Abstract
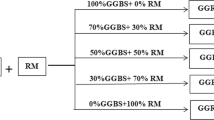
One of the major environmental problems in hot and arid locations is the production of dust. This study presents green slurries based on nanoclay—and blast furnace slag for stabilizing desert sands. The slurries introduced contain bentonite and kaolinite mineral nanoclays, along with blast furnace slag powder. Unconfined compressive strength, moisture content, and wind tunnel tests were conducted to evaluate the performance of the compounds in stabilizing sand and increasing its water-holding capacity. The mass percentages of bentonite nanoclay and blast furnace slag in the stabilizer slurry were optimized at 1–3% and 1–5%, respectively. The optimized mass percentages of kaolinite nanoclay and blast furnace slag slurry were 1–1% and 3–1%. The study found that soil stabilized with slurries increased compressive strength by three times compared to unstabilized soil. Additionally, the addition of stabilizers improved soil moisture retention by 50%. Sand surfaces stabilized with nanoclays and slag demonstrated excellent resistance to wind erosion, even at wind speeds of up to 100 km/h. Furthermore, there was no wind erosion observed at 60 °C. The suggested slurry compounds have shown a strong ability to enhance the mechanical properties of soil, increase soil water retention, and reduce wind erosion of sandy soil.













Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdelkader HAM, Hussein MMA, Ye H (2021) Influence of Waste Marble Dust on the Improvement of Expansive Clay Soils. Adv Civ Eng 2021:3192122. https://doi.org/10.1155/2021/3192122
Aboushook M, Al MMN, Fadol A, Abdelhaffez GS (2012) Different methods for stabilisation of sand dunes using calcium bentonite. Int J Environ Eng 4:79. https://doi.org/10.1504/ijee.2012.048103
Al-Husseiny RA, Ebrahim SE (2021) Synthesis of geopolymer for the removal of hazardous waste: a review. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/779/1/012102
Almajed AA (2017) Enzyme induced carbonate precipitation (EICP) for soil improvement
Almajed A, Lemboye K, Arab MG, Alnuaim A (2020) Mitigating wind erosion of sand using biopolymer-assisted EICP technique. Soils Found 60:356–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.sandf.2020.02.011
Almajed A, Lateef MA, Moghal AAB, Lemboye K (2021) State-of-the-art review of the applicability and challenges of microbial-induced calcite precipitation (MICP) and enzyme-induced calcite precipitation (EICP) techniques for geotechnical and geoenvironmental applications. Crystals. https://doi.org/10.3390/cryst11040370
Alzaidy MNJ (2019) Experimental study for stabilizing clayey soil with eggshell powder and plastic wastes. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 518:22008. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/518/2/022008
Aredes FGM, Campos TMB, Machado JPB et al (2015) Effect of cure temperature on the formation of metakaolinite-based geopolymer. Ceram Int 41:7302–7311. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2015.02.022
Arora A, Singh B, Kaur P (2019) Performance of Nano-particles in stabilization of soil: a comprehensive review. Mater Today Proc 17:124–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.06.409
Ayeldeen M, Negm A, El Sawwaf M, Gädda T (2018) Laboratory study of using biopolymer to reduce wind erosion. Int J Geotech Eng 12:228–240. https://doi.org/10.1080/19386362.2016.1264692
Babatunde QO, Yoon HK, Byun YH (2023) Rheological behavior of zein biopolymer and stiffness characteristic of biopolymer treated soil. Constr Build Mater 384:131466. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.131466
Bagheri P, Gratchev I, Son S, Rybachuk M (2023) Durability, strength, and erosion resistance assessment of lignin biopolymer treated Soil. Polymers (basel) 15:1–12. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym15061556
Barman D, Dash SK (2022) Stabilization of expansive soils using chemical additives: a review. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 14:1319–1342. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2022.02.011
Busscher W (1994) Fundamentals of soil behavior
Chang I, Prasidhi AK, Im J et al (2015) Soil treatment using microbial biopolymers for anti-desertification purposes. Geoderma 253–254:39–47. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.04.006
