Abstract
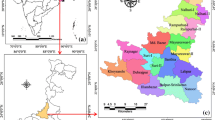
Groundwater resource is a crucial asset that makes a considerable contribution to the overall annual water resources toward industrial, domestic and agriculture purposes. However, overexploitation has resulted in severe reductions in groundwater supply. Evaluation of the possibility of groundwater recharge area is quite useful in order to conserve the groundwater resources. In this research, fourteen thematic maps (i.e., Lithology, Slope, Land use and Land cover, Drainage Density, Rainfall, Lineament Density, Distance from river, Hydrological Soil Group, Geomorphology, Topographic Wetness Index, Profile Curvature, Topographic Position Index, Plan Curvature and Roughness) undergo multicollinearity check followed by overlaying all of the thematic maps in ArcGIS software by considering ranks assigned to each thematic map using Analytical Hierarchy Process in order to develop the Groundwater potential zone map. The present research area was divided into four zones according to the Groundwater potential zone map, i.e., very high, high, moderate and low groundwater potential zone consisting of 22%, 45%, 26% and 7% of Jamsholaghat sub-basin, respectively. Most of the eastern part of the study area was found highly suitable for groundwater potential zones. This was due to favorable conditions such as lithology (laterite and quartz), geomorphology (flood plain/water bodies), slope (very gentle/gentle), high/moderate rainfall of the present research area. Nevertheless, the present study advises the adoption of sustainable aquifer recharge methods to enhance the groundwater resources of the deficit regions. These methods include rainwater harvesting and irrigation methods like micro as well as drip irrigation and sprinkler.



















Similar content being viewed by others
Data availability
The submitted article contains all of the data and models developed or utilized during the study. There is no separate data available with this manuscript.
References
Abrams W, Ghoneim E, Shew R, LaMaskin T, Al-Bloushi K, Hussein S, AbuBakr M, Al-Mulla E, Al-Awar M, El-Baz F (2018) Delineation of groundwater potential (GWP) in the northern United Arab Emirates and Oman using geospatial technologies in conjunction with simple additive weight (SAW), analytical hierarchy process (AHP), and probabilistic frequency ratio (PFR) techniques. J Arid Environ 157:77–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaridenv.2018.05.005
Agarwal E, Agarwal R, Garg R, Garg P (2013) Delineation of groundwater potential zone: an AHP/ANP approach. J Earth Syst Sci 122:887–898. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12040-013-0309-8
Ajay KV, Mondal NC, Ahmed S (2020) Identification of groundwater potential zones using RS, GIS and AHP techniques: a case study in a part of deccan volcanic province (DVP), Maharashtra. India J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48:497–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01086-3
Al-Djazouli MO, Elmorabiti K, Rahimi A, Amellah O, Fadil OAM (2020) Delineating of groundwater potential zones based on remote sensing, GIS and analytical hierarchical process: a case of Waddai, eastern Chad. GeoJournal 86:1881–1894. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10708-020-10160-0
Andualem TG, Demeke GG (2019) Groundwater potential assessment using GIS and remote sensing: a case study of Guna tana landscape, upper blue Nile Basin. Ethiopia. J. Hydrol. Reg. Stud. 24:100610
Arshad A, Zhang Z, Zhang W, Dilawar A (2020) Mapping favorable groundwater potential recharge zones using a GIS-based analytical hierarchical process and probability frequency ratio model: a case study from an agro-urban region of Pakistan. Geosci Front 11:1805–1819. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2019.12.013
Arulbalaji P, Padmalal D, Sreelash K (2019) GIS and AHP techniques based delineation of groundwater potential zones: a case study from Southern Western Ghats. India Sci Rep 9:2082. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-019-38567-x
Awawdeh M, Obeidat M, Al-Mohammad M, Al-Qudah K, Jaradat R (2013) Integrated GIS and remote sensing for mapping groundwater potentiality in the Tulul al Ashaqif, Northeast Jordan. Arab J Geosci 7:2377–2392. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0964-8
Benjmel K, Amraoui F, Boutaleb S, Ouchchen M, Tahiri A, Touab A (2020) Mapping of groundwater potential zones in crystalline terrain using remote sensing, gis techniques, and multicriteria data analysis (Case of the Ighrem Region, Western Anti-Atlas, Morocco). Water 12:471. https://doi.org/10.3390/w12020471
Çelik R (2019) Evaluation of groundwater potential by GIS-based multicriteria decision making as a spatial prediction tool: case study in the Tigris River Batman-Hasankeyf Sub-Basin. Turkey Water 11:2630. https://doi.org/10.3390/w11122630
Choubin B, Rahmati O, Soleimani F, Alilou H, Moradi E, Alamdari N (2019). Regional Groundwater Potential Analysis Using Classification and Regression Trees. In Spatial Modeling in GIS and R for Earth and Environmental Sciences 1st ed. Pourghasemi, H.R., Gokceoglu, C., Eds., Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-815226-3.00022-3.
