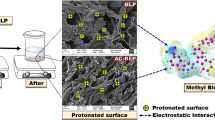
Abstract
In this study, the use of banana peels (BP) as a biosorbent which is considered agricultural waste for boron adsorption was investigated. The important operating parameters (pH, biosorbent dose, and contact time) affecting the batch adsorption system were examined. As a result of the conducted experiments, it was determined that the BP dose was 2 g/L, the initial pH was 6.07, and the contact time was 30 min. The maximum boron removal efficiency was achieved at approximately 66% under these conditions. In addition, different isotherms and kinetics were applied in this study. The R2 values of the pseudo-second-order kinetic model and the Freundlich isotherm were determined as 0.9694 and 0.9703, respectively. The maximum adsorption capacity of BP was calculated as 3.40 mg/g according to isotherms. SEM and FTIR analyses were performed to reveal the morphological and functional status of BP. The BP has a non-homogeneous macropores surface and predominantly hydroxyl (–OH), carboxyl (C–C), and amine (N–H) groups. As a result of the study, it was revealed that BP was an environmentally friendly, economical, and easily available biosorbent for boron removal.
Graphical abstract











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adetuyi BO, Ogundipe AE, Ogunlana OO, Egbuna C, Estella OU, Mishra AP, Akram M, Achar RR (2022) Banana peel as a source of nutraceuticals. In: Egbuna C, Sawicka B, Khan J (eds) Food and agricultural byproducts as important source of valuable nutraceuticals, 1st edn. Springer, Switzerland, pp 243–250
Ajmani A, Shahnaz T, Subbiah S, Narayanasamy S (2019) Hexavalent chromium adsorption on virgin, biochar, and chemically modified carbons prepared from Phanera vahlii fruit biomass: equilibrium, kinetics, and thermodynamics approach. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:32137–32150. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-06335-z
Akpomie KG, Conradie J (2020) Banana peel as a biosorbent for the decontamination of water pollutants. Rev Environ Chem Lett 18:1085–1112. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10311-020-00995-x
Akter M, Rahman FBA, Abedin MZ, Kabir SMF (2021) Adsorption characteristics of banana peel in the removal of dyes from textile effluent. Textiles 1:361–375. https://doi.org/10.3390/textiles1020018
Al-Ghouti MA, Al-Absi RS (2020) Mechanistic understanding of the adsorption and thermodynamic aspects of cationic methylene blue dye onto cellulosic olive stones biomass from wastewater. Sci Rep 10:15928. https://doi.org/10.1038/s41598-020-72996-3
Al-Ghouti MA, Salih NR (2018) Application of eggshell wastes for boron remediation from water. J Mol Liq 256:599–610. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.02.074
Alzate Acevedo S, Díaz Carrillo ÁJ, Flórez-López E, Grande-Tovar CD (2021) Recovery of banana waste-loss from production and processing: a contribution to a circular economy. Molecules 26:5282. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26175282
Ameri A, Tamjidi S, Dehghankhalili F, Farhadi A, Saati MA (2020) Application of algae as low cost and effective bio-adsorbent for removal of heavy metals from wastewater: a review study. Environ Technol Rev 9:85–110. https://doi.org/10.1080/21622515.2020.1831619
Babiker E, Al-Ghouti MA, Zouari N, McKay G (2019) Removal of boron from water using adsorbents derived from waste tire rubber. J Environ Chem Eng 7:102948. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2019.102948
Bai S, Han J, Du C, Li J, Ding W (2020) Removal of boron and silicon by a modified resin and their competitive adsorption mechanisms. Environ Sci Pollut Res 27:30275–30284. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-020-09308-9/Published
Bhagyaraj S, Al-Ghouti MA, Kasak P, Krupa I (2021) An updated review on boron removal from water through adsorption processes. Emerg Mater 4:1167–1186. https://doi.org/10.1007/s42247-021-00197-3/Published
Bilal M, Ihsanullah I, Younas M, Ul Hassan Shah M (2022) Recent advances in applications of low-cost adsorbents for the removal of heavy metals from water: a critical review. Sep Purif Technol 278:119510. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2021.119510
Çatlıoğlu F, Akay S, Turunç E, Gözmen B, Anastopoulos I, Kayan B, Kalderis D (2021) Preparation and application of Fe-modified banana peel in the adsorption of methylene blue: process optimization using response surface methodology. Environ Nanotechnol Monit Manag 16:100517. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enmm.2021.100517
Çelebi H (2020) Boron adsorption capacity of natural pumpkin seed shell. BEU J Sci 9:1698–1710
Chorghe D, Sari MA, Chellam S (2017) Boron removal from hydraulic fracturing wastewater by aluminum and iron coagulation: mechanisms and limitations. Water Res 126:481–487. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2017.09.057
Chruszcz-Lipska K, Winid B, Madalska GA, Macuda J, Łukánko Ł (2021) High content of boron in curative water: from the spa to industrial recovery of borates? (Poland as a case study). Minerals 11:8. https://doi.org/10.3390/min
