Abstract
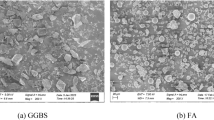
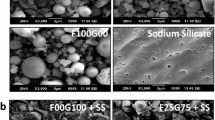
Conventional cement concrete has surfaced as a major construction material with considerable global warming potential. Alternatively, a fly ash (FA) ground-granulated blast furnace slag (GGBS)-based alkali-activated concrete is introduced to attain the goal of net zero emission and reduce the environmental impacts. In this study fixed proportions of concrete mixes matching with a designated strength of plain cement concrete mix have been determined. In addition to this, an ambient curing condition has been integrated that will be helpful for practical implementation in large-scale construction. Sodium silicate and sodium hydroxide were used as alkaline activator solutions to activate the FA and GGBS. The alkali activator reciprocity, i.e. Na2SiO3/NaOH (NS/NH), was set at 2.5. For various combinations of FA and GGBS, the main parameters considered in this study were molarity of sodium hydroxide and alkaline solution/binder ratio. The variation implemented in this experimentation includes: proportions of FA and GGBS (80–20, 75–25, 70–30, 65–35, 60–40, 55–45 and 50–50) and molarity of NaOH (10, 12, 14 M). Results concluded that the FA–GGBS-based alkali-activated concrete exhibits better performance as compared to conventional concrete. Furthermore, X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectrography, scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray are carried out to investigate the behaviour of microstructure of GPC. Life-cycle impact category values have also been estimated considering all possible construction scenarios.
























Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adjei S, Elkatatny S, Aggrey WN, Abdelraouf Y (2022) Geopolymer as the future oil-well cement: a review. J Pet Sci Eng 208:109485. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.petrol.2021.109485
Ahmed A, Kumar SS, Nanda RP (2021) Development of geopolymer concrete mixes with ambient air curing. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng 1116:012160. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/1116/1/012160
Albitar M, Visintin P, Ali M, Drechsler M (2015) Assessing behaviour of fresh and hardened geopolymer concrete mixed with class-F fly ash. KSCE J Civ Eng 19:1445–1455
Aliabdo AA, AbdElmoaty AEM, Salem HA (2016) Effect of water addition, plasticizer and alkaline solution constitution on fly ash based geopolymer concrete performance. Constr Build Mater 121:694–703. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.062
Al-mashhadani MM, Canpolat O (2020) Effect of various NaOH molarities and various filling materials on the behavior of fly ash based geopolymer composites. Constr Build Mater 262:120560. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120560
Anuradha R, Sreevidya V, Venkatasubramani R, Rangan BV (2012) Modified guidelines for geopolymer concrete mix design using Indian standard. Asian J Civ Eng Build Hous 13:353–364
Chindaprasirt P, Chareerat T, Sirivivatnanon V (2007) Workability and strength of coarse high calcium fly ash geopolymer. Cem Concr Compos 29:224–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2006.11.002
Code C-FM (1990) Comité Euro-International du Béton (CEB), 1993
ACI Committee 363 (1984) State-of-the-art Report on High-strength Concrete (ACI 363R-84). American Concrete Institute.
ACI Committee (2008) Building code requirements for structural concrete (ACI 318–08) and commentary. American Concrete Institute.
Cong P, Cheng Y (2021) Advances in geopolymer materials: a comprehensive review. J Traffic Transp Eng Engl Ed 8:283–314. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtte.2021.03.004
Davidovits J (1991) Geopolymers: inorganic polymeric new materials. J Therm Anal 37:1633–1656. https://doi.org/10.1007/BF01912193
Davidovits J (1999) Chemistry of Geopolymeric Systems, Terminology In: Proceedings of 99 International Conference.