Chang I, Im J, Cho G (2016a) Introduction of microbial biopolymers in soil treatment for future environmentally-friendly and sustainable geotechnical engineering. Sustainability 8:1–23. https://doi.org/10.3390/su8030251
Chang I, Im J, Cho G-C (2016b) Geotechnical engineering behaviors of gellan gum biopolymer treated sand. Can Geotech J 317:1–38
Chang I, Im J, Lee S, Cho G (2017) Strength durability of gellan gum biopolymer-treated Korean sand with cyclic wetting and drying. Constr Build Mater 143:210–221. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.061
Chappell A, Webb NP, Guerschman JP et al (2018) Improving ground cover monitoring for wind erosion assessment using MODIS BRDF parameters. Remote Sens Environ 204:756–768. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rse.2017.09.026
Cheraghalikhani M, Niroumand H, Balachowski L (2023) Micro- and nano- bentonite to improve the strength of clayey sand as a nano soil-improvement technique. Sci Rep 13:10913. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-023-37936-x
Darand M, Sohrabi MM (2018) Identifying drought- and flood-prone areas based on significant changes in daily precipitation over Iran. Nat Hazards 90:1427–1446. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3107-9
Darwish GS, Tangri AP (2019) Effects of ground granulated blast furnace slag and lime on the strength and durability of clayey soil. Int J Eng Adv Technol 8:920–926
Dejong JT, Soga K, Kavazanjian E et al (2013) Biogeochemical processes and geotechnical applications: progress, opportunities and challenges. Bio- Chemo- Mech Process Geotech Eng - Geotech Symp Print 2013:143–157. https://doi.org/10.1680/bcmpge.60531.014
Dejong J, Martinez B, Ginn T et al (2014) Development of a scaled repeated five-spot treatment model for examining microbial induced calcite precipitation feasibility in field applications. Geotech Test J 37:424–435. https://doi.org/10.1520/GTJ20130089
Dingwen Z, Libin F, Liu S, Yongfeng D (2013) Experimental investigation of unconfined compression strength and stiffness of cement treated salt-rich clay. Mar Georesour Geotechnol 31:360–374. https://doi.org/10.1080/1064119X.2012.690826
Dove JE, Bents DD, Wang J, Gao B (2006) Particle-scale surface interactions of non-dilative interface systems. Geotext Geomembr 24:156–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2006.01.002
Duniway MC, Pfennigwerth AA, Fick SE et al (2019) Wind erosion and dust from US drylands: a review of causes, consequences, and solutions in a changing world. Ecosphere 10:1–28. https://doi.org/10.1002/ecs2.2650
Erosion W (2008) Land-surface modelling. Phys Model Wind Eros. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4020-8895-7_4
Fatehi H, Abtahi SM, Hashemolhosseini H, Hejazi SM (2018) A novel study on using protein based biopolymers in soil strengthening. Constr Build Mater 167:813–821. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.02.028
Fatehi H, Ong DEL, Yu J, Chang I (2021) Biopolymers as green binders for soil improvement in geotechnical applications: a review. Geosci 11:1–39. https://doi.org/10.3390/geosciences11070291
Firoozi AA, Guney Olgun C, Firoozi AA, Baghini MS (2017) Fundamentals of soil stabilization. Int J Geo-Engineering 8:1–16. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40703-017-0064-9
Ghadir P, Ranjbar N (2018) Clayey soil stabilization using geopolymer and Portland cement. Constr Build Mater 188:361–371. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.07.207
Ghadir P, Razeghi HR (2022) Effects of sodium chloride on the mechanical strength of alkali activated volcanic ash and slag pastes under room and elevated temperatures. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.128113
Ghadir P, Zamanian M, Mahbubi-Motlagh N et al (2021) Shear strength and life cycle assessment of volcanic ash-based geopolymer and cement stabilized soil: a comparative study. Transp Geotech 31:100639. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100639
Han P, Ren C, Bai X, Chen YF (2015) Corrosion mechanisms for cemented soils in three different sulfate solutions. Acta Geotech Slov 12:77–85
Harkes MP, Van PLA, Booster JL et al (2010) Fixation and distribution of bacterial activity in sand to induce carbonate precipitation for ground reinforcement. Ecol Eng 36:112–117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoleng.2009.01.004
