Abstract
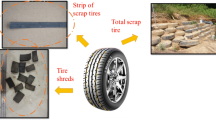
Rammed earth is known as a sustainable construction method due to its low energy consumption. Recently, environmental awareness has led to reduced energy consumption by using recycled materials. Moreover, end-of-life materials are causing environmental pollution. Tires are one of the most widely used materials by humans, and used tires result in remarkable pollution at the end of their life. Five series of rammed earth specimens with dimensions of 600 × 600 × 150 mm were constructed for the current experiments. The first was unstabilized rammed earth without the additive mixture and acted as the reference material. The second was an 8% cement-added. In addition to 8% cement, 2% and 4% waste tire textile fibers were added to the third and fourth, respectively. Finally, the fifth included a mixture of soil and 4% tire fibers without any cement addition. The specimens were tested according to the ASTM-E519 standard, as the diagonal shear behavior under compressive pressure in a particular loading system was developed for this research.The addition of cement increased the shear strength by more than 100% and reduced the ductility. In contrast, the use of tire fibers increased the ductility of the specimens. Failure patterns of diagonal tension were observed in the form of vertical cracks. In the samples without cement, in addition to vertical cracks, other cracks developed in the direction of compacted soil layers. Using tire fibers to reinforce rammed earth and improve its stabilization with cement can result in sustainable constructions with improved structural behavior and proper disposal of end-of-life tires.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abbaspour M, Aflaki E, Nejad FM (2019) Reuse of waste tire textile fibers as soil reinforcement. J Cleaner Prod 207:1059–1071. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.09.253
Abhilash HN, Walker P, Venkatarama Reddy BV et al (2020) Compressive strength of novel alkali-activated stabilized earth materials incorporating solid wastes. J Mater Civ Eng 32:04020118. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0003188
Alamo-Nole LA, Perales-Perez O, Roman-Velazquez FR (2011) Sorption study of toluene and xylene in aqueous solutions by recycled tires crumb rubber. J Hazard Mater 185:107–111. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.09.003
Alsheyab MAT (2021) Recycling of construction and demolition waste and its impact on climate change and sustainable development. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03217-1
Anggraini V, Asadi A, Farzadnia N et al (2016) Reinforcement Benefits of Nanomodified Coir Fiber in Lime-Treated Marine Clay. J Mater Civ Eng 28:06016005. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0001516
Araya-Letelier G, Concha-Riedel J, Antico FC et al (2018) Influence of natural fiber dosage and length on adobe mixes damage-mechanical behavior. Constr Build Mater 174:645–655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.04.151
Arrigoni A, Grillet AC, Pelosato R et al (2017) Reduction of rammed earth’s hygroscopic performance under stabilisation: an experimental investigation. Build Environ 115:358–367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.buildenv.2017.01.034
Arslan ME, Emiroğlu M, Yalama A (2017) Structural behavior of rammed earth walls under lateral cyclic loading: A comparative experimental study. Constr Build Mater 133:433–442. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.093
ASTM D5591 (2004) Standard Test Method for Thermal Shrinkage Force of Yarn and Cord With a Thermal. Am Soc Test Mater i:2–5
ASTM E 519-02 (2002) Standard Test Method for Diagonal Tension (Shear) in Masonry Assemblages. Am Soc Test Mater 5
ASTM-D885 (2003) Standard Test Methods for Tire Cords , Tire Cord Fabrics , and Industrial Filament Yarns Made from Manufactured Organic-Base Fibers 1. Am Soc Test Mater 1–39
Belabdelouahab F, Trouzine H (2014) Research and enhancement of used tyres, such as material innovative in Algeria. Phys Procedia 55:68–74. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.phpro.2014.07.011
Bernat-Maso E, Gil L, Escrig C (2016) Textile-reinforced rammed earth: Experimental characterisation of flexural strength and thoughness. Constr Build Mater 106:470–479. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.139