Dahiru M, Uba Zango Z, Haruna MA (2018) Cationic dyes removal using low-cost banana peel biosorbent. Am J Mater Sci 8:32–38. https://doi.org/10.5923/j.materials.20180802.02
Demey H, Barron-Zambrano J, Mhadhbi T, Miloudi H, Yang Z, Ruiz M, Sastre AM (2019) Boron removal from aqueous solutions by using a novel alginate-based sorbent: comparison with Al2O3 particles. Polymers (basel) 11:1509. https://doi.org/10.3390/polym11091509
Deshmukh PD, Khadse GK, Shinde VM, Labhasetwar P (2017) Cadmium removal from aqueous solutions using dried banana peels as an adsorbent: kinetics and equilibrium modeling. J Bioremediation Biodegrad 08:1000395. https://doi.org/10.4172/2155-6199.1000395
Dubinin MM, Radushkevich LV (1947) Equation of the characteristic curve of activated charcoal proceedings of the academy of sciences. Phys Chem Sect USSR 55:331–333
Duran H, Yavuz E, Sismanoglu T, Senkal BF (2019) Functionalization of gum arabic including glycoprotein and polysaccharides for the removal of boron. Carbohydr Polym 225:115139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115139
El Barnossi A, Moussaid F, Iraqi Housseini A (2021) Tangerine, banana and pomegranate peels valorisation for sustainable environment: a review. Biotechnol Rep 29:e00574. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.btre.2020.e00574
Eryildiz B, Yuksekdag A, Korkut S, Zeytuncu B, Pasaoglu ME, Koyuncu I (2020) Effect of operating parameters on removal of boron from wastewater containing high boron concentration by vacuum assisted air gap membrane distillation. J Water Process Eng 38:101579. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jwpe.2020.101579
Fabre E, Vale C, Pereira E, Silva CM (2019) Experimental measurement and modeling of Hg(II) removal from aqueous solutions using eucalyptus globulus bark: effect of pH, salinity and biosorbent dosage. Int J Mol Sci 20:5973. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20235973
Fabre E, Lopes CB, Vale C, Pereira E, Silva CM (2020) Valuation of banana peels as an effective biosorbent for mercury removal under low environmental concentrations. Sci Total Environ 709:135883. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135883
FAOSTAT (2020) Food and agricultural organization (FAO). https://www.fao.org/faostat/en/#home
Freundlich HMF (1906) Uber die adsorption in lasungen. J Phys Chem 57:370–385
Gkika D, Mitropoulos AC, Kyzas GZ (2022) Why reuse spent adsorbents? The latest challenges and limitations. Sci Total Environ 822:153612. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2022.153612
Goren AY, Okten HE (2021) Energy production from treatment of industrial wastewater and boron removal in aqueous solutions using microbial desalination cell. Chemosphere 285:131370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131370
Hall KR, Eagleton LC, Acrivos A, Vermeulen T (1966) Pore- and solid-diffusion kinetics in fixed-bed adsorption under constant-pattern conditions. Ind Eng Chem Fundam 5:212–223. https://doi.org/10.1021/i160018a011
Hikal WM, Said-Al Ahl HAH, Tkachenko KG, Sharifi-Rad J, Kacaniova M, Elhourri M, Atanassova M (2022) Banana peels: a waste treasure for human being. Evid-Bades Compl Alt 2022:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1155/2022/7616452
Ho Y-S (2006) Review of second-order models for adsorption systems. J Hazard Mater 136:681–689. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2005.12.043
Jarma YA, Çermikli E, İpekçi D, Altıok E, Kabay N (2021) Comparison of two electrodialysis stacks having different ion exchange and bipolar membranes for simultaneous separation of boron and lithium from aqueous solution. Desalination 500:114850. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2020.114850
Kabay N, Köseoğlu P, Yavuz E, Yüksel Ü, Yüksel M (2013) An innovative integrated system for boron removal from geothermal water using RO process and ion exchange-ultrafiltration hybrid method. Desalination 316:1–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2013.01.020
Kayranli B, Gok O, Yilmaz T, Gok G, Celebi H, Seckin IY, Kalat D (2021) Zinc removal mechanisms with recycled lignocellulose: from fruit residual to biosorbent then soil conditioner. Water Air Soil Pollut 232:311. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-021-05260-7
Khairiah K, Frida E, Sebayang K, Sinuhaji P, Humaidi S (2021) Data on characterization, model, and adsorption rate of banana peel activated carbon (Musa Acuminata) for adsorbents of various heavy metals (Mn, Pb, Zn, Fe). Data Br 39:107611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.dib.2021.107611
Kluczka J, Gnus M, Dudek G, Turczyn R (2017) Removal of boron from aqueous solution by composite chitosan beads. Sep Sci Technol 52:1559–1571. https://doi.org/10.1080/01496395.2017.1290659
Kluczka J, Tórz A, Łącka D, Kazek-Kęsik A, Adamek J (2018) Boron removal by adsorption on cobalt(ii) doped chitosan bio-composite. J Polym Environ 26:2039–2048. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10924-017-1099-x
