Abstract
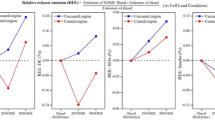
In the present scenario, the fast depletion of fossil fuels and energy crises motivated the researchers towards finding an alternative sources for energy. In this work, the performance, combustion and emission of hydrothermally synthesized (ZnO) nanoparticles-dispersed used sunflower oil methyl ester in a single-cylinder, four-stroke, direct injection diesel engine with eddy current dynamometer was investigated. The synthesized ZnO nanoparticles were characterized by X-ray diffraction, Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy, scanning electron microscopy and energy-dispersive X-ray spectroscopy to find crystallinity, functional groups, surface morphology and elemental composition. Used sunflower oil methyl ester was produced via conventional one-step alkali catalyst trans-esterification process. Test fuels were prepared with the dispersion of ZnO nanoparticles in the concentration of 10 ppm, 20 ppm and 30 ppm with B20 (20% used sunflower oil methyl ester and 80% diesel) with the aid of magnetic stirrer and ultra-sonication. The test results exposed that the addition of ZnO nanoparticles with B20 gave a better performance in terms of brake thermal efficiency and brake specific fuel consumption compared to B20. The addition of ZnO nanoparticles with 30 ppm concentration was identified as better fuel among all tested fuels. The addition of 30 ppm of ZnO nanoparticles with B20 records 1.78% increases in brake thermal efficiency and 10.34% decreases in brake specific fuel consumption. The emission like CO, HC and smoke was 20%, 15.4% and 17.39% lower than diesel. On the other hand, NOx was slightly higher than diesel but lower than B20.


















Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ZnO:
-
Zinc oxide
- ppm:
-
Parts per million
- BTE:
-
Brake thermal efficiency
- BSFC:
-
Brake specific fuel consumption
- CO:
-
Carbon monoxide
- CO2 :
-
Carbon dioxide
- UHC:
-
Unburned hydrocarbon
- NOx:
-
Oxides of nitrogen
- CA:
-
Crank angle
- MFB:
-
Mass fraction burned
- TDC:
-
Top dead centre
- XRD:
-
X-ray diffraction
- FTIR- Spectroscopy:
-
Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy
- SEM:
-
Scanning electron microscope
- TEM:
-
Transmission electron microscope
- EDX- Spectroscopy:
-
Energy dispersive X-ray spectroscopy
References
Abed KA, El Morsi AK, Sayed MM et al (2018) Effect of waste cooking-oil biodiesel on performance and exhaust emissions of a diesel engine. Egypt J Pet 27:985–989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejpe.2018.02.008
Afshari F, Afshari H, Afshari F, Ghasemi Zavaragh H (2018) The effects of nanofilter and nanoclay on reducing pollutant emissions from rapeseed biodiesel in a diesel engine. Waste Biomass Valorization 9:1655–1667. https://doi.org/10.1007/s12649-017-9913-1
Ağbulut Ü, Gürel AE, Sarıdemir S (2021) Experimental investigation and prediction of performance and emission responses of a CI engine fuelled with different metal-oxide based nanoparticles–diesel blends using different machine learning algorithms. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119076
Ahmed A, Shah AN, Azam A et al (2020) Environment-friendly novel fuel additives: investigation of the effects of graphite nanoparticles on performance and regulated gaseous emissions of CI engine. Energy Convers Manag. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2020.112748
Aldhaidhawi M, Chiriac R, Badescu V (2017) Ignition delay, combustion and emission characteristics of Diesel engine fueled with rapeseed biodiesel—a literature review. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 73:178–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2017.01.129
Ameen S, Akhtar MS, Shin HS (2015) Spindles shaped ZnO modified glassy carbon electrode for the selective monitoring of piperidine. Mater Lett 148:188–191. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matlet.2015.02.049
Anchupogu P, Rao LN, Banavathu B (2018) Effect of alumina nano additives into biodiesel-diesel blends on the combustion performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine with exhaust gas recirculation. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:23294–23306. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2366-7
Ashok B, Nanthagopal K, Mohan A et al (2017) Comparative analysis on the effect of zinc oxide and ethanox as additives with biodiesel in CI engine. Energy 140:352–364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2017.09.021
Bomila R, Suresh S, Srinivasan S (2019) Synthesis, characterization and comparative studies of dual doped ZnO nanoparticles for photocatalytic applications. J Mater Sci Mater Electron 30:582–592. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10854-018-0324-2
Cao Y, Chen TT, Wang W et al (2017) Construction and functional assessment of zein thin film incorporating spindle-like ZnO crystals. RSC Adv 7:2180–2185. https://doi.org/10.1039/c6ra25290g
