Abstract
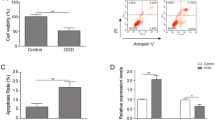
Human brain microvessel endothelial cells (HBMECs) are crucial for brain vascular repair and maintenance. The high-expressed expressions of microRNA-124 (miR-124) in brain have been investigated and revealed in many researches. In this work, we aimed to investigate the role of miR-124 in apoptosis of HBMECs and the underlying mechanism. Here, we found the low-expressed miR-124 in hypoxia-induced HBMECs using qRT-PCR analysis. MiR-124 targeting 3′-untranslated region (3′-UTR) of Bim mRNA was predicted by Targetscan database. Importantly, the decreased miR-124 expression and increased Bim expression, an opposite trend, were obtained in hypoxia-induced HBMECs. The further confirmation of the correlation between miR-124 and Bim was conducted by miR-124 overexpression and dual luciferase reporter assays. The inhibitory role of miR-124 in Bim expression was evidenced by results obtained from miR-124 overexpression analysis. Luciferase reporter assay further proved that miR-124 directly targeted the two conserved seed sites in the Bim 3′-UTR. The inhibited apoptosis of HBMECs was observed under both miR-124 overexpression and Bim knockdown condition in flow cytometry analysis. Collectively, these findings outline that miR-124 regulates apoptosis in hypoxia-induced HBMECs through targeting Bim, providing a better understanding of the role of miR-124 in apoptosis of HBMECs.





Similar content being viewed by others
Change history
08 May 2019
Following publication of the original article [1], the authors reported an updated affiliation for the first author, Jie Pu. The updated affiliation is shown below and reflected in the affiliation list of this Correction.
References
Kluijtmans LA, Young IS, Boreham CA, Murray L, McMaster D, McNulty H, Strain JJ, McPartlin J, Scott JM, Whitehead AS (2003) Genetic and nutritional factors contributing to hyperhomocysteinemia in young adults. Blood 101:2483–2488
Roitbak T (2018) Silencing a multifunctional microRNA is beneficial for stroke recovery. Front Mol Neurosci 11:58
Zhang X, Hamblin MH, Yin KJ (2018) Noncoding RNAs and stroke. Neuroscientist. 107385841876955
Nanetti L, Taffi R, Vignini A, Moroni C, Raffaelli F, Bacchetti T, Silvestrini M, Provinciali L, Mazzanti L (2007) Reactive oxygen species plasmatic levels in ischemic stroke. Mol Cell Biochem 303:19–25
Xing C, Arai K, Lo EH, Hommel M (2012) Pathophysiologic cascades in ischemic stroke. Int J Stroke 7:378–385
Edlow JA, Newman-Toker DE, Savitz SI (2008) Diagnosis and initial management of cerebellar infarction. Lancet Neurol 7:951–964
Kim J, Yao F, Xiao Z, Sun Y, Ma L (2018) MicroRNAs and metastasis: small RNAs play big roles. Cancer Metastasis Rev 37:5–15
He L, Hannon GJ (2004) MicroRNAs: small RNAs with a big role in gene regulation. Nat Rev Genet 5:522–531
Nicoloso MS, Calin GA (2008) MicroRNA involvement in brain tumors: from bench to bedside. Brain Pathol 18:122–129
Care A, Bellenghi M, Matarrese P, Gabriele L, Salvioli S, Malorni W (2018) Sex disparity in cancer: roles of microRNAs and related functional players. Cell Death Differ 25:477–485
Kim JO, Bae J, Kim J, Oh SH, An HJ, Han IB, Oh D, Kim OJ, Kim NK (2018) Association of MicroRNA biogenesis genes polymorphisms with ischemic stroke susceptibility and post-stroke mortality. J Stroke 20:110–121
Nampoothiri SS, Fayaz SM, Rajanikant GK (2018) A novel five-node feed-forward loop unravels miRNA-Gene-TF regulatory relationships in ischemic stroke. Mol Neurobiol
Khoshnam SE, Winlow W, Farbood Y, Moghaddam HF, Farzaneh M (2017) Emerging roles of microRNAs in ischemic stroke: as possible therapeutic agents. J Stroke 19:166–187
Ridolfi B, Abdel-Haq H (2017) Neurodegenerative disorders treatment: the MicroRNA role. Curr Gene Ther 17:327–363
Li L, Xu J, Wu M, Hu JM (2018) Protective role of microRNA-221 in Parkinson’s disease. Bratisl Lek Listy 119:22–27
Chen J, Qi Y, Liu CF, Lu JM, Shi Y (2018) MicroRNA expression data analysis to identify keymiRNAs associated with Alzheimer’s disease. J Gene Med e3014
Krichevsky AM, Sonntag KC, Isacson O, Kosik KS (2006) Specific microRNAs modulate embryonic stem cell-derived neurogenesis. Stem Cells 24:857–864