Kluczka J, Dudek G, Kazek-Kęsik A, Gnus M (2019a) Chitosan hydrogel beads supported with ceria for boron removal. Int J Mol Sci 20:1567. https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms20071567
Kluczka J, Pudło W, Krukiewicz K (2019b) Boron adsorption removal by commercial and modified activated carbons. Chem Eng Res Des 147:30–42. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2019.04.021
Kluczka J, Dudek G, Pudło W, Kazek-Kęsik A, Turczyn R (2021) Boron removal by sorption on modified chitosan hydrogel beads. Materials (basel) 14:5646. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14195646
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. Solids J Am Chem Soc 38:2221–2295. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02268a002
Lavanya KM, Florence JAK, Vivekanandan B, Lakshmipathy R (2021) Comparative investigations of raw and alkali metal free banana peel as adsorbent for the removal of Hg2+ ions. Mater Today Proc Article Press. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2021.07.410
Le N-D, Trogen M, Varley RJ, Hummel M, Byrne N (2021) Effect of boric acid on the stabilisation of cellulose-lignin filaments as precursors for carbon fibres. Cellulose 28:729–739. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10570-020-03584-x
Lin J-Y, Mahasti NNN, Huang Y-H (2021) Recent advances in adsorption and coagulation for boron removal from wastewater: a comprehensive review. J Hazard Mater 407:124401. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.124401
Liu X, Bouxin FP, Fan J, Budarin VL, Hu C, Clark JH (2020) Recent advances in the catalytic depolymerization of lignin towards phenolic chemicals: a review. Chem Sus Chem 13:4296–4317. https://doi.org/10.1002/cssc.202001213
Madeła M, Skuza M (2021) Towards a circular economy: analysis of the use of biowaste as biosorbent for the removal of heavy metals. Energies 14:5427. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14175427
Masindi V, Gitari MW, Tutu H, Debeer M (2016) Removal of boron from aqueous solution using magnesite and bentonite clay composite. Desalin Water Treat 57:8754–8764. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2015.1025849
Melliti A, Kheriji J, Bessaies H, Hamrouni B (2020) Boron removal from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from palm bark: kinetic, isotherms, optimisation and breakthrough curves modeling. Water Sci Technol 81:321–332. https://doi.org/10.2166/wst.2020.107
Negroiu M, Țurcanu AA, Matei E, Râpă M, Covaliu CI, Predescu AM, Pantilimon CM, Coman G, Predescu C (2021) Novel adsorbent based on banana peel waste for removal of heavy metal ions from synthetic solutions. Materials (basel) 14:3946. https://doi.org/10.3390/ma14143946
Nurain A, Sarker P, Rahaman MS, Rahman MM, Uddin MK (2021) Utilization of banana (musa sapientum) peel for removal of Pb2+ from aqueous solution. J Multidiscip Appl Nat Sci 1:117–128. https://doi.org/10.47352/jmans.v1i2.89
Ogunlalu O, Oyekunle IP, Iwuozor KO, Aderibigbe AD, Emenike EC (2021) Trends in the mitigation of heavy metal ions from aqueous solutions using unmodified and chemically-modified agricultural waste adsorbents. Curr Res Green Sustain Chem 4:100188. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.crgsc.2021.100188
Osorio LLDR, Flórez-López E, Grande-Tovar CD (2021) The potential of selected agri-food loss and waste to contribute to a circular economy: applications in the food, cosmetic and pharmaceutical industries. Molecules 26:515. https://doi.org/10.3390/molecules26020515
Pan J, Gao B, Guo K, Gao Y, Xu X, Yue Q (2022) Insights into selective adsorption mechanism of copper and zinc ions onto biogas residue-based adsorbent: theoretical calculation and electronegativity difference. Sci Total Environ 805:150413. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.150413
Patra C, Medisetti RMN, Pakshirajan K, Narayanasamy S (2019) Assessment of raw, acid-modified and chelated biomass for sequestration of hexavalent chromium from aqueous solution using Sterculia villosa Roxb. Shells. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:23625–23637. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05582-4
Pereira MAF, Cesca K, Poletto P, de Oliveira D (2021) New perspectives for banana peel polysaccharides and their conversion to oligosaccharides. Food Int 149:110706. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodres.2021.110706
Piol MN, Dickerman C, Ardanza MP, Saralegui A, Boeykens SP (2021) Simultaneous removal of chromate and phosphate using different operational combinations for their adsorption on dolomite and banana peel. J Environ Manag 288:112463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.112463
Scelsi E, Angelini A, Pastore C (2021) Deep eutectic solvents for the valorisation of lignocellulosic biomasses towards fine chemicals. Biomass 1:29–59. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomass1010003
