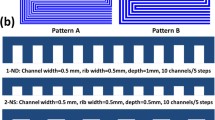
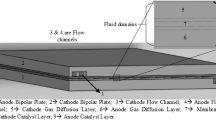
Abstract
The proton exchange membrane fuel cell (PEMFC) systems, clean, cost-effective, green-friendly, capable of using hydrogen as a direct fuel, have potential to compensate for our energy needs in the near future. The gas flow field, which is the backbone of the fuel cell, plays a vital role in both the reactant distribution and removal of water formed due to electrochemical reactions from the cell. Flow field configuration is one of the crucial design parameters influencing the PEMFC performance. The present study proposed a three-dimensional computational fluid dynamics CFD model based on the FLUENT with a 2.6 cm2 active area, has been researching the impact of the channel width to rib width ratio of the single serpentine flow field to obtain the top-level cell performance. The simulation model was operated at the pressure of 3 atm., the temperature of 343 K, and reactant gases were completely humidified. Here, the channel width to rib width ratio (Cw/Rw) is altered as 0.5, 1, and 2 values, respectively, to observe the performance alteration. The current density and power density diagrams, which define the PEMFC characteristic, were combined into one chart for better comparison. The present study discovered that the highest power density was 1.0896 W cm−2 when the Cw/Rw is 2 at 0.6 V operating voltage. We concluded that better water management obtained the best power density and current density values for the channel width to rib width 1 × 0.5 mm geometry.












Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- ρ :
-
Density (kg m−3)
- v :
-
Velocity (m s−1)
- p :
-
Pressure (Pa)
- J i :
-
Diffusion mass flux (kg m−2 s−1)
- Y i :
-
Mass fraction
- F :
-
Faraday constant (C mol−1)
- C :
-
Specific heat (J kg−1 K−1)
- T :
-
Fluid temperature (K)
- k :
-
Thermal conductivity (W m−1 K−1)
- i :
-
Current density (A cm−2)
- S m :
-
Source term (W m−3)
- S h :
-
Volumetric source term (W m−3)
- S p :
-
Momentum source term (W m−3)
- S s :
-
Solid phase source term (W m−3)
- S e :
-
Electrolyte source term (W m−3)
- M :
-
Molecular weight (kg kmol−1)
- \(\sigma_{{\text{s}}}\) :
-
Solid phase conductivity (ohm−1 m−1)
- \(\sigma_{{\text{e}}}\) :
-
Electrolyte conductivity (ohm−1 m−1)
- \(\phi_{{\text{s}}}\) :
-
Solid phase potential (V)
- \(\phi_{{\text{e}}}\) :
-
Electrolyte potential (V)
- ε :
-
Porosity
- μ :
-
Dynamic viscosity (kg m−1 s−1)
- \(\zeta\) :
-
Stoichiometric flow rate
References
Al-Dawery SK et al (2021) Parametric study for optimization of sediment-type microbial fuel cell. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18(5):1097–1108. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03236-y
Alizadeh E et al (2017) Numerical and experimental investigation of cascade type serpentine flow field of reactant gases for improving performance of PEM fuel cell. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42(21):14708–14724. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2017.04.212
Antunes RA et al (2010) Corrosion of metal bipolar plates for PEM fuel cells: a review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 35(8):3632–3647. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2010.01.059
Atabi F (2004) Renewable energy in Iran: challenges and opportunities for sustainable development. Int J Environ Sci Technol 1(1):69–80. https://doi.org/10.1007/bf03325818
Azarafza A, Ismail MS, Rezakazemi M (2019) Comparative study of conventional and unconventional designs of cathode flow fields in PEM fuel cell. Renew Sustain Energy Rev 116(June):109420. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.rser.2019.109420
Caglar A, Selim M (2020) Effective carbon nanotube supported metal ( M ¼ Au, Ag Co, Mn, Ni, V, Zn ) core Pd shell bimetallic anode catalysts for formic acid fuel cells. Renew Energy 150:78–90. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.renene.2019.12.104
Cai Y et al (2021) The effect of cathode channel blockages on the enhanced mass transfer and performance of PEMFC. Energy 222:119951. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2021.119951
Carcadea E et al (2020) Effects of geometrical dimensions of flow channels of a large-active-area PEM fuel cell: a CFD study. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46(2021):13572–13582. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.08.150
Chen X et al (2021) Performance investigation on a novel 3D wave flow channel design for PEMFC. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46(2021):11127–11139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.06.057
Das SK, Gibson HA (2021) Three dimensional multi-physics modeling and simulation for assessment of mass transport impact on the performance of a high temperature polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell. J Power Sources 499(2020):229844. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2021.229844
Demirbas A (2007) Fuel cells as clean energy converters. Energy Sources Part A 29(2):185–191. https://doi.org/10.1080/009083190948694
Durmaz U, Yalcinkaya O (2019) Experimental investigation on the ground heat exchanger with air fluid. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:5213–5218. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02205-w
Faruk O et al (2020) Novel carbon nanotube supported Co @ Ag @ Pd formic acid electrooxidation catalysts prepared via sodium borohydride sequential reduction method. Mater Chem Phys 241(2020):122422. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.matchemphys.2019.122422
Heidary H et al (2016) Numerical modelling of in-line and staggered blockages in parallel flowfield channels of PEM fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42(4):2265–2277. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.10.076
Hermann A, Chaudhuri T, Spagnol P (2005) Bipolar plates for PEM fuel cells: a review. Int J Hydrogen Energy 30(12):1297–1302. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2005.04.016