Dar T, Rai N, Bhat A (2020) Delineation of potential groundwater recharge zones using analytical hierarchy process (AHP). Geol Ecol Landscape 5(4):292–307. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2020.1726562
Das S (2019) Comparison among influencing factor, frequency ratio, and analytical hierarchy process techniques for groundwater potential zonation in Vaitarna basin, Maharashtra. India Groundw Sustain Dev 8:617–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsd.2019.03.003
Das B, Pal S, Malik S, Chakrabortty R (2018) Modeling groundwater potential zones of Puruliya district, West Bengal, India using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Geol Ecol Landsc 3:223–237. https://doi.org/10.1080/24749508.2018.1555740
Fashae O, Tijani M, Talabi A, Adedeji O (2014) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in the crystalline basement terrain of SW-Nigeria: An integrated GIS and remote sensing approach. Appl Water Sci 4:19–38. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-013-0127-9
Fenta AA, Kifle A, Gebreyohannes T, Hailu G (2014) Spatial analysis of groundwater potential using remote sensing and GIS-based multi-criteria evaluation in Raya Valley, northern Ethiopia. Hydrogeol J 23:195–206. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10040-014-1198-x
Ghosh P, Bandyopadhyay S, Jana N (2016) Mapping of groundwater potential zones in hard rock terrain using geoinformatics: A case of Kumari watershed in western part of West Bengal. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:1. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-015-0044-z
Gnanachandrasamy G, Yongzhang Z, Bagyaraj M, Venkatramanan S, Ramkumar T, Shugong W (2018) Remote sensing and GIS based groundwater potential Zone Mapping in Ariyalur District, Tamil Nadu. J Geol Soc India 92:484–490. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12594-018-1046-z
Hussein A, Govindu V, Nigusse A (2017) Evaluation of groundwater potential using geospatial techniques. Appl Water Sci 7:2447–2461. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-016-0433-0
Hutti B, Nijagunappa R (2011) Identification of groundwater potential zone using geoinformatics in Ghataprabha basin, North Karnataka. India Int J Geomat Geosci 2:91–109
Jahan CS, Rahaman MF, Arefin R, Ali MS, Mazumder QH (2019) Delineation of groundwater potential zones of Atrai-Sib river basin in north-west Bangladesh using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Sustain Water Resour Manag 5:689–702. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40899-018-0240-x
Jothibasu A, Anbazhagan S (2016) Modeling groundwater probability index in Ponnaiyar River basin of South India using analytic hierarchy process. Model Earth Syst Environ 2:109. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40808-016-0174-y
Kaliraj S, Chandrasekar N, Magesh N (2014) Identification of potential groundwater recharge zones in Vaigai upper basin, Tamil Nadu, using GIS-based analytical hierarchical process (AHP) technique. Arab J Geosci 7:1385–1401. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-013-0849-x
Kanagaraj G, Suganthi S, Elango L, Magesh N (2019) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in Vellore district, Tamil Nadu, India using geospatial techniques. Earth Sci Inf 12:211–223. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12145-018-0363-5
Kolli M, Opp C, Groll M (2020) Mapping of potential groundwater recharge zones in the Kolleru Lake catchment, India, by using remote sensing and GIS techniques. Nat Resour 11:127–145. https://doi.org/10.4236/nr.2020.113008
Kumar A, Krishna AP (2018) Assessment of groundwater potential zones in coal mining impacted hard-rock terrain of India by integrating geospatial and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) approach. Geocarto Int 33:105–129. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2016.1232314
Kumar T, Gautam A, Kumar T (2014) Appraising the accuracy of GIS-based multi-criteria decision-making technique for delineation of groundwater potential zones. Water Resour Manag 28:4449–4466. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-014-0663-6
Kumar V, Mondal N, Ahmed S (2020) Identification of groundwater potential zones using RS, GIS and AHP techniques: a case study in a part of deccan volcanic province (DVP), Maharashtra. India J Indian Soc Remote Sens 48:497–511. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12524-019-01086-3
Lakshmi S, Reddy Y (2018) Identification of groundwater potential zones using GIS and remote sensing. Int. J. Pure Appl. Math. 119:3195–3210
