Abstract
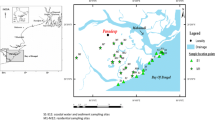
This study analyzed the spatial distribution, ecotoxicological and health risks and possible sources of 14 potential toxic elements from surface sediment samples in Kızılırmak River by using geographical information systems software, ecotoxicological indices, and multivariate statistical analysis. The results indicated that enrichment factor, Contamination factor and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) values were higher in the areas where domestic and industrial wastewater was discharged. For elements such as Cr, Ni, Cu, Zn, As, Pb, their potential ecological risk index values indicate that they have “low potential ecological risk” in all stations. For Hg metal, it is indicated as “Moderate potential ecological risk,” whereas for Cd, it is indicated as “Noticeable potential ecological risk.” Integrated pollution index (IPI), Toxic units (TUs) and Pollution load index (PLI) values were the highest in S1 station (IPI = 1.35, TUs = 10.02, PLI = 1.06) and were determined as the lowest in S6 station (IPI = 0.88, TUs = 6.38, PLI = 0.70). Ecotoxic risk level in river sediment (TRI); was at the level of “considerable toxic risk” in S1, S2, S3 stations, whereas it was at the level of “moderate toxic risk” in S4, S5, S6 stations. Total hazard index value being slightly above 1 (1.10) for children means that separate or combined effect of 14 metals present in the sediment may cause health risk even at a low rate. For adults, although potential noncarcinogenic health effects are not expected, lifetime carcinogenic risk values in terms of Cr and As might have a potential to cause carcinogenic risk even at low rate.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Akbulut A, Akbulut NE (2010) The study of heavy metal pollution and accumulation in water, sediment, and fish tissue in Kizilirmak River Basin in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 167:521–526
Akbulut NE, Tuncer AM (2011) Accumulation of heavy metals with water quality parameters in Kızılırmak River Basin (Delice River) in Turkey. Environ Monit Assess 173(1):387–395
Alkan N, Alkan A, Eruz C (2018) Determination of metals in water and sediment samples of the Surmene River, Turkey. Green Energy Technol 2:175–181
Antunes IMHR, Albuquerque MTD, Roque N (2018) Spatial environmental risk evaluation of potential toxic elements in stream sediments. Environ Geochem Health 40(6):2573–2585
Aras S, Findik O, Kalipci E, Sahinkaya S (2017) Assessment of concentration physicochemical parameters and heavy metals in Kızılırmak river, Turkey. Desalin Water Treat 72:328–334
Avumadi AM, Probst J (2019) Trace element distribution and enrichment in the stream sediments of the Lake Togo watersheds (South of Togo). Adv Ecol Environ Res 1:87–114
Aydin H, Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y, Soylu EN (2020) Assessment of water quality of streams in northeast Turkey by water quality index and multiple statistical methods. Environ Forensics 1–18.
Abbasi MN, Tufail M, Chaudhry MM (2013) Assessment of heavy elements in suspended dust along the Murree Highway near capital city of Pakistan. World Appl Sci J 21(9):1266–1275
Bakan G, Cuce H (2007) Water/sediment quality assessment and SOD studies in Kizilirmak River at the Black Sea coast of Turkey. Fresenius Environ Bull 16(12A):1544–1550
Bakan G, Ozkoc HB (2007) An ecological risk assessment of the impact of heavy metals in surface sediments on biota from the mid-Black Sea coast of Turkey. Int J Environ Stud 64:45–57
Bakan G, Özkoç HB, Tülek S, Cüce H (2010) Integrated environmental quality assessment of the Kızılırmak River and its coastal environment. Turk J Fish Aquat Sci 10(4):453–462
Barbieri M (2016) The importance of enrichment factor (EF) and geoaccumulation index (Igeo) to evaluate the soil contamination. J Geol Geophys 5(1):1–4
Cao Y, Lei K, Zhang X, Xu L, Lin C, Yang Y (2018) Contamination and ecological risks of toxic metals in the Hai River, China. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 164:210–218
Canpolat Ö, Varol M, Okan ÖÖ, Eriş KK, Çağlar M (2020) A comparison of trace element concentrations in surface and deep water of the Keban Dam Lake (Turkey) and associated health risk assessment. Environ Res 190:110012
Cüce H, Kalipci E, Tas B, Yılmaz M (2020) Evaluation of the ımpacts on water quality from meteorological changes due to differences in altitude by GIS: a comparison for two morphologically different lakes. Black Sea J Sci 10(1):1–26
Chai L, Li H, Yang Z, Min X, Liao Q, Liu Y, Men S, Yan Y, Xu J (2017) Heavy metals and metalloids in the surface sediments of the Xiangjiang River, Hunan, China: distribution, contamination, and ecological risk assessment. Environ Sci Pollut Res 24:874–885
Chen CW, Kao CM, Chen CF, Dong CD (2007) Distribution and accumulation of heavy metals in the sediments of Kaohsiung Harbor. Taiwan Chemosph 66(8):1431–1440
Dundar MS, Altundag H, Eyupoglu V, Keskin SC, Tutunoglu C (2012) Determination of heavy metals in lower Sakarya river sediments using a BCR-sequential extraction procedure. Environ Monit Assess 184:33–41
Eker ÇS (2020) Distinct contamination indices for evaluating potentially toxic element levels in stream sediments: a case study of the Harşit Stream (NE Turkey). Arab J Geosci 13(22):1–18
Fural Ş, Kükrer S, Cürebal I (2020) Geographical information systems based ecological risk analysis of metal accumulation in sediments of Ikizcetepeler Dam Lake (Turkey). Ecol Indicat 119:106784
IARC (International Agency for Research on Cancer) (2012) A Review of human carcinogens: personal habits and ındoor combustions. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans.