Harutyunyan LR, Lasareva EV (2023) Chitosan and its derivatives: a step towards green chemistry. Biointerface Res Appl Chem 13:1–25. https://doi.org/10.33263/BRIAC136.578
Hataf N, Ghadir P, Ranjbar N (2018) Investigation of soil stabilization using chitosan biopolymer. J Clean Prod 170:1493–1500. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.09.256
He JJ, Cai QG, Tang ZJ (2008) Wind tunnel experimental study on the effect of PAM on soil wind erosion control. Environ Monit Assess 145:185–193. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10661-007-0028-1
Horpibulsuk S, Phojan W, Suddeepong A et al (2012) Strength development in blended cement admixed saline clay. Appl Clay Sci 55:44–52. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2011.10.003
Hostler FS (1964) Soil Stabilization. Ind Eng Chem 56:27–33. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie50652a005
Indiramma P, Sudharani C, Needhidasan S (2020) Utilization of fly ash and lime to stabilize the expansive soil and to sustain pollution free environment—an experimental study. Mater Today Proc 22:694–700. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2019.09.147
Ivanov V, Stabnikov V (2017a) Bioclogging and biogrouts
Ivanov V, Stabnikov V (2017b) Construction biotechnology: biogeochemistry, microbiology and biotechnology of construction materials and processes
Izadi R, Mahinroosta M, Allahverdi A (2022) An overview of methods and materials for sandy soil stabilization: emerging advances and current applications. ECOPERSIA 10:333–347. https://doi.org/20.1001.1.23222700.2022.10.4.7.6
Jang J (2020) A review of the application of biopolymers on geotechnical engineering and the strengthening mechanisms between typical biopolymers and soils. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:1465709. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1465709
Kannan G, O’Kelly BC, Sujatha ER (2023) Effect of chitin, chitosan and NaCMC biopolymers on the consistency limits of organic silt. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05022-4
Katra I (2020) Soil erosion: dust control and sand stabilization. Appl Sci 10:1–3. https://doi.org/10.3390/app10228044
Khalid N, Arshad MF, Mukri M et al (2015) Influence of nano-soil particles in soft soil stabilization. Electron J Geotech Eng 20:731–738
Khalid U, Rehman ZU, Ijaz N et al (2023) Integrating wheat straw and silica fume as a balanced mechanical ameliorator for expansive soil: a novel agri-industrial waste solution. Environ Sci Pollut Res 30:73570–73589. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-023-27538-5
Khan K, Ishfaq M, Amin MN et al (2022) Evaluation of mechanical and microstructural properties and global warming potential of green concrete with wheat straw ash and silica fume. Materials (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma15093177
Kheirfam H, Asadzadeh F (2020) Stabilizing sand from dried-up lakebeds against wind erosion by accelerating biological soil crust development. Eur J Soil Biol 98:103189. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejsobi.2020.103189
Komaei A, Soroush A, Fattahi SM, Ghanbari H (2023) Wind erosion control using alkali-activated slag cement: experimental investigation and microstructural analysis. J Environ Manage 344:118633. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2023.118633
Laftah WA, Hashim S, Ibrahim AN (2011) Polymer hydrogels: a review. Polym-Plast Technol Eng 50:1475–1486. https://doi.org/10.1080/03602559.2011.593082
Lal R (2003) Soil erosion and the global carbon budget. Environ Int 29:437–450. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0160-4120(02)00192-7
Lee M, Chang I, Park DY, Cho GC (2023) Strengthening and permeability control in sand using Cr3+-crosslinked xanthan gum biopolymer treatment. Transp Geotech 43:101122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2023.101122
Liu D, Yang Y, An S et al (2018) The biogeographical distribution of soil bacterial communities in the loess plateau as revealed by high-throughput sequencing. Front Microbiol. https://doi.org/10.3389/fmicb.2018.02456
Majeed ZH, Taha MR (2013) A review of stabilization of soils by using nanomaterials. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 7:576–581
