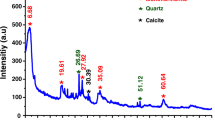
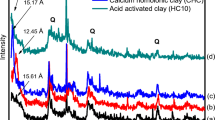
Abstract
Clay minerals present promising characteristics for adsorbing heavy metals in aqueous solutions due to their low cost, non-toxic nature, and abundance. However, they often face limitations such as low adsorption capacity and poor selectivity. To address these issues, this study focused on improving the lead (Pb) adsorption capacity of palygorskite clay by modifying it with Nafion. Characterization techniques like Field Emission Scanning Electron Microscopy (FESEM) and X-ray Diffraction (XRD) were employed to analyze the surface properties of both pristine and modified palygorskite clay, affirming the stability of the Nafion-palygorskite composite. Utilizing response surface methodology (RSM), the study examined the impact of various process parameters, including adsorbent dosage, Nafion amount, pH, and initial Pb concentration. Analysis of variance (ANOVA) revealed that these factors significantly influenced Pb removal efficiency, with pH and adsorbent dose being particularly impactful. The study found that a smooth Nafion-coated palygorskite clay surface, featuring sulfonate groups, led to improved Pb removal. Experimental results demonstrated that Pb removal efficiency increased from 3.6% to 69% using Nafion-palygorskite clay under specific conditions of pH and adsorbent dosage. Kinetic studies showed that both unmodified and modified palygorskite clay followed pseudo-first-order kinetics. Furthermore, the study explored machine learning (ML) algorithms for predicting aqueous Pb removal using Nafion-palygorskite adsorbent. Among these algorithms, the support vector machine (SVM) yielded the most accurate results, closely matching experimental findings. Overall, the research indicates that Nafion can effectively enhance the performance of clay-based adsorbents for treating heavy metal-contaminated water, offering potential for practical application in environmental remediation efforts.








Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
All relevant data are included in the paper.
References
Abolli S, Ahmadi Nasab M, Yaghmaeian K, Alimohammadi M (2022) Determination the effects of physicochemical parameters on groundwater status by water quality index (WQI). Desalination Water Treat 269:84–92. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.28755
Abolli S, Yaghmaeian K, Arab Aradani A, Alimohammadi M (2023) Comparing groundwater fluoride level with WHO guidelines and classifying at-risk age groups; based on health risk assessment. Int J Environ Anal Chem 103:747–760. https://doi.org/10.1080/03067319.2020.1863389
Alam G, Ihsanullah I, Naushad Mu, Sillanpää M (2022) Applications of artificial intelligence in water treatment for optimization and automation of adsorption processes: Recent advances and prospects. Chem Eng J 427:130011. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2021.130011
Al-Futaisi A, Jamrah A, Al-Hanai R (2007) Aspects of cationic dye molecule adsorption to palygorskite. Desalination 214:327–342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2006.10.024
Alkhudhiri A, Hakami M, Zacharof M-P et al (2020) Mercury, Arsenic and Lead Removal by Air Gap Membrane Distillation: Experimental Study. Water (basel) 12:1574. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12061574
Amini M, Younesi H, Bahramifar N et al (2008) Application of response surface methodology for optimization of lead biosorption in an aqueous solution by Aspergillus niger. J Hazard Mater 154:694–702. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.10.114
Anfar Z, Ait Ahsaine H, Zbair M et al (2020) Recent trends on numerical investigations of response surface methodology for pollutants adsorption onto activated carbon materials: A review. Crit Rev Environ Sci Technol 50:1043–1084. https://doi.org/10.1080/10643389.2019.1642835
Antonio S-MG, Iván G-CP, Luis G-RJ (2015) Influence of chemically treated palygorskite over the rheological behavior of polypropylene nanocomposites. Ingeniería, Investigación y Tecnología 16:491–501. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.riit.2015.09.002
Arora R (2019) Adsorption of heavy metals–a review. Mater Today Proc 18:4745–4750. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.07.462
Beigzadeh B, Bahrami M, Amiri MJ, Mahmoudi MR (2020) A new approach in adsorption modeling using random forest regression, Bayesian multiple linear regression, and multiple linear regression: 2,4-D adsorption by a green adsorbent. Water Sci Technol 82:1586–1602. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.440
Bi R, Yin D, Zhang S et al (2022) Efficient removal of Pb(II) and Hg(II) with eco-friendly polyaspartic acid/ layered double hydroxide by host-guest interaction. Appl Clay Sci 225:106536. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2022.106536