Iqbal J, Tirmizi SA, Shah MH (2013) Statistical apportionment and risk assessment of selected metals in sediments from Rawal Lake (Pakistan). Environ Monit Assess 185(1):729–743
Jafarabadi AR, Bakhtiyari AR, Toosi AS, Jadot C (2017) Spatial distribution, ecological and health risk assessment of heavy metals in marine surface sediments and coastal seawaters of fringing coral reefs of the Persian Gulf. Iran Chemosph 185:1090–1111
Kalipci E, Cüce H, Toprak S (2017) Spatial analysis of surface water quality of damsa dam (Nevşehir) by geographic information systems. Karaelmas Sci Eng J 7(1):312–319
Karadavut S, Delibas L, Kalipci E, Ozdemir C, Karadavut IS (2012) Evaluation of irrigation water quality of Aksaray region by using geographic information system. Carpath J Earth Environ Sci 7(2):171–182
Kalipci E, Varol S, Cüce H (2020) Evaluation of water quality and trophic condition of Yuvacık (Kocaeli) drinking water dam reservoir. Mugla J Sci Technol 6(2):128–139
Kırıs E, Baltas H (2020) Assessing pollution levels and health effects of heavy metals in sediments around Cayeli copper mine area, Rize, Turkey. Environ Forensics 22:372–384
Liu CW, Lin KH, Kuo YM (2003) Application of factor analysis in the assessment of groundwater quality in a blackfoot disease area in Taiwan. Sci Total Environ 313(1–3):77–89
Li C, Sun M, Song C, Tao P, Yin Y, Shao M (2017) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in the sediments of the shuangtaizi estuary using multivariate statistical techniques. Soil Sediment Contam 20(4):370–386
Loring DH (1991) Normalization of heavy-metal data from estuarine and coastal sediments. ICES J Mar Sci 48(1):101–115
MacDonald DD, Ingersoll CG, Berger TA (2000) Development and evaluation of consensus-based sediment quality guidelines for freshwater ecosystems. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 39:20–31
Maanan Mohamed Saddik M, Maanan Mehdi Chaibi M, Assobhei O, Zourarah B (2015) Environmental and ecological risk assessment of heavy metals in sediments of Nador lagoon, Morocco. Ecol Indic 48:616–626
Morillo J, Usero J, Gracia I (2002) Heavy metal fractionation in sediments from the Tinto River (Spain). Int J Environ Anal Chem 82:245–257
Ozdemir O (2016) Application of multivariate statistical methods for water quality assessment of karasu-sarmisakli creeks and Kizilirmak river in Kayseri. Turk Pol J Environ Stud 25(3):1149–1160
Pedersen F, Bjørnestad E, Andersen HV, Kjølholt J, Poll C (1998) Characterization of sediments from Copenhagen Harbour by use of biotests. Water Sci Technol 37(6–7):233–240
Suresh G, Ramasamy V, Meenakshisundaram V, Venkatachalapathy R, Ponnu-samy V (2011) Influence of mineralogical and heavy metal composition on natural radionuclide contents in the river sediments. Appl Radiat Isot 69:1466–1474
Song J, Liu Q, Sheng Y (2019) Distribution and risk assessment of trace metals in riverine surface sediments in gold mining area. Environ Monit Assess 191(3):1–13
Sari E, Cukrov N, Frančišković-Bilinski S, Kurt MA, Mihri H (2016) Contamination assessment of ecotoxic metals in recent sediments from the Ergene River, Turkey. Environ Earth Sci 75:1051–1064
Solgi E, Abbas ES, Alireza RB, Hadipour M (2012) Soil contamination of metals in the three industrial estates, Arak. Iran Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 88:634–638
Siddiqui E, Pandey J (2019) Assessment of heavy metal pollution in water and surface sediment and evaluation of ecological risks associated with sediment contamination in the Ganga River: a basin-scale study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 26:10926–10940
Türkmen M, Türkmen A, Tepe Y, Töre Y, Ateş A (2009) Determination of metals in fish species from Aegean and Mediterranean seas. Food Chem 113(1):233–237
Türkmen A, Akbulut S (2015) Heavy metal pollution in water and sediment from disembogue points of some creeks along Giresun coast. Turk J Agricult-Food Sci Technol 3(9):707–714
Turekian KK, Wedepohl KH (1961) Distribution of the elements in some major units of the earth’s crust. Geol Soc Am Bull 72(2):175–192
Tomlinson DL, Wilson JG, Harris CR, Jeffrey DW (1980) Problem in heavy metals in estuaries and the formation of a pollution index. Helgol Wiss Meeresunlter 33(1–4):566–575
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y (2019) Water quality and sediment contamination assessment of Pazarsuyu Stream, Turkey using multivariate statistical methods and pollution indicators. Int Soil Water Conserv Res 7(1):47–56
Ustaoğlu F (2020) Ecotoxicological risk assessment and source identification of heavy metals in the surface sediments of Çömlekci stream, Giresun. Turk Environ Forensics 22(1–2):130–142
Ustaoglu F, Islam MS (2020) Potential toxic elements in sediment of some rivers at Giresun, Northeast Turkey: a preliminary assessment for ecotoxicological status and health risk. Ecol Indicat 113:106237
Ustaoğlu F, Tepe Y (2018) Determination of the sediment quality of Pazarsuyu Stream (Giresun, Turkey) by multivariate statistical methods. Turk J Agricult-Food Sci Technol 6(3):304–312
USEPA (2004) Risk Assessment Guidance for Superfund (RAGS). Volume I. Human Health Evaluation Manual (HHEM). Part E. Supplemental Guidance for Dermal Risk Assessment. Washington, DC: United States Environmental Protection Agency.
