Abstract
Purpose
The International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis (ISTH) scoring system is a useful tool to diagnosis overt disseminated intravascular coagulation in clinical practice. The main purposes of this study were to investigate the prognostic value of the ISTH score in emergency department (ED) sepsis and compare the ISTH score with two established scoring systems, the Sequential Organ Failure Assessment (SOFA) score and Acute Physiology and Chronic Health Evaluation II (APACHE II) score, and two biomarkers,procalcitonin (PCT) and C-reactive protein (CRP).
Methods
Septic patients were consecutively enrolled from the ED of Beijing Chaoyang Hospital, China. The ISTH score, SOFA score and APACHE II score were calculated, and PCT and CRP levels were measured on enrollment. A 30-day follow-up was performed.
Results
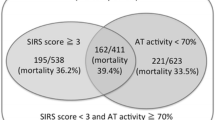
A total of 680 septic patients were enrolled in this study. The Cox regression analysis showed that the ISTH score had a greater effect on 30-day mortality prediction, and the receiver operating characteristic curve analysis showed that the accuracy of the ISTH score in prediction of 30-day mortality was better than the SOFA score, the APACHE II score, PCT and CRP. Combination of the ISTH score and CRP can enhance the predictive accuracy of 30-day mortality.
Conclusion
The ISTH score is a valuable scoring system in the prognosis evaluation in ED sepsis.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
van der Poll T, Opal SM. Host–pathogen interactions in sepsis. Lancet Infect Dis. 2008;8:32–43.
Amaral A, Opal SM, Vincent JL. Coagulation in sepsis. Intensive Care Med. 2004;30:1032–40.
Levi M. Disseminated intravascular coagulation. Crit Care Med. 2007;35:2191–5.
Zeerleder S, Hack CE, Wuillemin WA. Disseminated intravascular coagulation in sepsis. Chest. 2005;128:2864–75.
Dhainaut JF, Yan SB, Joyce DE, Pettila V, Basson B, Brandt JT, Sundin DP, Levi M. Treatment effects of drotrecogin alfa (activated) in patients with severe sepsis with or without overt disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2004;2:1924–33.
Kienast J, Juers M, Wiedermann CJ, Hoffmann JN, Ostermann H, Strauss R, Keinecke HO, Warren BL, Opal SM. Treatment effects of high-dose antithrombin without concomitant heparin in patients with severe sepsis with or without disseminated intravascular coagulation. J Thromb Haemost. 2006;4:90–7.
Taylor FB Jr, Toh CH, Hoots WK, Wada H, Levi M. Towards definition, clinical and laboratory criteria, and a scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Thromb Haemost. 2001;86:1327–30.
Bakhtiari K, Meijers JC, de Jonge E, Levi M. Prospective validation of the International Society of Thrombosis and Haemostasis scoring system for disseminated intravascular coagulation. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:2416–21.
Dempfle CE, Lorenz S, Smolinski M, Wurst M, West S, Houdijk WP, Quintel M, Borggrefe M. Utility of activated partial thromboplastin time waveform analysis for identification of sepsis and overt disseminated intravascular coagulation in patients admitted to a surgical intensive care unit. Crit Care Med. 2004;32:520–4.
Lissalde-Lavigne G, Combescure C, Muller L, Bengler C, Raillard A, Lefrant JY, Gris JC. Simple coagulation tests improve survival prediction in patients with septic shock. J Thromb Haemost. 2008;6:645–53.
Strehlow MC, Emond SD, Shapiro NI, Pelletier AJ, Camargo CA Jr. National study of emergency department visits for sepsis, 1992 to 2001. Ann Emerg Med. 2006;48:326–31.
Levy MM, Fink MP, Marshall JC, Abraham E, Angus D, Cook D, Cohen J, Opal SM, Vincent JL, Ramsay G. 2001 SCCM/ESICM/ACCP/ATS/SIS international sepsis definitions conference. Crit Care Med. 2003;31:1250–6.
Dellinger RP, Levy MM, Carlet JM, Bion J, Parker MM, Jaeschke R, Reinhart K, Angus DC, Brun-Buisson C, Beale R, Calandra T, Dhainaut JF, Gerlach H, Harvey M, Marini JJ, Marshall J, Ranieri M, Ramsay G, Sevransky J, Thompson BT, Townsend S, Vender JS, Zimmerman JL, Vincent JL. Surviving Sepsis Campaign: international guidelines for management of severe sepsis and septic shock: 2008. Crit Care Med. 2008;36:296–327.
Vincent JL, Moreno R, Takala J, Willatts S, De Mendonca A, Bruining H, Reinhart CK, Suter PM, Thijs LG. The SOFA (Sepsis-related Organ Failure Assessment) score to describe organ dysfunction/failure. Intensive Care Med. 1996;22:707–10.
