Abstract
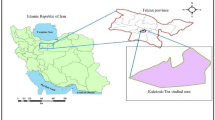
Inhalation of radon gas and its decay products is the first natural source of human exposure to radioactive radiation. Due to its health effects, the World Health Organization (WHO) has recommended guidelines (100 Bq/m3) for indoor environments. The aim of this study was to determine the radon concentration according to the characteristics of residential buildings. Detectors CR-39 were used to determine the radon concentration over a period of three months. Radon concentrations were different in villa buildings, apartment floors, and basements and depended on building materials, age, and ventilation.





Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdalla AM, El-Gamal S (2018) Measurement of indoor radon concentrations in different dwellings in Arar, Saudi Arabia. Nuclear Technol Radiat Protect 33(3):293–300
Abo-Elmagd M, Saleh A, Afifi G (2018) Evaluation of radon related parameters in environmental samples from Jazan city, Saudi Arabia. J Radiat Res Appl Sci 11(1):104–110
Ahmad S, Ajaz M, Ali Y, Younis H, Khan KH (2018) Measurement of indoor radon concentration in district Mardan, Khyber Pakhtunkhwa, Pakistan. Ядepнa фiзикa тa eнepгeтикa 19:190–195
Al-Kazwini AT, Al-Arnaout MM, Abdulkareem TR (2020) Radon-222 exposure and dose concentration levels in Jordanian dwellings. J Environ Public Health 2020:1–7
Aladeniyi K, Arogunjo AM, Pereira AJ, Ajayi OS, Fuwape IA (2020) Radiometric evaluation of indoor radon levels with influence of building characteristics in residential homes from southwestern Nigeria. Environ Monit Assess 192(12):1–15
Baradaran GM, Faghihi R, Karami M, Siavashpour Z, Owji H (2011) The effects of internal wall covering materials on hazards of indoor radon concentrations in houses of Iran
Elzain A-EA (2015) Radon exhalation rates from some building materials used in Sudan. Indoor and Built Environ 24(6):852–860
Khan SM, Gomes J, Krewski DR (2019) Radon interventions around the globe: a systematic review. Heliyon 5(5):e01737
Kim J-H, Ha M (2018) The disease burden of lung cancer attributable to residential radon exposure in Korean homes. J Korean Med Sci 33(29)
Kitson-Mills D, Sovoe S, Opoku-Ntim I, Kyei KA, Marnotey S, Anim-Sampong S, Kwabeng MA, Otoo F, Baiden F (2019) An assessment of indoor radon level in a suburb of Ghana. Enviro Res Commun 1(6):061002
Kumar M, Kaushal A, Sarin A, Kumar R, Sharma N (2018) Radon/thoron and progeny levels in dwellings: regional variations and effect of dwelling characteristics—a case study in Jalandhar district of Punjab, India. Indoor Built Environ 27(5):706–714
Lerma-Treviño C, Rubio-Arias H, Colmenero-Sujo LH, de Lourdes Villalba M, Ochoa-Rivero JM (2018) Indoor Radon Gas (222Rn) Levels in Homes in Aldama, Chihuahua, Mexico and the Risk of Lung Cancer. Int J Environ Res Public Health 15(7):1337
Li C, Wang C, Yu J, Fan Y, Liu D, Zhou W, Shi T (2020) Residential radon and histological types of lung cancer: a meta-analysis of case-control studies. Int J Environ Res Public Health 17(4):1457
López-Abente G, Núñez O, Fernández-Navarro P, Barros-Dios JM, Martín-Méndez I, Bel-Lan A, Locutura J, Quindós L, Sainz C, Ruano-Ravina A (2018) Residential radon and cancer mortality in Galicia, Spain. Sci Total Environ 610:1125–1132
Pirsaheb MF, Haghparast NA, Hemati L, Sharafi K, Kurd N (2016) The influence of internal wall and floor covering materials and ventilation type on indoor radon and thoron levels in hospitals of Kermanshah, Iran. Iranian Red Crescent Med J 18(10)
Ptiček Siročić A, Stanko D, Sakač N, Dogančić D, Trojko T (2020) Short-term measurement of indoor radon concentration in Northern Croatia. Appl Sci 10(7):2341
Saputra MA, Nugraha ED, Purwanti T, Arifianto R, Laksmana RI, Hutabarat RP, Hosoda M, Tokonami S (2020) Exposures from radon, thoron, and thoron progeny in high background radiation area in Takandeang, Mamuju, Indonesia. Nukleonika 65(2):89–94
Senitkova IJ, Kraus M (2019) Seasonal and floor variations of indoor radon concentration. IOP Conference series: earth and environmental science, IOP Publishing
Shahsavani S, Shamsedini N, Tabatabaei HR, Hoseini M (2019) Indoor radon concentrations in residential houses, processing factories, and mines in Neyriz, Iran. J Environ Health Sci Eng 17(2):979–987
Shikha D, Mehta V, Chauhan RP, Mudahar GS (2018) Measurement of variation of radon-thoron and their progeny concentrations in dwellings using pin hole based dosimeters. Aerosol Air Quality Res 18(3):811–819
Yang S, Goyette Pernot J, Hager Jörin C, Niculita-Hirzel H, Perret V, Licina D (2019) Radon investigation in 650 energy efficient dwellings in western Switzerland: impact of energy renovation and building characteristics. Atmosphere 10(12):777
Yu K (1993) The effects of typical covering materials on the radon exhalation rate from concrete surfaces. Radiat Prot Dosimetry 48(4):367–370
Acknowledgements
This study was funded by Semnan University of Medical Sciences (Grant No. 1433). The authors would like to thank the Semnan University of Medical Sciences for financial support. The authors of the article, also, would like to thank Dr. Mansour Jafarizadeh in Partopayesh equipment company for his cooperation and participation in the laboratory part of the research.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no known competing financial interests or personal relationships that could have appeared to influence the work presented in this paper.
Ethical approval
The study protocol was approved by the Ethics Committee of Semnan University of Medical Sciences under the ethical code of IR.SEMUMS.REC.1396.266.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Shurgashti, S., Rahmani, A., Dehdashti, A. et al. Determination of airborne Radon and its relationship with the type of residential buildings in Damghan, Iran. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 9601–9608 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04160-5
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04160-5