Abstract
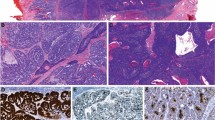
The papillary squamous cell carcinoma (PSCC) is a rare variant of the head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Established etiological factors can include tobacco smoking and heavy alcohol abuse. Moreover, human papillomavirus infection can be involved in the pathogenesis of PSCC. This tumor is more frequent in patients with immunosuppression including those who have received a transplant.
Most of the cases are produced by genotype HPV-6 and HPV-16, although there is a possibility of infection by other HPV subtypes. We present a case report of a PSCC and papilloma with oropharyngeal location in which high-risk HPV type 16 and low-risk HPV type 6, respectively, were identified by PCR in a renal transplant patient.
Similar content being viewed by others
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cobo, F., García, C., Talavera, P. et al. Human Papillomavirus Associated with Papillary Squamous Cell Carcinoma of the Oropharynx in a Renal Transplant Recipient. Infection 34, 176–180 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-006-5026-7
Received:
Accepted:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s15010-006-5026-7