Knaus WA, Draper EA, Wagner DP, Zimmerman JE. APACHE II: a severity of disease classification system. Crit Care Med. 1985;13:818–29.
Hanley JA, McNeil BJ. A method of comparing the areas under receiver operating characteristic curves derived from the same cases. Radiology. 1983;148:839–43.
Fluss R, Faraggi D, Reiser B. Estimation of the Youden Index and its associated cutoff value. Biom J. 2005;47:458–72.
Pepe MS, Thompson ML. Combining diagnostic test results to increase accuracy. Bistatistics. 2000;1:123–40.
Levi M, Schultz M, van der Poll T. Coagulation biomarkers in critically Ill patients. Crit Care Clin. 2011;27:281–7.
Dhainaut JF, Shorr AF, Macias WL, Kollef MJ, Levi M, Reinhart K, Nelson DR. Dynamic evolution of coagulopathy in the first day of severe sepsis: relationship with mortality and organ failure. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:341–8.
Kinasewitz GT, Zein JG, Lee GL, Nazir SA, Taylor FB Jr. Prognostic value of a simple evolving disseminated intravascular coagulation score in patients with severe sepsis. Crit Care Med. 2005;33:2214–21.
Voves C, Wuillemin WA, Zeerleder S. International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis score for overt disseminated intravascular coagulation predicts organ dysfunction and fatality in sepsis patients. Blood Coagul Fibrinolysis. 2006;17:445–51.
Cauchie P, Cauchie CH, Boudjeltia KZ, Carlier E, Deschepper N, Govaerts D, Migaud-Fressart M, Woodhams B, Brohee D. Diagnosis and prognosis of overt disseminated intravascular coagulation in a general hospital-meaning of the ISTH score system, fibrin monomers, and lipoprotein-C-reactive protein complex formation. Am J Hematol. 2006;81:414–9.
Hargrove J, Nguyen HB. Bench-to-bedside review: outcome predictions for critically ill patients in the emergency department. Crit Care. 2005;9:376–83.
Jones AE, Trzeciak S, Kline JA. The Sequential Organ Failure Assessment score for predicting outcome in patients with severe sepsis and evidence of hypoperfusion at the time of emergency department presentation. Crit Care Med. 2009;37:1649–54.
Nguyen HB, Banta JE, Cho TW, Van Ginkel C, Burroughs K, Wittlake WA, Corbett SW. Mortality predictions using current physiologic scoring systems in patients meeting criteria for early goal-directed therapy and the severe sepsis resuscitation bundle. Shock. 2008;30:23–8.
Nguyen HB, Van Ginkel C, Batech M, Banta J, Corbett SW. Comparison of predisposition, insult/infection, response, and organ dysfunction, acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II, and mortality in emergency department sepsis in patients meeting criteria for early goal-directed therapy and the severe sepsis resuscitation bundle. J Crit Care. 2012;27:362–9.
Angstwurm MW, Dempfle CE, Spannagl M. New disseminated intravascular coagulation score-A useful tool to predict mortality in comparison with acute physiology and chronic health evaluation II and logistic organ dysfunction scores. Crit Care Med. 2006;34:314–20.
Lichtenstern C, Brenner T, Bardenheuer HJ, Weigand MA. Predictors of survival in sepsis: what is the best inflammatory marker to measure? Curr Opin Infect Dis. 2012;25:328–36.
Simon L, Gauvin F, Amre DK, Saint-Louis P, Lacroix J. Serum procalcitonin and C-reactive protein levels as markers of bacterial infection-a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin Infect Dis. 2004;39:206–17.
Dahaba AA, Hagara B, Fall A, Rehak PH, List WF, Metzler H. Procalcitonin for early prediction of survival outcome in postoperative critically ill patients with severe sepsis. Br J Anaesth. 2006;97:503–8.
Silvestre J, Povoa P, Coelho L, Almeida E, Moreira P, Fernandes A, Mealha R, Sabino H. Is C-reactive protein a good prognostic marker in septic patients? Intensive Care Med. 2009;35:909–13.
Oberholzer A, Souza SM, Tschoeke SK, Oberholzer C, Abouhamze A, Pribble JP, Moldawer LL. Plasma cytokine measurements augment prognostic scores as indicators of outcome in patients with severe sepsis. Shock. 2005;23:488–93.
Acknowledgments
This study was supported by the National Clinical Key Specialty Construction Project Foundation (No. 2012-649) and Beijing Outstanding Doctoral Dissertation Foundation (No. 2012-1002501).
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states, for this paper, that none of the authors have any conflict of interest.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, Q., Liu, B., Chen, Y. et al. Prognostic value of the International Society on Thrombosis and Haemostasis scoring system for overt disseminated intravascular coagulation in emergency department sepsis. Infection 42, 629–637 (2014). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-014-0600-x
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-014-0600-x