Bui QB, Morel JC, Hans S, Meunier N (2009) Compression behaviour of non-industrial materials in civil engineering by three scale experiments: The case of rammed earth. Mater Struct Constr 42:1101–1116. https://doi.org/10.1617/s11527-008-9446-y
Bušić R, Miličević I, Šipoš TK, Strukar K (2018) Recycled rubber as an aggregate replacement in self-compacting concrete-literature overview. Materials (basel). https://doi.org/10.3390/ma11091729
Correia AAS, Venda Oliveira PJ, Custódio DG (2015) Effect of polypropylene fibres on the compressive and tensile strength of a soft soil, artificially stabilised with binders. Geotext Geomembranes 43:97–106. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geotexmem.2014.11.008
Das S, Subudhi S (2021) A review on different methodologies to study thermal comfort. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03210-8
Fagone M, Loccarini F, Ranocchiai G (2017) Strength evaluation of jute fabric for the reinforcement of rammed earth structures. Compos Part B Eng 113:1–13. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.12.054
Gagliano A, Patania F, Nocera F, Signorello C (2014) Assessment of the dynamic thermal performance of massive buildings. Energy Build 72:361–370. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enbuild.2013.12.060
Hussaini SMS, Toufigh V (2019) Strength and Fracture Behavior of Rammed-Earth Materials. J Mater Civ Eng 31:04019228. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0002876
Ip K, Miller A (2009) Thermal behaviour of an earth-sheltered autonomous building - The Brighton Earthship. Renew Energy 34:2037–2043. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2009.02.006
Irfan M, Siddiqui M, Bashir F et al (2020) Efficient removal of hydrogen sulfide from wastewater using waste-tire-derived rubber particles. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:3515–3524. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02724-x
Jairaj C, Prathap Kumar MT, Raghunandan ME (2018) Compaction characteristics and strength of BC soil reinforced with untreated and treated coir fibers. Innov Infrastruct Solut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s41062-017-0123-2
Jalal FE, Yongfu Xu, Jamhiri B, Memon SA (2020) On the recent trends in expansive soil stabilization using calcium-based stabilizer materials (CSMs): a comprehensive review. Adv Mater Sci Eng 2020:1–23. https://doi.org/10.1155/2020/1510969
Jayasinghe C, Fonseka WMCDJ, Abeygunawardhene YM (2016) Load bearing properties of composite masonry constructed with recycled building demolition waste and cement stabilized rammed earth. Constr Build Mater 102:471–477. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.10.136
Kariyawasam KKGKD, Jayasinghe C (2016) Cement stabilized rammed earth as a sustainable construction material. Constr Build Mater 105:519–527. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2015.12.189
Kosarimovahhed M, Toufigh V (2020) Sustainable usage of waste materials as stabilizer in rammed earth structures. J Clean Prod 277:123279. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.123279
Koutous A, Hilali E (2021) Reinforcing rammed earth with plant fibers: A case study. Case Stud Constr Mater 14:e00514. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00514
Kylili A, Fokaides PA (2016) Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) of Phase Change Materials (PCMs) for building applications: A review. J Build Eng 6:133–143. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2016.02.008
Landi D, Gigli S, Germani M, Marconi M (2018) Investigating the feasibility of a reuse scenario for textile fibres recovered from end-of-life tyres. Waste Manag 75:187–204. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2018.02.018
Lepakshi R, Venkatarama Reddy BV (2020) Shear strength parameters and Mohr-Coulomb failure envelopes for cement stabilised rammed earth. Constr Build Mater 249:118708. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118708
Miccoli L, Müller U, Fontana P (2014) Mechanical behaviour of earthen materials: A comparison between earth block masonry, rammed earth and cob. Constr Build Mater 61:327–339. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.03.009
Minke G (2000) Earth construction handbook: the building material earth in modern architecture
Mollaei S, Amidpour M, Sharifi M (2019) Analysis and development of conceptual model of low-carbon city with a sustainable approach. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:6019–6028. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1989-z