Ibrahimoglu B, Yilmazoglu MZ, Celenk S (2017) Investigation of spiral flow-field design on the performance of a PEM fuel cell. Fuel Cells 6:786–793. https://doi.org/10.1002/fuce.201700076
Kahveci EE, Taymaz I (2018) Assessment of single-serpentine PEM fuel cell model developed by computational fluid dynamics. Fuel 217(2018):51–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.fuel.2017.12.073
Lim BH et al (2017) Numerical analysis of modified parallel flow field designs for fuel cells. Int J Hydrogen Energy 42(14):9210–9218. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.189
Limjeerajarus N, Santiprasertkul T (2020) Novel hybrid serpentine-interdigitated flow field with multi-inlets and outlets of gas flow channels for PEFC applications. Int J Hydrogen Energy 45(25):13601–13611. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.12.160
Lingchao X et al (2021) Numerical study of vapor behavior in high temperature PEM fuel cell under key material and operating parameters. Int J Green Energy. https://doi.org/10.1080/15435075.2021.1960354
Mancusi E et al (2014) Numerical study of two-phase flow patterns in the gas channel of PEM fuel cells with tapered flow field design. Int J Hydrogen Energy 39(5):2261–2273. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2013.11.106
Manso AP et al (2011) Numerical analysis of the influence of the channel cross-section aspect ratio on the performance of a PEM fuel cell with serpentine flow field design. Int J Hydrogen Energy 36(11):6795–6808. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2011.02.099
Mojica F et al (2021) Study of converging-diverging channel induced convective mass transport in a proton exchange membrane fuel cell. Energy Convers Manag 237(2021):114095. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2021.114095
Mortazavi M (2021) Two-phase flow pressure drop in PEM fuel cell flow channel bends. Int J Multiph Flow 143(2021):103759. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmultiphaseflow.2021.103759
Ozdemir SN, Taymaz I (2021) Numerical investigation of the effect of blocked gas flow field on PEM fuel cell performance. Int J Environ Sci Technol 18:3581–3596. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03075-3
Rahman MA et al (2019) Development of 1-D multiphysics PEMFC model with dry limiting current experimental validation. Electrochim Acta 320:134601. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.electacta.2019.134601
Robin C et al (2015) Development and experimental validation of a PEM fuel cell 2D-model to study heterogeneities effects along large-area cell surface. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40(32):10211–10230. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.05.178
Schröder M et al (2021) Optimal operating conditions of PEM fuel cells in commercial aircraft. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46(2021):33218–33240. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.07.099
Tawfik H, Hung Y, Mahajan D (2007) Metal bipolar plates for PEM fuel cell—a review. J Power Sources 163(2):755–767. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2006.09.088
Tian P et al (2021) Deep learning from three-dimensional multiphysics simulation in operational optimization and control of polymer electrolyte membrane fuel cell for maximum power. Appl Energy 288(2021):116632. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2021.116632
Vazifeshenas Y, Sedighi K, Shakeri M (2015) Numerical investigation of a novel compound flow- field for PEMFC performance improvement. Int J Hydrogen Energy 40(43):15032–15039. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2015.08.077
Wang L et al (2003) A parametric study of PEM fuel cell performances. Int J Hydrogen Energy 28(11):1263–1272. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-3199(02)00284-7
Wu J et al (2008) A review of PEM fuel cell durability: degradation mechanisms and mitigation strategies. J Power Sources 184(1):104–119. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpowsour.2008.06.006
Yin Y et al (2018) Numerical investigation on the characteristics of mass transport and performance of PEMFC with baffle plates installed in the flow channel. Int J Hydrogen Energy 43(16):8048–8062. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2018.03.037
Zang L, Hao L (2020) Numerical study of the cold-start process of PEM fuel cells with different current density operating modes. J Energy Eng 146(6):04020057. https://doi.org/10.1061/(asce)ey.1943-7897.0000705
Zhang G et al (2021) Three-dimensional multi-phase simulation of PEM fuel cell considering the full morphology of metal foam flow field. Int J Hydrogen Energy 46(3):2978–2989. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.263
Acknowledgements
This study has not been supported financially neither is a part of a broader project.
Funding
This study has not been supported financially; neither is it a part of a broader project.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Contributions
SO Conceptualization, CFD analysis, writing-original draft, data curation, literature review; IT Conceptualization, editing, and supervision.
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
All authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Consent to participate
All the authors agree to submit the manuscript to the renowned journal ‘Journal of Environmental Science and Technology.’
Consent for publication
The manuscript is original. It has not been published previously by any of the authors and is even not under consideration in any other journal at the time of submission.
Ethical approval
This article does not contain any studies with human participants or animals performed by any authors.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Q. Aguilar-Virgen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Ozdemir, S.N., Taymaz, I. Assessment of the PEMFC performance: a CFD study based on channel width to rib width ratio effect. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 12329–12344 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03962-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-022-03962-x