Abstract
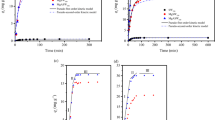
Composite biochar derived from crop straw and activated sludge may have great potential for remediating polluted environments. Few studies have addressed the influences of different modifying agents and modification procedures on the adsorption performance of composite biochar. In this work, the pre/post-KOH or H3PO4-modified composite biochar were generated from corn straw and activated sludge through co-pyrolysis at different blending ratios at 650 °C, and were tested for adsorption performance using methylene blue as an indicator pollutant. Results showed that the pseudo-second-order and Langmuir equations were deemed suitable for describing adsorption kinetics and adsorption isotherms, respectively. KOH modification was more favorable to improving the adsorption capacity than H3PO4 modification. The post-KOH or H3PO4 modification could not enhance adsorption capacity. The optimal blending ratio of corn straw and activated sludge was 80:20 (wt.%). The most promising result was obtained by the composite biochar with an 80:20 mass ratio of corn straw and activated sludge fabricated through pre-KOH modification, with excellent adsorption capacity for methylene blue (186.48 mg/g), which is attributed to increased oxygen-containing functional groups, aromaticity, and improved surface texture. The adsorption capacity of this composite biochar was significantly increased by increases of pH, MB concentration, and temperature. The optimal operational conditions for methylene blue adsorption on this composite biochar were 0.3 g/L of biochar dosage, 120 mg/L of methylene blue, a pH of 3, and 20 °C. This study revealed that the adsorption capacity of modified composite biochar highly depends on the blending ratio of corn straw and activated sludge and modification procedures.




Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad M, Rajapaksha AU, Lim JE, Zhang M, Bolan N, Mohan D, Vithanage M, Lee SS, Ok YS (2014) Biochar as a sorbent for contaminant management in soil and water: a review. Chemosphere 99:19–33. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.10.071
Ahmed MJ, Hameed BH (2020) Insight into the co-pyrolysis of different blended feedstocks to biochar for the adsorption of organic and inorganic pollutants: a review. J Clean Prod 265:121762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.121762
Ahmed MJ, Theydan SK (2013) Microporous activated carbon from siris seed pods by microwave-induced KOH activation for metronidazole adsorption. J Anal Appl Pyrol 99:101–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2012.10.019
Ahmed MB, Zhou J, Ngo HH, Guo W, Chen M (2016) Progress in the preparation and application of modified biochar for improved contaminant removal from water and wastewater. Bioresour Technol 214:836–851. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.05.057
Ai L, Zhang C, Liao F, Wang Y, Li M, Meng L, Jiang J (2001) Removal of methylene blue from aqueous solution with magnetite loaded multi-wall carbon nanotube: kinetic, isotherm and mechanism analysis. J Hazard Mater 198:282–290. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2011.10.041
Bazan-Wozniak A, Nowicki P, Pietrzak R (2018) Production of new activated bio-carbons by chemical activation of residue left after supercritical extraction of hops. Environ Res 161:456–463. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2017.11.041
Chu G, Zhao J, Huang Y, Zhou D, Liu Y, Wu M, Peng H, Zhao Q, Pan B, Steinberg CEW (2018) Phosphoric acid pretreatment enhances the specific surface areas of biochars by generation of micropores. Environ Pollut 240:1–9. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2018.04.003
Danish M, Ahmad T (2018) A review on utilization of wood biomass as a sustainable precursor for activated carbon production and application. Renew Sust Energ Rev 87:1–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2018.02.003
Deng H, Li Z, Jin Z, Zhang T (2016) Process optimization of char prepared from co-pyrolysis of cotton stalk and sludge and analysis on its structure and adsorption capacity. Trans Chin Soc Agric Eng 32(24):248–254
Elmouwahidi A, Bailón-García E, Pérez-Cadenas AF, Maldonado-Hódar FJ, Carrasco-Marín F (2017) Activated carbons from KOH and H3PO4-activation of olive residues and its application as supercapacitor electrodes. Electrochim Acta 229:219–228. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2017.01.152