Majeed ZH, Taha MR, Jawad IT (2014) Stabilization of soft soil using nanomaterials. Res J Appl Sci Eng Technol 8:503–509. https://doi.org/10.19026/rjaset.8.999
Manzoor SO, Yousuf A (2020) Stabilisation of soils with lime : a review. J Mater Environ Sci 11:1538–1551
Mekonnen E, Kebede A, Tafesse T, Tafesse M (2020) Application of microbial bioenzymes in soil stabilization. Int J Microbiol 2020:1725482. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1725482
Meng X, Liang L, Liu B (2017) Synthesis and sand-fixing properties of cationic poly(vinyl acetate-butyl acrylate-2-hydroxyethyl acrylate-DMC) copolymer emulsions. J Polym Environ 25:487–498. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-016-0826-z
Miftah A, Tirkolaei HK, Bilsel H (2020) Bio-precipitation of CaCO 3 for soil improvement : a review. In: 5th International Conference on New Advances in Civil Engineering, p 800
Miraki H, Shariatmadari N, Ghadir P et al (2022) Clayey soil stabilization using alkali-activated volcanic ash and slag. J Rock Mech Geotech Eng 14:576–591. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrmge.2021.08.012
Modarres R, Sadeghi S (2018) Spatial and temporal trends of dust storms across desert regions of Iran. Nat Hazards 90:101–114. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11069-017-3035-8
Mohanan H, Shivhare S (2023) A review on subgrade soil stabilization using bio enzymes. Arab J Geosci. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-023-11257-9
Nguyen DT, Phan VTA (2021) Engineering properties of soil stabilized with cement and fly ash for sustainable road construction. Int J Eng Trans B Appl 34:2665–2671. https://doi.org/10.5829/IJE.2021.34.12C.12
Nouri H, Ghadir P, Fatehi H et al (2022) Effects of protein-based biopolymer on geotechnical properties of salt-affected sandy soil. Geotech Geol Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-022-02245-z
Obuzor GN, Kinuthia JM, Robinson RB (2012) Soil stabilisation with lime-activated-GGBS—a mitigation to flooding effects on road structural layers/embankments constructed on floodplains. Eng Geol 151:112–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2012.09.010
Osinubi KJ, Eberemu AO, Ijimdiya TS et al (2020) Review of the use of microorganisms in geotechnical engineering applications. SN Appl Sci 2:207. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-1974-2
Pathak AK, Pandey V, Singh KMJP (2014) Soil stabilisation using ground granulated blast furnace slag. Int J Eng Res 4:164–171
Payá J, Monzó J, Roselló J et al (2020) Sustainable soil-compacted blocks containing blast furnace slag (BFS) activated with olive stone BIOMASS ash (OBA). Sustainability. https://doi.org/10.3390/su12239824
Persoff BP, Apps J, Moridis G, Whang JM (1999) C ontaminants on S and G routed. Manager 125:461–469
Pokharel B, Siddiqua S (2021) Effect of calcium bentonite clay and fly ash on the stabilization of organic soil from Alberta, Canada. Eng Geol 293:106291. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106291
Programme UNE (2006) Deserts & drylands. TUNZA 24
Qureshi MU, Chang I, Al-Sadarani K (2017) Strength and durability characteristics of biopolymer-treated desert sand. Geomech Eng 12:785–801. https://doi.org/10.12989/gae.2017.12.5.785
Rajalaxmi B (2010) Stabilization of red soil using blast furnace slag. NIT Rourkela 1:391–395
Ravi S, Zobeck TM, Over TM et al (2006) On the effect of moisture bonding forces in air-dry soils on threshold friction velocity of wind erosion. Sedimentology 53:597–609. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1365-3091.2006.00775.x
Ror CK, Tejyan S, Kumar N (2022) Effect of marble dust reinforcement in composites for different applications: a review. Mater Today Proc 60:1120–1124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.02.246
Sadeghian F, Haddad A, Jahandari SS et al (2020) Effects of electrokinetic phenomena on the load-bearing capacity of different steel and concrete piles: a small-scale experimental study. Can Geotech J. https://doi.org/10.1139/cgj-2019-0650
Safarzadeh I, Rahimi MH, Bagherzadeh KA (2019) Investigating the effect of nanoclay additives on the geotechnical properties of clay and silt soil. J Civ Eng MaterApp 3:65–77