Elyamany HE, AbdElmoaty AEM, Diab ARA (2022) Properties of slag geopolymer concrete modified with fly ash and silica fume. Can J Civ Eng 49:183–191. https://doi.org/10.1139/cjce-2019-0757
Etxeberria M, Marí AR, Vázquez E (2007) Recycled aggregate concrete as structural material. Mater Struct 40:529–541. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-006-9161-5
Ferdous MW, Kayali O, Khennane A (2013) a detailed procedure of mix design for fly ash based geopolymer concrete. In: Page 1 Fourth Asia-Pacific Conference on FRP in Structures. Melbourne, Australia
Garcia-Lodeiro I, Palomo A, Fernández-Jiménez A, Macphee DE (2011) Compatibility studies between N-A-S-H and C-A-S-H gels. Study in the ternary diagram Na2O–CaO–Al2O3–SiO2–H2O. Cem Concr Res 41:923–931. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2011.05.006
Gardner N, Poon S (1976) Time and temperature effects on tensile, bond, and compressive strengths. J Proc 73(7):405–409
Hadi MNS, Al-Azzawi M, Yu T (2018) Effects of fly ash characteristics and alkaline activator components on compressive strength of fly ash-based geopolymer mortar. Constr Build Mater 175:41–54. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.092
Hardjjito D, Rangan BV (2005) Development and Properties of Low-calcium Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Concrete. Res Rep GC1 Curtin Univ Technol Aus.
IS:13311–1 (1992): Non-destructive testing of Concrete- Methods of test, Part 1-Ultrasonic Pulse Velocity.
IS:13311–2 (1992): Non-destructive testing of Concrete- Methods of test, Part 2-Rebound Hammer.
IS:2386a (1963): Indian Standard Specification, Methods of test for aggregates for concrete: Part 1, Particle size and shape, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
IS:2386b (1963): Indian Standard Specification, Methods of Test for Aggregates for Concrete: Part 3, Specific Gravity, Density, Voids, Absorption and Bulking, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi [Reaffirmed in 2002].
IS:2386c (1963): Indian Standard Specification, Methods of Test for Aggregates for Concrete: Part 4, Mechanical Properties, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi [Reaffirmed in 2002].
IS:3812–1, (2003) Specification for Pulverized Fuel Ash, Part 1 (Bureau of Indian standards) New Delhi India
IS:383 (1970): Indian standard specification for coarse and fine aggregate from natural sources, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
IS:516 (1959): Method of tests for strength of concrete, Bureau of Indian Standards, New Delhi.
IS:5816 (1999): Splitting Tensile Strength of Concrete – Method of Test, Bureau of Indian standards, New Delhi, India.
IS:7320 (1974) (Reaffirmed 2008): Specification for concrete slump test apparatus.
Jena S, Panigrahi R (2019) Performance assessment of geopolymer concrete with partial replacement of ferrochrome slag as coarse aggregate. Constr Build Mater 220:525–537. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.045
Kumar S, Kumar R, Mehrotra SP (2010) Influence of granulated blast furnace slag on the reaction, structure and properties of fly ash based geopolymer. J Mater Sci 45:607–615. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10853-009-3934-5
Lee S, Shin S (2019) Prediction on compressive and split tensile strengths of GGBFS/FA based GPC. Materials 12:4198. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma12244198
Limbachiya M, Meddah MS, Ouchagour Y (2011) Use of recycled concrete aggregate in fly-ash concrete. Constr Build Mater. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.07.023
Majhi RK, Nayak AN, Mukharjee BB (2018) Development of sustainable concrete using recycled coarse aggregate and ground granulated blast furnace slag. Constr Build Mater 159:417–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.10.118
Mehta A, Siddique R (2018) Sustainable geopolymer concrete using ground granulated blast furnace slag and rice husk ash: strength and permeability properties. J Clean Prod 205:49–57. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.08.313
Nath P, Sarker PK (2014) Effect of GGBFS on setting, workability and early strength properties of fly ash geopolymer concrete cured in ambient condition. Constr Build Mater 66:163–171. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.05.080
Patankar SV, Ghugal YM, Jamkar SS (2015) Mix design of fly ash based geopolymer concrete. In: Matsagar V (ed) Adv Struct Eng. Springer India, New Delhi