Chacko N, Jeyaseelan T (2020) Comparative evaluation of graphene oxide and graphene nanoplatelets as fuel additives on the combustion and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fuelled with diesel and biodiesel blend. Fuel Process Technol. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuproc.2020.106406
Chandrasekaran V, Arthanarisamy M, Nachiappan P et al (2016) The role of nano additives for biodiesel and diesel blended transportation fuels. Transp Res Part D Transp Environ 46:145–156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trd.2016.03.015
Cooney CP, Yeliana WJJ, Naber JD (2009) Combustion characterization in an internal combustion engine with ethanol—gasoline blended fuels varying compression ratios and ignition timing. Energy Fuels 23:2319–2324. https://doi.org/10.1021/ef800899r
Deepak Kumar T, Hussain SS, Ramesha DK (2019) Effect of a zinc oxide nanoparticle fuel additive on the performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine fuelled with cotton seed biodiesel blends. Mater Today Proc 26:2374–2378. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matpr.2020.02.509
Devarajan Y, Mahalingam A, Munuswamy DB, Arunkumar T (2018a) Combustion, performance, and emission study of a research diesel engine fueled with palm oil biodiesel and its additive. Energy Fuels 32:8447–8452. https://doi.org/10.1021/acs.energyfuels.8b01125
Devarajan Y, Munuswamy DB, Mahalingam A (2018b) Influence of nano-additive on performance and emission characteristics of a diesel engine running on neat neem oil biodiesel. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:26167–26172. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2618-6
Devarajan Y, Munuswamy DB, Mahalingam A (2019) Investigation on behavior of diesel engine performance, emission, and combustion characteristics using nano-additive in neat biodiesel. Heat Mass Transf Und Stoffuebertragung 55:1641–1650. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00231-018-02537-2
Dhanarasu M, RameshKumar KA, Maadeswaran P (2021) Effect of acetone as an oxygenated additive with used sunflower oil biodiesel on performance, combustion and emission in diesel engine. Environ Technol (u k). https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2021.1931471
Dülger Z, Aslan S, Arici M et al (2014) Performance and emissions of a micro-turbine fueled with JP8-canola biodiesel mixtures. Proc ASME Turbo Expo. https://doi.org/10.1115/GT2014-27340
El-Seesy AI, Attia AMA, El-Batsh HM (2018) The effect of Aluminum oxide nanoparticles addition with Jojoba methyl ester-diesel fuel blend on a diesel engine performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Fuel 224:147–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.03.076
El-Seesy AI, Hassan H, Ookawara S (2018) Performance, combustion, and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with Jatropha methyl ester and graphene oxide additives. Energy Convers Manag 166:674–686. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.04.049
Elkelawy M, Alm-Eldin Bastawissi H, Esmaeil KK et al (2019) Experimental studies on the biodiesel production parameters optimization of sunflower and soybean oil mixture and DI engine combustion, performance, and emission analysis fueled with diesel/biodiesel blends. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.115791
Gad MS, Jayaraj S (2020) A comparative study on the effect of nano-additives on the performance and emissions of a diesel engine run on Jatropha biodiesel. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117168
Ganapathi A, Muralidharan K (2020) Impact of Indian geranium grass biodiesel blends on performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Int J Thermophys. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10765-020-02706-8
Hoseini SS, Najafi G, Ghobadian B et al (2020) Performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine using graphene oxide (GO) nano-particles additives in biodiesel-diesel blends. Renew Energy 145:458–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.06.006
Hosseini SE, Wahid MA (2012) Necessity of biodiesel utilization as a source of renewable energy in Malaysia. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 16:5732–5740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2012.05.025
Hosseinzadeh-Bandbafha H, Tabatabaei M, Aghbashlo M et al (2018) A comprehensive review on the environmental impacts of diesel/biodiesel additives. Energy Convers Manag 174:579–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.08.050
Hui A, Dong S, Kang Y et al (2019) Hydrothermal fabrication of spindle-shaped ZnO/palygorskite nanocomposites using nonionic surfactant for enhancement of antibacterial activity. Nanomaterials. https://doi.org/10.3390/nano9101453
Hussain F, Soudagar MEM, Afzal A et al (2020) Enhancement in combustion, performance, and emission characteristics of a diesel engine fueled with Ce-ZnO nanoparticle additive added to soybean biodiesel blends. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en13174578