Ertugay N, Malkoc E (2014) Adsorption isotherm, kinetic, and thermodynamic studies for methylene blue from aqueous solution by needles of Pinus sylvestris L. Pol J Environ Stud 23(6):1995–2006
Fagbayigbo BO, Opeolu BO, Fatoki OS, Akenga TA, Olatunji OS (2017) Removal of PFOA and PFOS from aqueous solutions using activated carbon produced from Vitis vinifera leaf litter. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:13107–13120. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8912-x
Fan S, Tang J, Wang Y, Li H, Zhang H, Tang J, Wang Z, Li X (2016) Biochar prepared from co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and tea waste for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions: Kinetics, isotherm, thermodynamic and mechanism. J Mol Liq 220:432–441. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2016.04.107
Gao Y, Yue Q, Gao B, Li A (2020) Insight into activated carbon from different kinds of chemical activating agents: a review. Sci Total Environ 746:141094. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.141094
Ho YS, McKay G (1998) Sorption of dye from aqueous solution by peat. Chem Eng J 70(2):115–124. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0923-0467(98)00076-1
Ho YS, McKay G (1999) Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem 34(5):451–465. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5
Hong Y, Xu Z, Feng C, Xu D, Wu F (2019) The preparation of biochar particles from sludge and corncobs and its Pb2+ adsorption properties. B Environ Contam Tox 103(6):848–853. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-019-02736-5
Huang H, Yang T, Lai F, Wu G (2017) Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and sawdust/rice straw for the production of biochar. J Anal Appl Pyrol 125:61–68. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2017.04.018
Huang W, Chen J, Zhang J (2018) Adsorption characteristics of methylene blue by biochar prepared using sheep, rabbit and pig manure. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:29256–29266. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2906-1
Jin H, Capareda S, Chang Z, Gao J, Xu Y, Zhang J (2014) Biochar pyrolytically produced from municipal solid wastes for aqueous As(V) removal: Adsorption property and its improvement with KOH activation. Bioresour Technol 169:622–629. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2014.06.103
Jin J, Wang M, Cao Y, Wu S, Liang P, Li Y, Zhang J, Zhang J, Wong MH, Shan S, Christie P (2017) Cumulative effects of bamboo sawdust addition on pyrolysis of sewage sludge: biochar properties and environmental risk from metals. Bioresour Technol 228:218–226. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2016.12.103
Kończak M, Oleszczuk P (2020) Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and biomass in carbon dioxide as a carrier gas affects the total and leachable metals in biochars. J Hazard Mater 400:123144. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123144
Kwon G, Bhatnagar A, Wang H, Kwon EE, Song H (2020) A review of recent advancements in utilization of biomass and industrial wastes into engineered biochar. J Hazard Mater 400:123242. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123242
Laskar N, Kumar U (2019) Removal of brilliant green dye from water by modified Bambusa tulda: adsorption isotherm, kinetics and thermodynamics study. Int J Environ Sci Te 16(3):1649–1662. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-018-1760-5
Leng L, Yuan X, Huang H, Shao J, Wang H, Chen X, Zeng G (2015) Bio-char derived from sewage sludge by liquefaction: characterization and application for dye adsorption. Appl Surf Sci 346:223–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2015.04.014
Li G, Zhu W, Zhang C, Zhang S, Liu L, Zhu L, Zhao W (2016) Effect of a magnetic field on the adsorptive removal of methylene blue onto wheat straw biochar. Bioresour Technol 206:16–22. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.12.087
Li H, Dong X, da Silva EB, de Oliveira LM, Chen Y, Ma L (2017) Mechanisms of metal sorption by biochars: biochar characteristics and modifications. Chemosphere 178:466–478. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.03.072
Li H, Gao P, Cui J, Zhang F, Wang F, Cheng J (2018a) Preparation and Cr(VI) removal performance of corncob activated carbon. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:20743–20755. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2026-y
