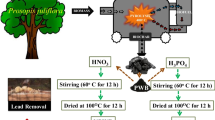
Abstract
Water contamination currently threatens human health, which is still a major environmental issue. Scientists are paying attention, in particular, to lead poisoning of water caused by industrial wastes on a global scale. In order to reduce agricultural waste and promote sustainable development, this study created a straightforward process for using leftover rice husks to create biochar. At first, the rice husk biochar was prepared; then, following the immersion of biochar with precursors of Fe2+ and Fe3+ and precipitation under alkaline condition, the Fe3O4 was formed and laid onto biochar to create another magnetic adsorbent known as ferrous-modified biochar. The success of loading Fe3O4 was confirmed by SEM, XRD, FTIR, and BET measurements. The delivered ferrous-modified biochar has a high surface area and correct functional groups for the adsorption process. In order to remove Pb (II) from wastewater, rice husk biochar and ferrous-modified biochar materials were used. Under optimized conditions, synthesized ferrous-modified biochar has a lead adsorbent effectiveness of 95.0% that is related to varying pathways as co-precipitation reaction, complexation reaction, conjugation adsorption, ion exchange, and Fe–O coordination. The Pb2+ adsorption capacity of modified biochar is three times greater than rice husk biochar with 73.68 mg/g. Another evidence of the ferrous-modified biochar adsorbent’s excellent recyclable properties is the remaining lead efficiency, which was over 41.2% even after six recycling cycles. Therefore, by this approach of synthesizing Fe3O4 loaded on biochar, the research provided new opportunities for developing low-cost and highly efficient adsorbent to remove heavy metals from water.






Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Ghani N, Hefny M, El-Chaghaby GA (2007) Removal of lead from aqueous solution using low cost abundantly available adsorbents. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:67–73
Amuda OS, Giwa AA, Bello IA (2007) Removal of heavy metal from industrial wastewater using modified activated coconut shell carbon. Biochem Eng J 36(2):174–181
Bastami TR, Khaknahad S, Malekshahi M (2020) Sonochemical versus reverse-precipitation synthesis of CuxO/Fe2O3/MoC nano-hybrid: removal of reactive dyes and evaluation of smartphone for colorimetric detection of organic dyes in water media. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:9364–9381
Cheng AW, Wang X, Liu X, He C (2023) Wet-process-modified blue-green algae biochar by K2FeO4 for the efficient adsorption of Cr(VI) from water. Processes 11:1489
Clarkson TW (1997) The toxicology of mercury. Crit Rev Clin Lab Sci 34(4):369–403
Cui X, Zhang S-S, Geng Y, Zhen J, Zhan J, Cao C, Ni S-Q (2021) Synergistic catalysis by Fe3O4-biochar/peroxymonosulfate system for the removal of bisphenol a. Sep Purif Technol 276:119351
Ding W, Dong X, Ime IM, Gao B, Ma LQ (2014) Pyrolytic temperatures impact lead sorption mechanisms by bagasse biochars. Chemosphere 105:68–74
Eizi R, Bastami TR, Mahmoudi V, Ayati A, Babaei H (2023) Facile ultrasound-assisted synthesis of CuFe-Layered double hydroxides/g-C3N4 nanocomposite for alizarin red S sono-sorption. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 145:104844
Feng Y, Liu P, Wang Y, Zou-Finfrock Y, Xie X, Su C, Liu N, Yang Y, Xu Y (2020) Distribution and speciation of iron in Fe-modified biochars and its application in removal of As(V), As(III), Cr(VI), and Hg(II): an X-ray absorption study. J Hazard Mater 384:121342
Ho S-H, Chen Y-d, Yang Z-k, Nagarajan D, Chang J-S, Ren N-q (2017) High-efficiency removal of lead from wastewater by biochar derived from anaerobic digestion sludge. Bioresour Technol 246:142–149
Jianhua Q, Zhang B, Tong H, Liu Y, Wang S, Wei S, Wang L, Wang Y, Zhang Y (2023) High-efficiency decontamination of Pb(II) and tetracycline in contaminated water using ball-milled magnetic bone derived biochar. J Clean Prod 385:135683