Janakiraman S, Lakshmanan T, Chandran V, Subramani L (2020) Comparative behavior of various nano additives in a DIESEL engine powered by novel Garcinia gummi-gutta biodiesel. J Clean Prod. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.118940
Jasrotia A, Shukla AK, Kumar N (2020) Impact of nanoparticles on the performance and emissions of diesel engine using mahua biodiesel. Smart Innov Syst Technol 174:49–59. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-15-2647-3_5
Jiaqiang E, Zhang Z, Chen J et al (2018) Performance and emission evaluation of a marine diesel engine fueled by water biodiesel-diesel emulsion blends with a fuel additive of a cerium oxide nanoparticle. Energy Convers Manag 169:194–205. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2018.05.073
Jurčević M, Nižetić S, Arıcı M et al (2021) Thermal constant analysis of phase change nanocomposites and discussion on selection strategies with respect to economic constraints. Sustain Energy Technol Assess. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seta.2020.100957
Kim HY, Ge JC, Choi NJ (2019) Effects of fuel injection pressure on combustion and emission characteristics under low speed conditions in a diesel engine fueled with palm oil biodiesel. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en12173264
Klajn FF, Gurgacz F, Lenz AM et al (2020) Comparison of the emissions and performance of ethanol-added diesel–biodiesel blends in a compression ignition engine with those of pure diesel. Environ Technol (u k) 41:511–520. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1504122
Kumar MV, Babu AV, Kumar PR (2019a) Influence of metal-based cerium oxide nanoparticle additive on performance, combustion, and emissions with biodiesel in diesel engine. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:7651–7664. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-04075-0
Kumar S, Dinesha P, Rosen MA (2019b) Effect of injection pressure on the combustion, performance and emission characteristics of a biodiesel engine with cerium oxide nanoparticle additive. Energy 185:1163–1173. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2019.07.124
Manigandan S, Sarweswaran R, Booma Devi P et al (2020) Comparative study of nanoadditives TiO2, CNT, Al2O3, CuO and CeO2 on reduction of diesel engine emission operating on hydrogen fuel blends. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2019.116336
Nanthagopal K, Ashok B, Tamilarasu A et al (2017) Influence on the effect of zinc oxide and titanium dioxide nanoparticles as an additive with Calophyllum inophyllum methyl ester in a CI engine. Energy Convers Manag 146:8–19. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2017.05.021
Norhafana M, Noor MM, Sharif PM et al (2019) A review of the performance and emissions of nano additives in diesel fuelled compression ignition-engines. IOP Conf Ser Mater Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1088/1757-899X/469/1/012035
Palani Y, Devarajan C, Manickam D, Thanikodi S (2021) Performance and emission characteristics of biodiesel-blend in diesel engine: a review. Environ Eng Res. https://doi.org/10.4491/eer.2020.338
Prabhahar M, Deh Kiani MK, Bhaskar K et al (2019) Studies on pongamia oil methyl ester fueled direct injection diesel engine to increase efficiency and to reduce harmful emissions. Adv Biofuels Appl Technol Environ Sustain. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-08-102791-2.00009-X
Prabhu S, Pudukudy M, Sohila S et al (2018) Synthesis, structural and optical properties of ZnO spindle/reduced graphene oxide composites with enhanced photocatalytic activity under visible light irradiation. Opt Mater (amst) 79:186–195. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.optmat.2018.02.061
Prabu A (2018) Nanoparticles as additive in biodiesel on the working characteristics of a DI diesel engine. Ain Shams Eng J 9:2343–2349. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.asej.2017.04.004
Prabu A, Anand RB (2016) Emission control strategy by adding alumina and cerium oxide nano particle in biodiesel. J Energy Inst 89:366–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2015.03.003
Pudukudy M, Yaakob Z (2014) Simple chemical synthesis of novel ZnO nanostructures: role of counter ions. Solid State Sci 30:78–88. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.solidstatesciences.2014.02.008
Rajak U, Nashine P, Verma TN (2019) Assessment of diesel engine performance using spirulina microalgae biodiesel. Energy 166:1025–1036. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2018.10.098
Ramalingam S, Rajendran S (2019) Assessment of performance, combustion, and emission behavior of novel annona biodiesel-operated diesel engine. In: Advances in eco-fuels for a sustainable environment, pp 391–405