Li X, Wang C, Tian J, Liu J, Chen G (2020) Comparison of adsorption properties for cadmium removal from aqueous solution by Enteromorpha prolifera biochar modified with different chemical reagents. Environ Res 186:109502. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.109502
Li Y, Yu H, Liu L, Yu H (2021) Application of co-pyrolysis biochar for the adsorption and immobilization of heavy metals in contaminated environmental substrates. J Hazard Mater 420:126655. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126655
Li N, Zhang H, Meng J, Lu J, Wang Z (2018b) Preparation of biochar from sewage sludge with different biomass by co-pyrolysis and its land application. Renew Energy Resour 36(10):1423–1430 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTotal-NCNY2018b10001.htm
Liu H, Zhang J, Bao N, Cheng C, Ren L, Zhang C (2012) Textural properties and surface chemistry of lotus stalk-derived activated carbons prepared using different phosphorus oxyacids: adsorption of trimethoprim. J Hazard Mater 235–236:367–375. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2012.08.015
Liu N, Liu Y, Zeng G, Gong J, Tan X, Wen J, Liu S, Jiang L, Li M, Yin Z (2020) Adsorption of 17β-estradiol from aqueous solution by raw and direct/pre/post-KOH treated lotus seedpod biochar. J Environ Sci 87:10–23. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2019.05.026
Liu X, Zhang H, Lu X, Wang C (2014) Study on the adsorption of two kinds of dyes by adsorbent derived from sludge and rice husk. Ind Water Treat 34(5):33–37 (in Chinese with English abstract) http://www.cnki.com.cn/Article/CJFDTOTAL-GYSC201405010.htm
Ma H, Li JB, Liu WW, Miao M, Cheng BJ, Zhu SW (2015) Novel synthesis of a versatile magnetic adsorbent derived from corncob for dye removal. Bioresour Technol 190:13–20. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2015.04.048
Mao H, Zhou D, Hashisho Z, Wang S, Chen H, Wang H (2015) Preparation of pinewood-and wheat straw-based activated carbon via a microwave-assisted potassium hydroxide treatment and an analysis of the effects of the microwave activation conditions. BioResources 10(1):809–821
Meng Q, Zhang Y, Meng D, Liu X, Zhang Z, Gao P, Lin A, Hou L (2020) Removal of sulfadiazine from aqueous solution by in-situ activated biochar derived from cotton shell. Environ Res 191:110104. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envres.2020.110104
Mohd Din AT, Hameed BH, Ahmad AL (2009) Batch adsorption of phenol onto physiochemical-activated coconut shell. J Hazard Mater 161(2–3):1522–1529. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.05.009
Namasivayam C, Kavitha D (2002) Removal of Congo Red from water by adsorption onto activated carbon prepared from coir pith, an agricultural solid waste. Dyes Pigments 54(1):47–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0143-7208(02)00025-6
Otowa T, Nojina Y, Miyazaki T (1997) Development of KOH activated high surface area carbon and its application to drinking water purification. Carbon 35(5):1315–1319. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0008-6223(97)00076-6
Que W, Jiang L, Wang C, Liu Y, Zeng Z, Wang X, Ning Q, Liu S, Zhang P, Liu S (2018) Influence of sodium dodecyl sulfate coating on adsorption of methylene blue by biochar from aqueous solution. J Environ Sci 70:166–174. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2017.11.027
Rizwan M, Lin Q, Chen X, Li Y, Li G, Zhao X, Tian Y (2020) Synthesis, characterization and application of magnetic and acid modified biochars following alkaline pretreatment of rice and cotton straws. Sci Total Environ 714:136532. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.136532
Salame II, Bandosz TJ (2000) Comparison of the surface features of two wood-based activated carbons. Ind Eng Chem Res 39(2):301–306. https://doi.org/10.1021/ie9906316
Shi L, Zhang G, Wei D, Yan T, Xue X, Shi S, Wei Q (2014) Preparation and utilization of anaerobic granular sludge-based biochar for the adsorption of methylene blue from aqueous solutions. J Mol Liq 198:334–340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2014.07.023
Son EB, Poo KM, Chang JS, Chae KJ (2018) Heavy metal removal from aqueous solutions using engineered magnetic biochars derived from waste marine macro-algal biomass. Sci Total Environ 615:161–168. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.171
Sun J, Lian F, Liu Z, Zhu L, Song Z (2014) Biochars derived from various crop straws: Characterization and Cd(II) removal potential. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 106:226–231. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ecoenv.2014.04.042
