universidade Estadual Paulista (UNESP)
Vergine P, Lonigro A, Salerno C, Rubino P, Berardi G, Pollice A (2017) Nutrient recovery and crop yield enhancement in irrigation with reclaimed wastewater: a case study. Urban Water J 14:325–330
WHO (2006) Guidelines for the safe use of wastewater, excreta and greywater. World Health Organization 1:114
Wang Z, Li J, Li Y (2017) Using reclaimed water for agricultural and landscape irrigation in China: a review. Irrig Drain 66:672–686
World Health Organization (2006) Safe Use of Wastewater , Excreta and Greywater Guidelines for the Safe Use of. II:204
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank the Ministry of Science, Technology and Higher Technical Professional Education (Ministério da Ciência e Tecnologia Ensino Superior Técnico Profissional-MCTESTP, Mozambique) for the scholarship, the Lúrio University (Universidade de Lúrio; FCA—UniLúrio) for the trust and the Coordination for the Improvement of Higher Education Personnel (Coordenação de Aperfeiçoamento de Pessoal de Nível Superior- CAPES, Brazil) for the support.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
VSJP designed the experiment, analyzed the data and prepared the manuscript. RMSR and JGTQ participated in the review of the manuscript. TLS participated in the collection and analysis of treated effluent samples, and JJG participated in the data collection concerning the development and production of plants.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors agree on the content of the paper and have no conflict of interest to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pitoro, V.S.J., Sánchez-Román, R.M., Queluz, J.G.T. et al. Production and Sanitary Quality of Kale (Brassica oleracea L. var. acephala) Irrigated with Domestic Wastewater Treated in Vertical Anaerobic Filters. Agric Res 11, 229–239 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-021-00566-8
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s40003-021-00566-8