Karam DS, Nagabovanalli P, Rajoo KS, Ishak CF, Abdu A, Rosli Z, Muharam FM, Zulperi D (2022) An overview on the preparation of rice husk biochar, factors affecting its properties, and its agriculture application. J Saudi Soc Agric Sci 21:149–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jssas.2021.07.005
Liang M, Ding Y, Zhang Q et al (2020) Removal of aqueous Cr (VI) by magnetic biochar derived from bagasse. Sci Rep 10(1):1–13
Miller WH Jr, Schipper HM, Lee JS et al (2002) Mechanisms of action of arsenic trioxide. Can Res 62(14):3893–3903
Mohan D, Pittman CU, Bricka M, Smith F, Yancey B, Mohammad J, Steele PH, Alexandre-Franco MF, Gómez-Serrano V, Gong H (2007) Sorption of arsenic, cadmium, and lead by chars produced from fast pyrolysis of wood and bark during bio-oil production. J Colloid Interface Sci 310(1):57–73
Najafi M, Bastami TR, Binesh N, Ayati A, Emamverdi S (2022) Sono-sorption versus adsorption for the removal of congo red from aqueous solution using NiFeLDH/Au nanocomposite: kinetics, thermodynamics, isotherm studies, and optimization of process parameters. J Ind Eng Chem 116:489–503
Qian J, Yang X, Jiang L, Zhu C, Mao H, Wang K (2014) Facile preparation of Fe3O4 nanospheres/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites with high peroxidase-like activity for sensitive and selective colorimetric detection of acetylcholine. Sens Actuat B Chem 201:160–166
Ravishankar H, Moazzem S, Jegatheesan V (2019) Performance evaluation of A2O MBR system with graphene oxide (GO) blended polysulfone (PSf) composite membrane for treatment of high strength synthetic wastewater containing lead. Chemosphere 234:148–161
Ren M, Qian X, Chen Y et al (2022) Potential lead toxicity and leakage issues on lead halide perovskite photovoltaics. J Hazard Mater 426:127848
Sekar M, Sakthi V, Rengaraj S (2004) Kinetics and equilibrium adsorption study of lead (II) onto activated carbon prepared from coconut shell. J Colloid Interface Sci 279(2):307–313
Shen Z, Zhang J, Hou D, Tsang DCW, Ok YS, Alessi DS (2019) Synthesis of MgO-coated corncob biochar and its application in lead stabilization in a soil washing residue. Environ Int 122:357–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envint.2018.11.045
Thảo VTM, Khánh NM, Nguyên NTH et al (2021) Ảnh hưởng của nhiệt độ nhiệt phân đến tính chất hóa lý của than sinh học từ trấu. TẠP CHÍ KHOA học đại học mở THÀNH PHỐ hồ CHÍ MINH-kỹ THUẬT và CÔNG NGHỆ 16(1):126–141
Tripathy S, Sahu S, Patel RK, Panda RB, Kar PK (2022) Novel Fe3O4-modified biochar derived from citrus bergamia peel: a green synthesis approach for adsorptive removal of methylene blue. Chemistry Select 7:e202103595. https://doi.org/10.1002/slct.202103595
Wang C, Wand H (2018) Pb (II) sorption from aqueous solution by novel biochar loaded with nano-particles. Chemosphere 192:1–4. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.10.125
Wang W, Zheng L, Lu F et al (2017) Facile synthesis and characterization of magnetochromatic Fe3O4 nanoparticles. AIP Adv 7(5):056317
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
TTVH contributed to conceptualization, methodology, validation, writing draft, and writing—review and editing. NMV contributed to methodology, investigation, writing draft, supervision, and writing draft. VTQ and NTLH contributed to experiment conduction and sample analysis.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: T. Y. Wu.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ha, T.T.V., Viet, N.M., Quan, V.T. et al. Novel Fe3O4-modified biochar generated from rice husk: a sustainable strategy for strengthening lead absorption in wastewater. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05626-4
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-024-05626-4