Sajad S, Singh H (2022) Stimulation of black cotton soil via stone dust and pet fibre. Mater Today Proc 48:1633–1637. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.09.516
Schlesinger WH, Reynolds JF, Cunningham GL et al (1990) Biological feedbacks in global desertification. Science (80- ) 247:1043–1048. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.247.4946.1043
Shariatmadari N, Reza M, Tasuji A, et al (2020) Experimental study on the effect of chitosan biopolymer on sandy soil stabilization. 6007:22–26
Shariatmadari N, Hasanzadehshooiili H, Ghadir P et al (2021) Compressive strength of sandy soils stabilized with alkali-activated volcanic ash and slag. J Mater Civ Eng 33:1–20. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0003845
Sharma T, Singh S (2021) Experimental study on stabilisation of clayey soil using cement and bagasse ash. IOP Conf Ser Earth Environ Sci 889:0–13. https://doi.org/10.1088/1755-1315/889/1/012010
Sharma NK, Swain SK, Sahoo UC (2012) Stabilization of a clayey soil with fly ash and lime: a micro level investigation. Geotech Geol Eng 30:1197–1205. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10706-012-9532-3
Shrivastava A, Saxena A, Sachan A (2022) Effect of guar gum biopolymer on shear strength and liquefaction response of coal ash. Indian Geotech Conf IGC, pp 1–12
Smitha S, Rangaswamy KT (2020) Effect of biopolymer treatment on pore pressure response and dynamic properties of silty sand. J Mater Civ Eng 32:4020217
Tiwari SK, Sharma JP, Yadav JS (2016) Akademia baru behaviour of dune sand and its stabilization techniques. J Adv Res Appl Mech ISSN 19:2289–7895
Tonini de Araújo M, Tonatto Ferrazzo S, Jordi Bruschi GJ, Consoli NC (2021) Mechanical and environmental performance of eggshell lime for expansive soils improvement. Transp Geotech 31:100681. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trgeo.2021.100681
Wang Z, Zhang N, Ding J et al (2018) Experimental study on wind erosion resistance and strength of sands treated with microbial-induced calcium carbonate precipitation. Adv Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1155/2018/3463298
Yang F, Zhang B, Pan C, Zeng Y (2009) Traditional mortar represented by sticky rice lime mortar-One of the great inventions in ancient China. Sci China, Ser E Technol Sci 52:1641–1647. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11431-008-0317-0
Yi Y, Zheng X, Liu S, Al-Tabbaa A (2015) Comparison of reactive magnesia- and carbide slag-activated ground granulated blastfurnace slag and Portland cement for stabilisation of a natural soil. Appl Clay Sci 111:21–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.clay.2015.03.023
Yu Z, Xu G, Kang X et al (2016) Unconfined compressive strength of sulphate saline soil with different salt content and lime proportion. Electron J Geotech Eng 21:10203–10214
Yu C, Cui C, Wang Y et al (2021) Strength performance and microstructural evolution of carbonated steel slag stabilized soils in the laboratory scale. Eng Geol 295:106410. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enggeo.2021.106410
Zang YX, Gong W, Xie H et al (2015) Chemical sand stabilization: a review of material, mechanism, and problems. Environ Technol Rev 4:119–132. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2015.1105307
Acknowledgements
This study was supported by MatSoil Company (No 06C/2022).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Conceptualization contributed by Rahman Izadi, Mostafa Mahinroosta, and Ali Allahverdi]; methodology contributed by Rahman Izadi, Mostafa Mahinroosta, Ali Allahverdi, and Pooria Ghadir; formal analysis and investigation contributed by Rahman Izadi, Mostafa Mahinroosta, Ali Allahverdi, and Pooria Ghadir; writing—original draft preparation contributed by Rahman Izadi and Mostafa Mahinroosta; writing—review and editing contributed by Mostafa Mahinroosta; resources contributed by Ali Allahverdi and Pooria Ghadir; supervision contributed by Mostafa Mahinroosta and Ali Allahverdi.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: F. Şen.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Izadi, R., Mahinroosta, M., Allahverdi, A. et al. Stabilizers based on nanoclay and blast furnace slag to reduce wind erosion of sandy soil green stabilization of sandy soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05630-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05630-8