Magesh N, Chandrasekar N, Soundranayagam J (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in Theni district, Tamil Nadu, using remote sensing, GIS and MIF techniques. Geosci Front 3:189–196. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.gsf.2011.10.007
Maity D, Mandal S (2017) Identification of groundwater potential zones of the Kumari river basin, India: An RS & GIS based semi-quantitative approach. Environ Dev Sustain 21:1013–1034. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10668-017-0072-0
Montgomery DC, Peck EA, Vining GG (2013) Introduction to Linear Regression Analysis. John Wiley & Sons New Jersey, USA
Mukherjee P, Singh C, Mukherjee S (2012) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in arid region of India—A remote sensing and GIS approach. Water Resour Manag 26:2643–2672. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11269-012-0038-9
Murmu P, Kumar M, Lal D, Sonker I, Singh SK (2019) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using geospatial techniques and analytical hierarchy process in Dumka district, Jharkhand. India. Groundw. Sustain. Dev. 9:100239
Nasir M, Khan S, Zahid H, Khan A (2018) Delineation of groundwater potential zones using GIS and multi influence factor (MIF) techniques: a study of district Swat, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa. Pakistan Environ Earth Sci 77:367. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12665-018-7522-3
Patra S, Mishra P, Mahapatra S (2018) Delineation of groundwater potential zone for sustainable development: a case study from Ganga Alluvial Plain covering Hooghly district of India using remote sensing, geographic information system and analytic hierarchy process. J Clean Prod 172:2485–2502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.11.161
Pinto D, Shrestha S, Babel M, Ninsawat S (2017) Delineation of groundwater potential zones in the Comoro watershed, Timor Leste using GIS, remote sensing and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) technique. Appl Water Sci 7:503–519. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13201-015-0270-6
Rahmati O, Nazari SA, Mahdavi M, Pourghasemi HR, Zeinivand H (2015) Groundwater potential mapping at Kurdistan region of Iran using analytic hierarchy process and GIS. Arab J Geosci 8:7059–7071. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12517-014-1668-4
Raju R, Raju G, Rajasekhar M (2019) Identification of groundwater potential zones in Mandavi River basin, Andhra Pradesh, India using remote sensing. GIS and MIF Tech Hydro Res 2:1–11. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.hydres.2019.09.001
Saaty RW (1987) The analytic hierarchy process-what it is and how it is used. Math Model 9:161–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/0270-0255(87)90473-8
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48:9–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/0377-2217(90)90057-I
Saaty TL (2008) Decision making with the analytic hierarchy process. Int J Serv Sci 1(1):83–98. https://doi.org/10.1504/IJSSCI.2008.017590
Shekhar S, Pandey AC (2015) Delineation of groundwater potential zone in hard rock terrain of India using remote sensing, geographical information system (GIS) and analytic hierarchy process (AHP) techniques. Geocarto Int 30:402–421. https://doi.org/10.1080/10106049.2014.894584
Yeh H, Cheng Y, Lin H, Lee C (2016) Mapping groundwater recharge potential zone using a GIS approach in Hualian River. Taiwan Sustain Environ Res 26:33–43. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.serj.2015.09.005
Funding
No funding was obtained for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
The author contributed to the study conception, design, material preparation, data collection and analysis. The first draft of the manuscript was written by Dr. S. K. Ray. The author read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that there is no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper. The author has no conflicts of interest to declare.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Shahid Hussain.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Ray, S.K. Identifying the groundwater potential zones in Jamsholaghat sub-basin by considering GIS and multi-criteria decision analysis. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 21, 515–540 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04923-8
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-023-04923-8