Boudriche L, Calvet R, Hamdi B, Balard H (2011) Effect of acid treatment on surface properties evolution of attapulgite clay: An application of inverse gas chromatography. Colloids Surf A Physicochem Eng Asp 392:45–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2011.09.031
Box GEP, Cox DR (1964) An Analysis of Transformations. J Roy Stat Soc: Ser B (methodol) 26:211–243. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.2517-6161.1964.tb00553.x
Cha J-E, Jang S, Seo D-J et al (2023) A reinforced composite membrane of two-layered asymmetric structure with Nafion ionomer and polyethylene substrate for improving proton exchange membrane fuel cell performance. Chem Eng J 454:140091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2022.140091
Chen H, Zhao Y, Wang A (2007) Removal of Cu(II) from aqueous solution by adsorption onto acid-activated palygorskite. J Hazard Mater 149:346–354. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2007.03.085
Choudhary V, Patel M, Pittman CU, Mohan D (2020) Batch and continuous fixed-bed lead removal using himalayan pine needle biochar: isotherm and kinetic studies. ACS Omega 5:16366–16378. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsomega.0c00216
Deng S, Chen Y (2019) A study by response surface methodology (RSM) on optimization of phosphorus adsorption with nano spherical calcium carbonate derived from waste. Water Sci Technol 79:188–197. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2019.048
du Plessis A (2022) Persistent degradation: global water quality challenges and required actions. One Earth 5:129–131. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.oneear.2022.01.005
El-Naggar IM, Ahmed SA, Shehata N et al (2019) A novel approach for the removal of lead (II) ion from wastewater using Kaolinite/Smectite natural composite adsorbent. Appl Water Sci 9:7. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-018-0845-0
Fan Q, Li Z, Zhao H et al (2009) Adsorption of Pb(II) on palygorskite from aqueous solution: Effects of pH, ionic strength and temperature. Appl Clay Sci 45:111–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2009.04.009
Gan F, Zhou J, Wang H et al (2009) Removal of phosphate from aqueous solution by thermally treated natural palygorskite. Water Res 43:2907–2915. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2009.03.051
Ghasemi M, Daud WRW, Ismail AF et al (2013) Simultaneous wastewater treatment and electricity generation by microbial fuel cell: performance comparison and cost investigation of using Nafion 117 and SPEEK as separators. Desalination 325:1–6. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.06.013
Günay A, Arslankaya E, Tosun İ (2007) Lead removal from aqueous solution by natural and pretreated clinoptilolite: adsorption equilibrium and kinetics. J Hazard Mater 146:362–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2006.12.034
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Proc Biochem 34:451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Huang R, Lin Q, Zhong Q et al (2020) Removal of Cd(II) and Pb(II) from aqueous solution by modified attapulgite clay. Arab J Chem 13:4994–5008. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2020.01.022
Hussaini M, Vohra M (2022) LDH-TiO2 Composite for selenocyanate (SeCN−) photocatalytic degradation: characterization, treatment efficiency. React Intermed Model Nanomaterials 12:2035. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano12122035
Ibrahim AIA, Vohra MS (2023) Mg-Fe-LDH for Aquatic selenium treatment: adsorption, RSM modeling, and machine learning neural network. Water Air Soil Pollut 234:433. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-023-06444-z
Ibrahim A, Vohra MS, Bahadi SA et al (2022) Heavy metals adsorption onto graphene oxide: effect of mixed systems and response surface methodology modeling. Desalination Water Treat 266:78–90. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2022.28615
Ibrahim AI, Onaizi SA, Vohra MS (2023) Novel CTAB functionalized graphene oxide for selenium removal: adsorption results and ANN & RSM modeling. Emergent Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00570-4
Ismail UM, Onaizi SA, Vohra MS (2023a) Novel MgCuAl-layered triple hydroxide for aqueous selenite and selenate treatment. Emergent Mater. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-023-00462-7
Ismail UM, Onaizi SA, Vohra MS (2023b) Aqueous Pb(II) removal using ZIF-60: adsorption studies, response surface methodology and machine learning predictions. Nanomaterials 13:1402. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano13081402
Ismail UM, Onaizi SA, Vohra MS (2024a) Crystal violet removal using ZIF-60: batch adsorption studies, mechanistic & machine learning modeling. Environ Technol Innov 33:103456. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2023.103456