Leung LY, Chan CP, Leung YK, Jiang HL, Abrigo JM, de Wang F, Chung JS, Rainer TH, Graham CA (2014) Comparison of miR-124-3p and miR-16 for early diagnosis of hemorrhagic and ischemic stroke. Clin Chim Acta 433:139–144
Liu X, Li F, Zhao S, Luo Y, Kang J, Zhao H, Yan F, Li S, Ji X (2013) MicroRNA-124-mediated regulation of inhibitory member of apoptosis-stimulating protein of p53 family in experimental stroke. Stroke 44:1973–1980
Wang SW, Deng LX, Chen HY, Su ZQ, Ye SL, Xu WY (2018) MiR-124 affects the apoptosis of brain vascular endothelial cells and ROS production through regulating PI3 K/AKT signaling pathway. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 22:498–505
Lagosquintana M, Rauhut R, Yalcin A, Meyer J, Lendeckel W, Tuschl T (2002) Identification of tissue-specific microRNAs from mouse. Curr Biol 12:735–739
Weng H, Shen C, Hirokawa G, Ji X, Takahashi R, Shimada K, Kishimoto C, Iwai N (2011) Plasma miR-124 as a biomarker for cerebral infarction. Biomed Res 32:135–141
Lo EH, Dalkara T, Moskowitz MA (2003) Mechanisms, challenges and opportunities in stroke. Nat Rev Neurosci 4:399–415
Pan LJ, Wang X, Ling Y, Gong H (2017) MiR-24 alleviates cardiomyocyte apoptosis after myocardial infarction via targeting BIM. Eur Rev Med Pharmacol Sci 21:3088–3097
Harraz MM, Dawson TM, Dawson VL (2011) MicroRNAs in Parkinson’s disease. J Chem Neuroanat 42:127–130
Sonntag KC (2010) MicroRNAs and deregulated gene expression networks in neurodegeneration. Brain Res 1338:48–57
Ponomarev ED, Veremeyko T, Barteneva N, Krichevsky AM, Weiner HL (2011) MicroRNA-124 promotes microglia quiescence and suppresses EAE by deactivating macrophages via the C/EBP-alpha-PU.1 pathway. Nat Med 17:64–70
Mitsios N, Gaffney J, Krupinski J, Mathias R, Wang Q, Hayward S, Rubio F, Kumar P, Kumar S, Slevin M (2007) Expression of signaling molecules associated with apoptosis in human ischemic stroke tissue. Cell Biochem Biophys 47:73–86
Tregub PP, Malinovskaya NA, Kulikov VP, Salmina AB, Nagibaeva ME, Zabrodina AS, Gertsog GE, Antonova SK (2016) Inhibition of apoptosis is a potential way to improving ischemic brain tolerance in combined exposure to hypercapnia and hypoxia. Bull Exp Biol Med 161:666–669
Wu X, Li L, Zhang L, Wu J, Zhou Y, Zhou Y, Zhao Y, Zhao J (2015) Inhibition of thioredoxin-1 with siRNA exacerbates apoptosis by activating the ASK1-JNK/p38 pathway in brain of a stroke model rats. Brain Res 1599:20–31
Wang H, Ye Y, Zhu Z, Mo L, Lin C, Wang Q, Wang H, Gong X, He X, Lu G, Lu F, Zhang S (2016) MiR-124 regulates apoptosis and autophagy process in MPTP model of Parkinson’s disease by targeting to Bim. Brain Pathol 26:167–176
Floyd DH, Zhang Y, Dey BK, Kefas B, Breit H, Marks K, Dutta A, Herold-Mende C, Synowitz M, Glass R, Abounader R, Purow BW (2014) Novel anti-apoptotic microRNAs 582-5p and 363 promote human glioblastoma stem cell survival via direct inhibition of caspase 3, caspase 9, and Bim. PLoS ONE 9:e96239
Qian L, Van Laake LW, Huang Y, Liu S, Wendland MF, Srivastava D (2011) miR-24 inhibits apoptosis and represses Bim in mouse cardiomyocytes. J Exp Med 208:549–560
Park S, Ito K, Olcott W, Katsyv I, Halstead-Nussloch G, Irie H (2015) PTK6 inhibition promotes apoptosis of Lapatinib-resistant Her2(+) breast cancer cells by inducing Bim. Breast Cancer Res 17:86
Sun Y, Gui H, Li Q, Luo ZM, Zheng MJ, Duan JL, Liu X (2013) MicroRNA-124 protects neurons against apoptosis in cerebral ischemic stroke. CNS Neurosci Ther 19:813–819
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by General Program of Natural Science Foundation of the Inner Mongolia Autonomous region, China (No. 2015MS08151, No. 2015MS08152).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no conflict of interest.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Pu, J., Long, Y., Zhou, J. et al. MiR-124 regulates apoptosis in hypoxia-induced human brain microvessel endothelial cells through targeting Bim. Appl Biol Chem 61, 689–696 (2018). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-018-0407-z
Received:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13765-018-0407-z