Tabassum M, Bardhan M, Novera TM, Islam MA, Hadi Jawad A, Islam MA (2020) NaOH-activated betel nut husk hydrochar for efficient adsorption of methylene blue dye. Water Air Soil Pollut 231(8):398. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-020-04762-0
Tang L, Yu J, Pang Y, Zeng G, Deng Y, Wang J, Ren X, Ye S, Peng B, Feng H (2018) Sustainable efficient adsorbent: alkali-acid modified magnetic biochar derived from sewage sludge for aqueous organic contaminant removal. Chem Eng J 336:160–169. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.11.048
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KS (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC technical report). Pure Appl Chem 87(9–10):1051–1069. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Ur Rehman M, Kim I, Rashid N, Umer M, Sajid M, Han J (2016) Adsorption of brilliant green dye on biochar prepared from lignocellulosic bioethanol plant waste. Clean-Soil Air Water 44(1):55–62. https://doi.org/10.1002/clen.201300954
Wang Z, Xie L, Liu K, Wang J, Zhu H, Song Q, Shu X (2019) Co-pyrolysis of sewage sludge and cotton stalks. Waste Manage 89:430–438. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.wasman.2019.04.033
Wang Z, Li G, Wang G, Lu J, Wang J (2018) Preparation of biochar from co-pyrolysis of sludge-sawdust and its application in soil. Modern Chemical Industry, 37(1): 147–152. http://en.cnki.com.cn/Article_en/CJFDTotal-XDHG201701035.htm
Yang R, Liu G, Xu X, Li M, Zhang J, Hao X (2011) Surface texture, chemistry and adsorption properties of acid blue 9 of hemp (Cannabis sativa L.) bast-based activated carbon fibers prepared by phosphoric acid activation. Biomass Bioenerg 35(1):437–445. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biombioe.2010.08.061
Yang Y, Cui M, Ren Y, Guo J, Zheng Z, Liu H (2020) Towards understanding the mechanism of heavy metals immobilization in biochar derived from co-pyrolysis of sawdust and sewage sludge. B Environ Contam Tox 104(4):489–496. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00128-020-02801-4
Yin X, Xi M, Li Y, Kong F, Jiang Z (2021) Improvements in physicochemical and nutrient properties of sewage sludge biochar by the co-pyrolysis with organic additives. Sci Total Environ 779:146565. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2021.146565
Zhang S, Yue X, Yin Z, Pan T, Dong M, Sun T (2009) Study of the co-pyrolysis behavior of sewage-sludge/rice-straw and the kinetics. Earth Planet Sci 1(1):661–666. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeps.2009.09.104
Zhao B, Xu X, Xu S, Chen X, Li H, Zeng F (2017) Surface characteristics and potential ecological risk evaluation of heavy metals in the bio-char produced by co-pyrolysis from municipal sewage sludge and hazelnut shell with zinc chloride. Bioresour Technol 243:375–383. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2017.06.032
Zhao B, Xu X, Zeng F, Li H, Chen X (2018) The hierarchical porous structure bio-char assessments produced by co-pyrolysis of municipal sewage sludge and hazelnut shell and Cu(II) adsorption kinetics. Environ Sci Pollut Res 25:19423–19435. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-018-2079-y
Zhou P, Gu L, Rao S, Huang Y, Yuan H, Zhu N (2013) Preparation of sludge-straw based activated carbon and its adsorption for 1-diazo-2-naphtol-4-sulfonic acid. Environ Chem 32(1):106–111. https://doi.org/10.7524/j.issn.0254-6108.2013.01.016
Zhou Q, Liao B, Lin L, Qiu W, Song Z (2018) Adsorption of Cu(II) and Cd(II) from aqueous solutions by ferromanganese binary oxide biochar composites. Sci Total Environ 615:115–122. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2017.09.220
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (Project No. 41661096); the Open Foundation of Key laboratory for Ecotourism of Hunan Province, China (Project No. STLV1805); and the Scientific Research Innovation Project for Graduate Student of Hunan Province, China (Project No. CX20190864).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Abhishek RoyChowdhury.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Xiang, J., Luo, B.X., Li, J.M. et al. Development of KOH and H3PO4-modified composite biochar from corn straw and activated sludge for removing methylene blue. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 1673–1688 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04062-6
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04062-6