Ismail UM, Vohra MS, Onaizi SA (2024b) Adsorptive removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: progress of adsorbents development and their effectiveness. Environ Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2024.118562
Kausar A, Ahmad I, Maaza M, Eisa MH (2022) State-of-the-art of polymer/fullerene C60 nanocomposite membranes for water treatment: conceptions. Str Diversity Topogr Membr (basel) 13:27. https://doi.org/10.3390/membranes13010027
Kavak D (2013) Removal of lead from aqueous solutions by precipitation: statistical analysis and modeling. Desalin Water Treat 51:1720–1726. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2012.714652
Kooh MRR, Thotagamuge R, Chou Chau Y-F et al (2022) Machine learning approaches to predict adsorption capacity of Azolla pinnata in the removal of methylene blue. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 132:104134. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2021.11.001
Kumar V, Dwivedi SK, Oh S (2022) A critical review on lead removal from industrial wastewater: recent advances and future outlook. J Water Process Eng 45:102518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2021.102518
Lalmi A, Bouhidel KE, Sahraoui B, el Houda Anfif C (2018) Removal of lead from polluted waters using ion exchange resin with Ca(NO3)2 for elution. Hydrometallurgy 178:287–293. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.05.009
Lazaratou CV, Panagiotaras D, Panagopoulos G et al (2020) Ca treated Palygorskite and Halloysite clay minerals for Ferrous Iron (Fe+2) removal from water systems. Environ Technol Innov 19:100961. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.100961
Li M, Wei D, Liu T et al (2019) EDTA functionalized magnetic biochar for Pb(II) removal: Adsorption performance, mechanism and SVM model prediction. Sep Purif Technol 227:115696. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2019.115696
Lingamdinne LP, Amelirad O, Koduru JR et al (2023) Functionalized bentonite for removal of Pb(II) and As(V) from surface water: Predicting capability and mechanism using artificial neural network. J Water Proc Eng 51:103386. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2022.103386
Liu P (2007) Polymer modified clay minerals: a review. Appl Clay Sci 38:64–76. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2007.01.004
Mansoorian HJ, Mahvi AH, Jafari AJ (2014) Removal of lead and zinc from battery industry wastewater using electrocoagulation process: influence of direct and alternating current by using iron and stainless steel rod electrodes. Sep Purif Technol 135:165–175. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2014.08.012
McCulloch WS, Pitts W (1943) A logical calculus of the ideas immanent in nervous activity. Bull Math Biophys 5:115–133. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF02478259
Nasef MM, Yahaya AH (2009) Adsorption of some heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions on Nafion 117 membrane. Desalination 249:677–681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2008.12.059
Nguyen XC, Ly QV, Nguyen TTH et al (2022) Potential application of machine learning for exploring adsorption mechanisms of pharmaceuticals onto biochars. Chemosphere 287:132203. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.132203
Potgieter JH, Potgieter-Vermaak SS, Kalibantonga PD (2006) Heavy metals removal from solution by palygorskite clay. Miner Eng 19:463–470. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.mineng.2005.07.004
Qasem NAA, Mohammed RH, Lawal DU (2021) Removal of heavy metal ions from wastewater: a comprehensive and critical review. NPJ Clean Water 4:36. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41545-021-00127-0
Renu AM, Singh K (2017) Heavy metal removal from wastewater using various adsorbents: a review. J Water Reuse Desalin 7:387–419. https://doi.org/10.2166/wrd.2016.104
Revellame ED, Fortela DL, Sharp W et al (2020) Adsorption kinetic modeling using pseudo-first order and pseudo-second order rate laws: a review. Clean Eng Technol 1:100032. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clet.2020.100032
Rusmin R, Sarkar B, Tsuzuki T et al (2017) Removal of lead from aqueous solution using superparamagnetic palygorskite nanocomposite: material characterization and regeneration studies. Chemosphere 186:1006–1015. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.08.036
Sabbagh MF, Al-Malack MH (2021) Highly competitive multicomponent adsorption of organic and heavy metals using activated mangrove charcoal. Desalin Water Treat 242:162–177. https://doi.org/10.5004/dwt.2021.27851