Semerjian L (2018) Removal of heavy metals (Cu, Pb) from aqueous solutions using pine (Pinus halepensis) sawdust: equilibrium, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies. Environ Technol Innov 12:91–103. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2018.08.005
Sen E, Özdemir S, Uğuzdoğan E (2021) Extraction and characterization of pectin from waste of fruit peels. Pamukkale Univ J Eng Sci 27:863–872. https://doi.org/10.5505/pajes.2021.91033
Shawgi N, Li SX, Wang S (2017) A novel method of synthesis of high purity nano plated boron carbide powder by a solidstate reaction of poly (vinyl alcohol) and boric acid. Ceram Int 43:10554–10558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ceramint.2017.05.120
Sigiro M (2021) Natural biowaste of banana peel-derived porous carbon for in-vitro antibacterial activity toward Escherichia coli. Ain Shams Eng J 12:4157–4165. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2021.03.021
Stavrinou A, Aggelopoulos CA, Tsakiroglou CD (2018) Exploring the adsorption mechanisms of cationic and anionic dyes onto agricultural waste peels of banana, cucumber and potato: Adsorption kinetics and equilibrium isotherms as a tool. J Environ Chem Eng 6:6958–6970. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.063
Tejada-Tovar C, Gonzalez-Delgado AD, Villabona-Ortiz A (2019) Characterization of residual biomasses and its application for the removal of lead ions from aqueous solution. Appl Sci 9:4486. https://doi.org/10.3390/app9214486
Temkin MJ, Pyzhev V (1940) Recent modifications to langmuir isotherms, acta physical chemistry. Acta Phys Chem 12:217–225
Tibolla H, Pelissari FM, Martins JT, Vicente AA, Menegalli FC (2018) Cellulose nanofibers produced from banana peel by chemical and mechanical treatments: characterization and cytotoxicity assessment. Food Hydrocoll 75:192–201. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodhyd.2017.08.027
Tulun Ş, Akgül G, Alver A, Çelebi H (2021) Adaptive neuro-fuzzy interference system modelling for chlorpyrifos removal with walnut shell biochar. Arab J Chem 14:103443. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.arabjc.2021.103443
Türker OC, Yakar A, Gür N (2017) Bioaccumulation and toxicity assessment of irrigation water contaminated with boron (B) using duckweed (Lemna gibba L.) in a batch reactor system. J Hazard Mater 324:151–159. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.10.044
Türker OC, Yakar A, Türe C, Saz Ç (2019) Cost-effectiveness of boron (B) removal from irrigation water: an economic water treatment model (EWTM) for farmers to prevent boron toxicity. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:18777–18789. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-019-05268-x
Uddin KMA, Ago M, Rojas OJ (2017) Hybrid films of chitosan, cellulose nanofibrils and boric acid: flame retardancy, optical and thermo-mechanical properties. Carbohyd Poly 177:108589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.08.116
Van Eynde E, Mendez JC, Hiemstra T, Comans RNJ (2020) Boron adsorption to ferrihydrite with implications for surface speciation in soils: experiments and modeling. ACS Earth Sp Chem 4:1269–1280. https://doi.org/10.1021/acsearthspacechem.0c00078
Yang J, Tu J, Liu H, Wen L, Jiang Y, Yang B (2019) Identification of an immunostimulatory polysaccharide in banana. Food Chem 277:46–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.foodchem.2018.10.043
Zhang J, Cai Y, Liu K (2019) Extremely effective boron removal from water by stable metal organic framework ZIF-67. Ind Eng Chem Res 58:4199–4207. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.iecr.8b05656
Zhang J, Koubaa A, Xing D, Liu W, Wang Q, Wang X, Wang H (2020) Improving lignocellulose thermal stability by chemical modification with boric acid for incorporating into polyamide. Mater Des 191:108589. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matdes.2020.108589
Acknowledgements
This research study was undertaken in the Wastewater Laboratory at Aksaray University Engineering Faculty Environmental Engineering Department, Aksaray, Turkey. I am grateful for the help, feedback, comments, and advice provided by the International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology editors and referees.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
HC helped in conceptualization, investigation, methodology, resources, validation, IS was involved in data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology, writing—review and editing. TB performed data curation, formal analysis, investigation, resources, validation, visualization, writing—review and editing. ST contributed to data curation, formal analysis, investigation, methodology.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Çelebi, H., Şimşek, İ., Bahadir, T. et al. Use of banana peel for the removal of boron from aqueous solutions in the batch adsorption system. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 161–176 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04566-1
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04566-1