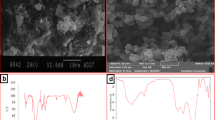
Abstract
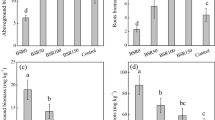
Electrokinetic remediation is a promising technology for removal of heavy metals from soil, but its effect on arsenic remains poorly understood. Biogas slurry (10%, 25%, and 50% by mass) and sucrose (2%, 5%, and 10% by mass) were added to soil contaminated by mine drainage to enhance arsenic migration ability. Chemical sequential extraction, flame atomic absorption spectrometry, hydride generation atomic fluorescence spectrometry, and high-throughput sequencing were used to determine the iron and arsenic speciation, arsenic removal rate, and microbial community structure. Electroosmotic flow was found to play the main role in the treatment. The electroosmotic flow rate of the sucrose treatment was lower than that of the biogas slurry treatment. The sucrose could maintain a lower pH in soil compared with biogas slurry. It could also form a stronger reducing environment (redox potential, − 274 mV) and increase the abundance of iron oxide reducing bacteria. The amorphous iron oxide content increased at the end of the experiment. The removed arsenic was mainly from the residual fraction. The 25% biogas slurry and 5% sucrose treatments, could quickly remove 13.7% and 13.4% of the arsenic in one week, respectively. The highest removal rate was 14.3% in the 5% sucrose treatment at the end of the experiment and was about three times higher than the untreated control. Moreover, sucrose addition was more helpful than the biogas slurry treatment to stabilize the current and reduce energy consumption. These findings provide theoretical support to enhance microbial activity to improve this technology for removal of soil arsenic.






Similar content being viewed by others
Availability of data and material
The datasets used or analyzed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request
Code availability
Not applicable.
References
Ajith N, Swain KK (2019) Study on the performance and interaction of different synthetic iron oxides for arsenic uptake using 76As radiotracer. Appl Radiat Isot 153:108807. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apradiso.2019.108807
Alazard D, Joseph M, Battaglia-Brunet F, Cayol JL, Ollivier B (2010) Desulfosporosinus acidiphilus sp. Nov.: a moderately acidophilic sulfate-reducing bacterium isolated from acid mining drainage sediments: New taxa: Firmicutes (Class Clostridia, Order Clostridiales, Family Peptococcaceae). Extremophiles 14(3):305–312. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00792-010-0309-4
Bose P, Sharma A (2002) Role of iron in controlling speciation and mobilization of arsenic in subsurface environment. Water Res 36(19):4916–4926
Cameselle C, Pena A (2016) Enhanced electromigration and electro-osmosis for the remediation of an agricultural soil contaminated with multiple heavy metals. Process Saf Environ Prot 104:209–217. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2016.09.002
Chen Z, Wang Y, Jiang X, Fu D, Xia D, Wang H (2017) Dual roles of AQDS as electron shuttles for microbes and dissolved organic matter involved in arsenic and iron mobilization in the arsenic-rich sediment. Sci Total Environ 574:1684–1694. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2016.09.006
Choong TSY, Chuah TG, Robiah Y, Gregory Koay FL, Azni I (2007) Arsenic toxicity, health hazards and removal techniques from water: an overview. Desalination 217(1–3):139–166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.desal.2007.01.015
Cundy AB, Hopkinson L (2005) Electrokinetic iron pan generation in unconsolidated sediments: implications for contaminated land remediation and soil engineering. Appl Geochem 20(5):841–848. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apgeochem.2004.11.014
Gunina A, Kuzyakov Y (2015) Sugars in soil and sweets for microorganisms: Review of origin, content, composition and fate. Soil Biol Biochem 90:87–100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.soilbio.2015.07.021
Husson O (2013) Redox potential (Eh) and pH as drivers of soil/plant/microorganism systems: a transdisciplinary overview pointing to integrative opportunities for agronomy. Plant Soil 362(1–2):389–417. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11104-012-1429-7
Iftikhar S, Turan V, Tauqeer HM, Rasool B, Zubair M, Rahman M, Khan MA, Akhtar S, Khan SA, Basharat Z, Zulfiqar I (2019) Phytomanagement of As-contaminated matrix: physiological and molecular basis. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 183:109594. https://doi.org/10.1016/B978-0-12-819382-2.00005-3