Sadek AH, Fahmy OM, Nasr M, Mostafa MK (2023) Predicting Cu(II) adsorption from aqueous solutions onto nano zero-valent aluminum (nZVAl) by machine learning and artificial intelligence Techniques. Sustainability 15:2081. https://doi.org/10.3390/su15032081
Sato J, Shiota K, Takaoka M (2020) Stabilization of lead with amorphous solids synthesized from aluminosilicate gel. J Hazard Mater 385:121109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121109
Sevim F, Lacin O, Ediz EF, Demir F (2021) Adsorption capacity, isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies on adsorption behavior of malachite green onto natural red clay. Env Prog Sust Energy. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13471
Shamsayei M, Yamini Y, Asiabi H (2018) Evaluation of reusable organic-inorganic nafion/layered double hydroxide nanohybrids for highly efficient uptake of mercury ions from aqueous solution. Appl Clay Sci 162:534–542. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2018.05.022
Sharma DK, Li F, Wunan Y (2014) Electrospinning of Nafion and polyvinyl alcohol into nanofiber membranes: a facile approach to fabricate functional adsorbent for heavy metals. Coll Surf A Phys Eng Asp 457:236–243. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.colsurfa.2014.05.038
Sousa HR, Silva LS, Sousa PAA et al (2019) Evaluation of methylene blue removal by plasma activated palygorskites. J Market Res 8:5432–5442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jmrt.2019.09.011
Sreekumar N, Udayan A, Srinivasan S (2020) Algal bioremediation of heavy metals. Removal of toxic pollutants through microbiological and tertiary treatment. Elsevier, Amsterdam, pp 279–307
Takemura H, Nakashima S, Kon N et al (2001) A study of C−F···M+ interaction: metal complexes of fluorine-containing cage compounds. J Am Chem Soc 123:9293–9298. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja0043587
Tan KL, Hameed BH (2017) Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 74:25–48. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2017.01.024
Tee GT, Gok XY, Yong WF (2022) Adsorption of pollutants in wastewater via biosorbents, nanoparticles and magnetic biosorbents: a review. Environ Res 212:113248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2022.113248
Uddin MK (2017) A review on the adsorption of heavy metals by clay minerals, with special focus on the past decade. Chem Eng J 308:438–462. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2016.09.029
Villena-Martínez EM, Alvizuri-Tintaya PA, Lora-García J et al (2022) Reverse osmosis modeling study of lead and arsenic removal from drinking water in tarija and la paz. Boliv Proces 10:1889. https://doi.org/10.3390/pr10091889
Vohra MS, Labaran BA (2020) Photocatalytic treatment of mixed selenocyanate and phenol streams: process modeling, optimization, and kinetics. Environ Prog Sustain Energy 39:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1002/ep.13401
Vohra M, Al-Suwaiyan M, Hussaini M (2020) Gas phase toluene adsorption using date palm-tree branches based activated carbon. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17:9287. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijerph17249287
Vohra M, Hussaini M, Mohammad T (2023) Olive branches activated carbon: synthesis, phenol adsorption and modeling. Chem Pap 77:485–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11696-022-02457-w
Wang Z, Jiang Y, Mo X et al (2021) Speciation transformation of Pb during palygorskite sorption-calcination process: Implications for Pb sequestration. Appl Geochem 124:104850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2020.104850
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge the necessary support for this work by the King Fahd University of Petroleum & Minerals (KFUPM) and the Civil and Environmental Engineering Department at KFUPM, including the lab facilities.
Funding
The authors did not receive support from any organization for the submitted work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Mohamed Sabbagh: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft. Minaam Hussaini: Formal analysis, Investigation, Writing—Original Draft, Writing—Review & Editing. Usman Ismail: Software, Formal analysis, Writing—Review & Editing. Habib-ur-Rehman Ahmed: Supervision, Resources. Mohammad Al-Suwaiyan: Supervision, Resources. Muhammad Vohra: Conceptualization, Methodology, Supervision, Resources, Writing—Review & Editing, Validation, Project administration.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no competing interests to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Q. Aguilar-Virgen.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Sabbagh, M., Hussaini, M., Ismail, U. et al. Novel nafion-palygorskite composite for Pb/Lead treatment. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05661-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05661-1