Abstract
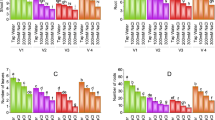
Salinity represents one of the most abiotic stress factors affecting plant growth and production around the world. In this experiment, in vitro multiplication of Musa acuminata has been standardized. The physiological and morphological responses of the crop against salt stress have been identified. To study the effects of salicylic acid (SA) and abscisic acid (ABA) on salt stress in banana (Musa acuminata), the explants were treated with varying SA and ABA concentrations and incubated on MS media having various concentrations (0, 50, 100, 150, 200, 250, 300 mM) of NaCl in vitro; hence, their physiological and morphological responses were identified. Two months after, propagation rate, rise of fresh weight, comparative water content, chlorophyll level and proline accumulations were estimated and examined. The outcomes demonstrated that with developing degrees of NaCl, spread rate, new weight, relative water substance and chlorophyll were intriguingly diminished. Use of SA and ABA assisted with impacts of salt insufficiency on banana recovers in vitro and in vivo condition. This work includes image processing and Internet of Things to screen the plant and to gather the natural factors.












Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adams P, Thomas JC, Vernon DM, Bohnert HJ, Jensen RG (1992) Distinct cellular and organismic responses to salt stress. Plant Cell Physiol 33:1215–1223
Ashraf M, Hasnain S, Berge O (2006) Effect of exo-polysaccharides producing bacterial inoculation on growth of roots of wheat (Triticum aestivum L.) plants grown in a salt-affected soil. Int J Environ Sci Technol 3:43–51
Bates LS, Waldren RP, Teare ID (1973) Rapid determination of free proline for water stress studies. J Plant Soil 39:205–207
Bibaj E, Lysigaki K, Nolan JW et al (2019) Activated carbons from banana peels for the removal of nickel ions. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:667–680
Borsani O, Valpuesta V, Botella MA (2001) Evidence for a role of salicylic in the oxidative damage generated by NaCl and osmotic stress in Arabidopsis seedlings. J Plant Physiol 126:1024–1030
Braganza CAB Mendoza AMD (2019) The development of a Larvicidal tablet using Saba banana (Musa acuminata x balbisiana) peel extract. In: IEEE integrated STEM education conference, Princeton, NJ, USA, pp 15–17
Cai J, Guan Y, Li F et al (2019) Biomass and pigments production of a newly isolated photosynthetic bacterium Ectothiorhodospira shaposhnikovii P2 from saline wastewater. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:7487–7496
Cherian S, Reddy MP (2003) Evaluation of NaCl tolerance in the callus cultures of Suaeda nudiflora. Moq. Biol Plant 46:193–198
Cote ADF, Teisson C (1993) Comparison of methods of liquid medium culture for banana micro-propagation: effects of temporary immersion of explants. Plant Cell Tissue Organ Cult 32:55–60
Delavari PM, Baghizadeh A, Enteshari SH, Kalantari KhM, Yazdanpanah A et al (2010) The effects of salicylic on some of biochemical and morphological characteristic of Ocimum Basilicucm under salinity stress. Aust J Basic Appl Sci 4:4832–4845
Endris S, Mohammad MJ (2007) Nutrient acquisition and yield response of Barley exposed to salt stress under different levels of potassium nutrition. Int J Environ Sci Technol 4:323–330
Fu Y, Meng XJ, Lu NN et al (2019) Characteristics changes in banana peel coagulant during storage process. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:7747–7756
Getachew T, Hussen A, Rao VM (2015) Defluoridation of water by activated carbon prepared from banana (Musa paradisiaca) peel and coffee (Coffea arabica) husk. Int J Environ Sci Technol 12:1857–1866
Gotovtsev PM, Dyakov AV (2016) Biotechnology and Internet of Things for green smart city application. In: IEEE 3rd world forum on Internet of Things (WF-IoT), Reston, VA, pp 542–546
Gotovtsev PM, Konova IA (2019) Synthetic biology as a bridge to integration of bio objects into Internet of Things. In: International conference on sensing and instrumentation in IoT Era (ISSI), Lisbon, Portugal, pp 1–6
Gsangaya KR, Hajjaj SSH, Sultan MTH et al (2020) Portable, wireless, and effective internet of things-based sensors for precision agriculture. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:3901–3916
Hasegawa PM, Bressan RA, Zhu JK, Bohnert HJ (2000) Plant cellular and molecular responses to high salinity. Plant Mol Biol 51:463–499
Hongxia M, Yuan WJL, Caihong J, Wei Hu, Peiguang S et al (2014) Molecular cloning and expression analysis of the MaASR1 gene in banana and functional characterization under salt stress. Electron J Biotechnol 17:287–295