Jaafar M, Shrivastava A, Rai Bose S, Felipe-Sotelo M, Ward NI (2021) Transfer of arsenic, manganese and iron from water to soil and rice plants: an evaluation of changes in dietary intake caused by washing and cooking rice with groundwater from the Bengal Delta, India. J Food Compos Anal. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jfca.2020.103748
Jiang T, Hu A, Qin H (1990) Frectionation of soil zinc, copper, iron and manganese. Acta Sci Circum 10(3):280–286
Kim EJ, Baek K (2015) Enhanced reductive extraction of arsenic from contaminated soils by a combination of dithionite and oxalate. J Hazard Mater 284:19–26. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.11.004
Kim EJ, Lee JC, Baek K (2015) Abiotic reductive extraction of arsenic from contaminated soils enhanced by complexation: arsenic extraction by reducing agents and combination of reducing and chelating agents. J Hazard Mater 283:454–461. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.09.055
Ko MS, Lee S, Kim KW (2019) Reductive dissolution and sequestration of arsenic by microbial iron and thiosulfate reduction. Environ Geochem Health 41(1):461–467. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10653-018-0086-z
Lee JC, Kim EJ, Kim HW, Baek K (2016) Oxalate-based remediation of arsenic bound to amorphous Fe and Al hydrous oxides in soil. Geoderma 270:76–82. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.geoderma.2015.09.015
Li FB, Li XM, Zhou SG, Zhuang L, Cao F, Huang DY (2010) Enhanced reductive dechlorination of DDT in an anaerobic system of dissimilatory iron-reducing bacteria and iron oxide. Environ Pollut 158(5):1733–1740. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.envpol.2009.11.020
Li J, Ding Y, Wang K, Li N, Qian G, Xu Y (2020) Comparison of humic and fulvic acid on remediation of arsenic contaminated soil by electrokinetic technology. Chemosphere 241:125038. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125038
Rasool B, Rahman M, Ramzani PMA, Zubair M, Khan MA, Lewinska K, Turan V, Karczewska A, Khan SA, Farhad M, Tauqeer HM, Iqbal M (2021) Impacts of oxalic acid-activated phosphate rock and root-induced changes on Pb bioavailability in the rhizosphere and its distribution in mung bean plant. Environ Pollut 280:116903
Ryu BG, Park GY, Yang JW, Baek K (2011) Electrolyte conditioning for electrokinetic remediation of As, Cu, and Pb-contaminated soil. Sep Purif Technol 79(2):170–176. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.seppur.2011.02.025
Ryu SR, Jeon EK, Baek K (2017) A combination of reducing and chelating agents for electrolyte conditioning in electrokinetic remediation of As-contaminated soil. J Taiwan Inst Chem Eng 70:252–259. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jtice.2016.10.058
Shen B, Wang X, Zhang Y, Zhang M, Wang K, Xie P (2020) The optimum pH and Eh for simultaneously minimizing bioavailable cadmium and arsenic contents in soils under the organic fertilizer application. Sci Total Environ 711:135229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.135229
Shin SY, Park SM, Baek K (2017) Soil moisture could enhance electrokinetic remediation of arsenic-contaminated soil. Environ Sci Pollut Res Int 24(10):9820–9825. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-017-8720-3
Snoeyenbos-West OL, Nevin KP, Anderson RT, Lovley DR (2000) enrichment of geobacter species in response to stimulation of Fe(III) reduction in sandy aquifer sediments. Microb Ecol 39(2):153–167. https://doi.org/10.1007/s002480000018
Song Y, Cang L, Zuo Y, Yang J, Zhou D, Duan T (2020) EDTA-enhanced electrokinetic remediation of aged electroplating contaminated soil assisted by combining dual cation-exchange membranes and circulation methods. Chemosphere 243:125439. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.125439
Tauqeer HM, Karczewska A, Lewińska K, Fatima M, Khan SA, Farhad M, Turan V, Ramzani PMA, Iqbal M (2020) Environmental concerns associated with explosives (HMX, TNT, and RDX), heavy metals and metalloids from shooting range soils: prevailing issues, leading management practices, and future perspectives. Handbook of bioremediator. Elsevier, Netherlands, pp 569–590
Tauqeer HM, Fatima M, Rashid A, Shahbaz AK, Ramzani PMA, Farhad M, Basharat Z, Turan V, Iqbal M (2021) The current scenario and prospects of immobilization remediation technique for the management of heavy metals contaminated soils. In: Hasanuzzaman (ed) Approaches to the remediation of inorganic pollutants, Springer, Berlin, pp. 155–185
Torres CM, Arce PE, Justel FJ, Romero L, Ghorbani Y (2018) Joule heating effects in electrokinetic remediation: role of non-uniform soil environments: temperature profile behavior and hydrodynamics. Environments. https://doi.org/10.3390/environments5080092