Rangabashiam D, Rathinam S, Subbiah G et al (2020) Emission behaviour studies on the cause of ZnO nanoparticle inclusion in neat biodiesel. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 42:1989–1996. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1604909
Ranjan A, Dawn SS, Jayaprabakar J et al (2018) Experimental investigation on effect of MgO nanoparticles on cold flow properties, performance, emission and combustion characteristics of waste cooking oil biodiesel. Fuel 220:780–791. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2018.02.057
Reang NM, Dey S, Debbarma B et al (2020) Experimental investigation on combustion, performance and emission analysis of 4-stroke single cylinder diesel engine fuelled with neem methyl ester-rice wine alcohol-diesel blend. Fuel. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2020.117602
Sabir S, Arshad M, Chaudhari SK (2014) Zinc oxide nanoparticles for revolutionizing agriculture: synthesis and applications. Sci World J. https://doi.org/10.1155/2014/925494
Sadhik Basha J (2018) Impact of carbon nanotubes and Di-Ethyl Ether as additives with biodiesel emulsion fuels in a diesel engine—An experimental investigation. J Energy Inst 91:289–303. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.joei.2016.11.006
Sajin JB, Pillai GO, Kesavapillai M, Varghese S (2019) Effect of nanoparticle on emission and performance characteristics of biodiesel. Int J Ambient Energy. https://doi.org/10.1080/01430750.2019.1611650
Saxena V, Kumar N, Saxena VK (2017) A comprehensive review on combustion and stability aspects of metal nanoparticles and its additive effect on diesel and biodiesel fuelled C.I. engine. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 70:563–588. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2016.11.067
Senthilkumar G, Sajin JB, Yuvarajan D, Arunkumar T (2020) Evaluation of emission, performance and combustion characteristics of dual fuelled research diesel engine. Environ Technol (u k) 41:711–718. https://doi.org/10.1080/09593330.2018.1509888
Shaheen I, Ahmad KS, Zequine C et al (2021) Facile ZnO-based nanomaterial and its fabrication as a supercapacitor electrode: synthesis, characterization and electrochemical studies. RSC Adv 11:23374–23384. https://doi.org/10.1039/D1RA04341B
Sivakumar M, ShanmugaSundaram N, Ramesh Kumar R, Syed Thasthagir MH (2018) Effect of aluminium oxide nanoparticles blended pongamia methyl ester on performance, combustion and emission characteristics of diesel engine. Renew Energy 116:518–526. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2017.10.002
Soudagar MEM, Mujtaba MA, Safaei MR et al (2021) Effect of Sr@ZnO nanoparticles and Ricinus communis biodiesel-diesel fuel blends on modified CRDI diesel engine characteristics. Energy. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2020.119094
Soudagar MEM, Nik-Ghazali NN, Kalam MA et al (2020) An investigation on the influence of aluminium oxide nano-additive and honge oil methyl ester on engine performance, combustion and emission characteristics. Renew Energy 146:2291–2307. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.08.025
Tan PQ, Hu ZY, Lou DM, Li ZJ (2012) Exhaust emissions from a light-duty diesel engine with Jatropha biodiesel fuel. Energy 39:356–362. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.01.002
Tomar M, Kumar N (2020) Influence of nanoadditives on the performance and emission characteristics of a CI engine fuelled with diesel, biodiesel, and blends–a review. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff 42:2944–2961. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2019.1623347
Venu H, Appavu P (2020) An experimental assessment on the influence of nanoparticles in calophyllum inophyllum biodiesel operated diesel engine. Energy Sources Part A Recover Util Environ Eff. https://doi.org/10.1080/15567036.2020.1839599
Yaqoob H, Teoh YH, Sher F et al (2021) Potential of waste cooking oil biodiesel as renewable fuel in combustion engines: a review. Energies. https://doi.org/10.3390/en14092565
Zhou K, Zhang Q, Shi Y et al (2013) A facile method for preparation ZnO with different morphology and their optical property. J Alloys Compd 577:389–394. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jallcom.2013.06.013
Acknowledgements
One of the authors (M. Dhanarasu) sincerely acknowledges the Periyar University, Salem, for providing University Research Fellowship (PU/AD-3/URF/024981/2018).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no conflicts of interest to declare that are relevant to the content of this article.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Q. Aguilar-Virgen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Dhanarasu, M., RameshKumar, K.A. & Maadeswaran, P. Performance and emission evaluation of diesel engine fueled with zinc oxide-dispersed used sunflower oil methyl ester. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 6351–6364 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04312-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04312-7