Mucsi G, Szenczi Á, Nagy S (2018) Fiber reinforced geopolymer from synergetic utilization of fly ash and waste tire. J Clean Prod 178:429–440. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2018.01.018
Mukherjee K, Mishra AK (2017) The Impact of Scrapped Tyre Chips on the Mechanical Properties of Liner Materials. Environ Process 4:219–233. https://doi.org/10.1007/s40710-017-0210-6
Narani SS, Zare P, Abbaspour M et al (2021) Evaluation of fiber-reinforced and cement-stabilized rammed-earth composite under cyclic loading. Constr Build Mater 296:123746. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123746
Nouri H, Safehian M, Mir Mohammad Hosseini SM (2021) Life cycle assessment of earthen materials for low-cost housing a comparison between rammed earth and fired clay bricks. Int J Build Pathol Adapt Ahead-of-p: https://doi.org/10.1108/IJBPA-02-2021-0021
Oquendo-Di Cosola V, Olivieri F, Ruiz-García L, Bacenetti J (2020) An environmental Life Cycle Assessment of Living Wall Systems. J Environ Manage 254:109743. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2019.109743
Pavan GS, Ullas SN, Nanjunda Rao KS (2020a) Interfacial behavior of cement stabilized rammed earth: Experimental and numerical study. Constr Build Mater 257:119327. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119327
Pavan GS, Ullas SN, Nanjunda Rao KS (2020b) Shear behavior of cement stabilized rammed earth assemblages. J Build Eng 27:100966. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jobe.2019.100966
Ramirez GGD, Casagrande MDT, Folle D et al (2015) Behavior of granular rubber waste tire reinforced soil for application in geosynthetic reinforced soil wall. Rev IBRACON Estruturas e Mater 8:567–576. https://doi.org/10.1590/s1983-41952015000400009
Rashad AM (2016) A comprehensive overview about recycling rubber as fine aggregate replacement in traditional cementitious materials. Int J Sustain Built Environ 5:46–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijsbe.2015.11.003
Sabeen AH, Kamaruddin SNB, Noor ZZ (2019) Environmental impacts assessment of industrial wastewater treatment system using electroless nickel plating and life cycle assessment approaches. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:3171–3182. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1974-6
Sameh SH (2014) Promoting earth architecture as a sustainable construction technique in Egypt. J Clean Prod 65:362–373. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2013.08.046
Serrano S, Rincón L, González B et al (2017) Rammed earth walls in Mediterranean climate: Material characterization and thermal behaviour. Int J Low-Carbon Technol 12:281–288. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctw022
Shenal Jayawardane V, Anggraini V, Emmanuel E et al (2020) Expansive and Compressibility Behavior of Lime Stabilized Fiber-Reinforced Marine Clay. J Mater Civ Eng 32:04020328. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)mt.1943-5533.0003430
Walker P, Keable R, Martin J, Maniatidis V (2005) Rammed earth: design and construction guidelines
Zare P, Sheikhi Narani S, Abbaspour M et al (2020) Experimental investigation of non-stabilized and cement-stabilized rammed earth reinforcement by Waste Tire Textile Fibers (WTTFs). Constr Build Mater 260:120432. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120432
Zhou T, Zhang Z, Su Z, Tian P (2021) Seismic performance test of rammed earth wall with different structural columns. Adv Struct Eng 24:107–118. https://doi.org/10.1177/1369433220944506
Acknowledgments
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with any financial interest (such as honoraria; educational grants; participation in speakers’ bureaus; membership, employment, consultancies, stock ownership, or other equity interest; and expert testimony or patent-licensing arrangements), or non-financial interest (such as personal or professional relationships, affiliations, knowledge, or beliefs) in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
About this article
Cite this article
Nouri, H., Safehian, M. & Hosseini, S.M.M.M. Rammed earth structures reinforced by waste tire textile fibers as an attempt to reduce the environmental impacts. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 437–450 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04534-9
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04534-9