Pilehvar S, Cao VD, Szczotok AM et al (2018) Physical and mechanical properties of fly ash and slag geopolymer concrete containing different types of micro-encapsulated phase change materials. Constr Build Mater 173:28–39. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.016
Poon CS, Shui ZH, Lam L (2004) Effect of microstructure of ITZ on compressive strength of concrete prepared with recycled aggregates. Constr Build Mater 18:461–468. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2004.03.005
Prusty SR, Panigrahi R, Jena S (2022) Mechanical and micro-structural properties of blended fly Ash-slag based alkali activated concrete. Mater Today Proc 65:1748–1754. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2022.04.795
Qaidi SMA, Dinkha YZ, Haido JH et al (2021) Engineering properties of sustainable green concrete incorporating eco-friendly aggregate of crumb rubber: A review. J Clean Prod 324:129251. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.129251
Rafeet A, Vinai R, Soutsos M, Sha W (2017) Guidelines for mix proportioning of fly ash/GGBS based alkali activated concretes. Constr Build Mater 147:130–142. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.04.036
Rashad AM (2014) A comprehensive overview about the influence of different admixtures and additives on the properties of alkali-activated fly ash. Mater Des 53:1005–1025. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2013.07.074
Ryu GS, Lee YB, Koh KT, Chung YS (2013) The mechanical properties of fly ash-based geopolymer concrete with alkaline activators. Constr Build Mater 47:409–418. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.05.069
Sata V, Sathonsaowaphak A, Chindaprasirt P (2012) Resistance of lignite bottom ash geopolymer mortar to sulfate and sulfuric acid attack. Cem Concr Compos 34:700–708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2012.01.010
Silva PD, Sagoe-Crenstil K, Sirivivatnanon V (2007) Kinetics of geopolymerization: role of Al2O3 and SiO2. Cem Concr Res 37:512–518. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2007.01.003
Sofi M, van Deventer JSJ, Mendis PA, Lukey GC (2007) Engineering properties of inorganic polymer concretes (IPCs). Cem Concr Res 37:251–257. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconres.2006.10.008
Somna K, Jaturapitakkul C, Kajitvichyanukul P, Chindaprasirt P (2011) NaOH-activated ground fly ash geopolymer cured at ambient temperature. Fuel 90:2118–2124. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2011.01.018
Tangchirapat W, Buranasing R, Jaturapitakkul C, Chindaprasirt P (2008) Influence of rice husk–bark ash on mechanical properties of concrete containing high amount of recycled aggregates. Constr Build Mater 22:1812–1819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2007.05.004
Teing TT, Huat BBK, Shukla SK et al (2019) Effects of alkali-activated waste binder in soil stabilization. GEOMATE J 17:82–89
Temuujin J, Minjigmaa A, Lee M et al (2011) Characterisation of class F fly ash geopolymer pastes immersed in acid and alkaline solutions. Cem Concr Compos 33:1086–1091. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2011.08.008
Turner LK, Collins FG (2013) Carbon dioxide equivalent (CO2-e) emissions: a comparison between geopolymer and OPC cement concrete. Constr Build Mater 43:125–130. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2013.01.023
Yan S, Zhang F, Wang L et al (2019) A green and low-cost hollow gangue microsphere/geopolymer adsorbent for the effective removal of heavy metals from wastewaters. J Environ Manage 246:174–183. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.05.120
Yang KH, Song JK, Lee KS, Ashour AF (2009) Flow and compressive strength of alkali-activated mortars. ACI Mater J 106:50–58
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
On behalf of all authors, the corresponding author states that there is no competing interest and the study received no financial assistance from any source that could have influenced the work.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Prusty, S.R., Panigrahi, R. & Jena, S. Characterisation and life-cycle assessment of alkali-activated concrete using industrial wastes. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 2923–2938 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05100-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-05100-7