Voza D, Vukovic M, Takic L, Nikolic D, Mladenovic-Ranisavljevic I (2015) Application of multivariate statistical techniques in the water quality assessment of Danube river, Serbia. Arch Environ Prot 41:96–103
Varol M (2020) Environmental, ecological and health risks of trace metals in sediments of a large reservoir on the Euphrates River (Turkey). Environ Res 187:109664
Varol M (2011) Assessment of heavy metal contamination in sediments of the Tigris River (Turkey) using pollution indices and multivariate statistical techniques. J Hazard Mater 195:355–364
Wang YB, Liu CW, Wang SW (2015) Characterization of heavy-metal-contaminated sediment by using unsupervised multivariate techniques and health risk assessment. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 113:469–476
Wang J, Baskaran M, Kumar A, Bilhan O, Miller CJ (2021) Reconstruction of temporal variations of metal concentrations using radiochronology (239+ 240 Pu and 137 Cs) in sediments from Kizilirmak River. Turk J Paleolimnol 65(1):137–149
Wei B, Yang L (2010) A review of heavy metal contaminations in urban soils, urban road dusts and agricultural soils from China. Microchem J 94(2):99–107
Walker TR, MacAskill D, Weaver P (2013) Environmental recovery in Sydney Harbour, Nova Scotia: evidence of natural and anthropogenic sediment capping. Mar Pollut Bull 74(1):446–452
Walker TR, Willis R, Gray T, MacLean B, Mcmillan S, Leroy M, Smith M (2015) Ecological risk assessment of sediments in sydney harbour, Nova Scotia, Canada. Soil Sediment Contam Int J 24(5):471–493
Williams JA, Antoine J (2020) Evaluation of the elemental pollution status of Jamaican surface sediments using enrichment factor, geoaccumulation index, ecological risk and potential ecological risk index. Mar Pollut Bull 157:111288
Zhang G, Bai J, Zhao Q, Lu Q, Jia J, Wen X (2016) Heavy metals in wetland soils along a wetland-forming chronosequence in the Yellow River Delta of China: levels, sources and toxic risks. Ecol Ind 69:331–339
Zhang Z, Lu Y, Li H, Tu Y, Liu B, Yang Z (2018) Assessment of heavy metal contamination, distribution and source identification in the sediments from the Zijiang River, China. Sci Total Environ 645:235–243
Zhang H, Walker TR, Davis E, Ma G (2019) Spatiotemporal characterization of metals in small craft harbour sediments in Nova Scotia, Canada. Mar Pollut Bull 140:493–502
Zhang J, Liu CL (2002) Riverine composition and estuarine geochemistry of particulate metals in China-weathering features, anthropogenic impact and chemical fluxes. Estuarine Coast Shelf Sci 54(6):1051–1070
Zhuang S, Lu X, Yu B, Fan X, Yang Y (2021) Ascertaining the pollution, ecological risk and source of metal (loid) s in the upstream sediment of Danjiang River. China. Ecol Indicat 125:107502
Acknowledgements
This study was carried out with the laboratory support of Nevsehir HBV University and Sinop University, Scientific and technological researches application and research center (SUBITAM). We would like to thank İlknur KAYNAR, undergraduate student, for her help in the laboratory and field work at the first stage of the study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors state that they have no known competing financial interests or personal ties that could have influenced the research presented in this study.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Supplementary Information
Below is the link to the electronic supplementary material.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Cüce, H., Kalipci, E., Ustaoglu, F. et al. Ecotoxicological health risk analysis of potential toxic elements accumulation in the sediments of Kızılırmak River. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 10759–10772 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03869-z
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03869-z