Turan V (2021a) Calcite in combination with olive pulp biochar reduces Ni mobility in soil and its distribution in chili plant. Int J Phytoremediat. https://doi.org/10.1080/15226514.2021.1929826
Turan V (2021b) Arbuscular mycorrhizal fungi and pistachio husk biochar combination reduces Ni distribution in mungbean plant and improves plant antioxidants and soil enzymes. Physiol Plant 173(1):418–429. https://doi.org/10.1111/ppl.13490
Turan V, Ramzani PMA, Ali Q, Abbas F, Iqbal M, Irum A, Khan WD (2018) Alleviation of nickel toxicity and an improvement in zinc bioavailability in sunflower seed with chitosan and biochar application in pH adjusted nickel contaminated soil. Arch Agron Soil Sci 64(8):1053–1067. https://doi.org/10.1080/03650340.2017.1410542
Wang L, Giammar DE (2015) Effects of pH, dissolved oxygen, and aqueous ferrous iron on the adsorption of arsenic to lepidocrocite. J Colloid Interface Sci 448:331–338. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jcis.2015.02.047
Wang Z, Xiao D, Bush RT, Liu J (2015) Coprecipitated arsenate inhibits thermal transformation of 2-line ferrihydrite: implications for long-term stability of ferrihydrite. Chemosphere 122:88–93. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.11.017
Wang Y, Ma F, Zhang Q, Peng C, Wu B, Li F (2017) An evaluation of different soil washing solutions for remediating arsenic-contaminated soils. Chemosphere 173:368–372. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2017.01.068
Wen D, Fu R, Li Q (2021) Removal of inorganic contaminants in soil by electrokinetic remediation technologies: a review. J Hazard Mater 401:123345. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2020.123345
Xi B, Dang Q, Wei Y, Li X, Zheng Y, Zhao X (2020) Biogas slurry as an activator for the remediation of petroleum contaminated soils through composting mediated by humic acid. Sci Total Environ 730:139117. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.scitotenv.2020.139117
Xu Y, Lu Q, Li J, Wan L, Chen S, Lu Y (2021) Effect of humus on the remediation of arsenic-contaminated soil by electrokinetic technology. Environ Technol Innov. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.eti.2020.101297
Yamaguchi N, Nakamura T, Dong D, Takahashi Y, Amachi S, Makino T (2011) Arsenic release from flooded paddy soils is influenced by speciation, Eh, pH, and iron dissolution. Chemosphere 83(7):925–932. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2011.02.044
Yan X, Liu Q, Wang J, Liao X (2017) A combined process coupling phytoremediation and in situ flushing for removal of arsenic in contaminated soil. J Environ Sci (china) 57:104–109. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jes.2016.10.015
Yang JS, Kwon MJ, Choi J, Baek K, O’Loughlin EJ (2014) The transport behavior of As, Cu, Pb, and Zn during electrokinetic remediation of a contaminated soil using electrolyte conditioning. Chemosphere 117:79–86. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2014.05.079
Yang G, Yin Y, Wang JL (2019) Microbial community diversity during fermentative hydrogen production inoculating various pretreated cultures. Int J Hydrogen Energy 44:13147–13156. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.03.216
Zhang C, Wu P, Tang C, Han Z, Sun J (2013) Assessment of arsenic distribution in paddy soil and rice plants of a typical karst basin affected by acid mine drainage in Southwest China. Environ and Pollut. https://doi.org/10.5539/ep.v2n2p27
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1612442 and No. 41403088) and the Foundation of Guizhou University (No. GZU [2020]72).
Funding
This study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China (No. U1612442 and No. 41403088) and the Foundation of Guizhou University (No. GZU [2020]72).
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
Chipeng Zhang contributed to the conception of the study and wrote the manuscript. Yaoling Hao performed the experiment and contributed to analysis. Kaixuan Zhang contributed to manuscript preparation. Shuang Chen contributed to manuscript preparation. Zeyan Yang performed the experiment.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Ethics approval
Not applicable.
Consent to participate
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Not applicable.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: J Aravind.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zhang, C., Hao, Y., Zhang, K. et al. Effect of biogas slurry and sucrose addition on electrokinetic removal of arsenic from paddy soil. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 20, 703–714 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04006-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-04006-0