Jain SM (2001) Tissue culture-derived variation in crop improvement. Euphytica 118:153–166
Khoshmanzar E, Aliasgharzad N, Neyshabouri MR et al (2020) Effects of Trichoderma isolates on tomato growth and inducing its tolerance to water-deficit stress. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:869–878
Korkmaz A, Korkmaz Y, Demirkıran AR (2010) Enhancing chilling stress tolerance of pepper seedlings by exogenous application of 5-aminolevulinic. Environ Exp Bot 67:495–501
Liao W, Ochoa D, Zhao Y, Villegas Rugel GM, Philips W (2018) Banana disease detection by fusion of close range hyperspectral image and high-resolution Rgb image. In: IEEE international geoscience and remote sensing symposium, Valencia, pp 1744–1747
Liu W, Yu XZ, Lei SY et al (2020) Assessment of ammonium fertilization as a stimulus for proline accumulation in Oryza sativa L. during cyanide assimilation. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:2811–2818
Lutts S, Majerus V, Kinet JM (1999) NaCl effects on proline metabolism in rice (Oryza sativa) seedlings. Physiol Plant 105:450–458
Madukasi EI, Chunhua H, Zhang G (2011) Isolation and application of a wild strain photosynthetic bacterium to environmental waste management. Int J Environ Sci Technol 8:513–522
Munns R, Tester M (2008) Mechanisms of salinity tolerance. Ann Rev Plant Biol 59:651–681
Neumann P (1997) Salinity resistance and plant growth revisited. Plant Cell Environ 20:1193–1198
Ramakala R, Thayammal S, Ramprakash A, Muneeswaran V (2017) Impact of ICT and IOT strategies for water sustainability: a case study in Rajapalayam-India. In: IEEE international conference on computational intelligence and computing research (ICCIC), Coimbatore, pp 1–4
Rani D, Kumar N, Bhushan B (2019) Implementation of an automated irrigation system for agriculture monitoring using IoT communication. In: International conference on signal processing, computing and control (ISPCC), Solan, India, pp 138–143
Rezapour I, Jasemizad T, Ayatollahi M et al (2016) The presentation of a new inhibitor to prevent enzymatic browning in mushroom, banana, and apple. Int J Environ Sci Technol 13:1109–1122
Rizvi A, Khan MS (2019) Heavy metal-mediated toxicity to maize: oxidative damage, antioxidant defence response and metal distribution in plant organs. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:4873–4886
Saha HN et al (2017) Internet of Things (IoT) on bio-technology. In: 8th annual industrial automation and electromechanical engineering conference (IEMECON), Bangkok, pp 364–369
Sharif P, Seyedsalehi M, Paladino O et al (2018) Effect of drought and salinity stresses on morphological and physiological characteristics of canola. Int J Environ Sci Technol 15:1859–1866
Shavalikohshori O, Zalaghi R, Sorkheh K et al (2020) The expression of proline production/degradation genes under salinity and cadmium stresses in Triticum aestivum inoculated with Pseudomonas sp. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:2233–2242
Uzaribara E, Nachegowda V, Ansar H, Sathyanarayana BN, Taj A (2015) In vitro propagation of red banana (Musa acuminata). The Bioscan 10:125–129
Verma E, Singh S, Niveshika, et al (2019) Salinity-induced oxidative stress-mediated change in fatty s composition of cyanobacterium Synechococcus sp. PCC7942. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:875–886
Windsperger B, Windsperger A, Bird DN et al (2019) Greenhouse gas emissions due to national product consumption: from demand and research gaps to addressing key challenges. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:1025–1038
Yamaguchi N, Sugita R, Miki A, Takemura N, Kawabata J et al (2006) Gastrointestinal Candida colonisation promotes sensitisation against food antigens by affecting the mucosal barrier in mice. Pub Med 55:954–960
Yuli M, Puig R, Fuentes MA et al (2019) Eco-innovation in garden irrigation tools and carbon footprint assessment. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:2937–2950
Zhang X et al (2018) Distributed compressive sensing augmented wideband spectrum sharing for cognitive IoT. IEEE Internet of Things J 5(4):3234–3245
Zhao S, Liu X, Duo L (2020) Effects of different size fractions of municipal solid waste compost on growth of Lolium perenne L. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:3705–3714
Acknowledgements
Authors would like to thank Bannari Amman Institute of Technology, India to carry out this research work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
Authors declared that no conflicts of interest for this research article. This research work is not funded by any funding agencies.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Manojkumar, P., Dheepanchakkravarthy, A., Senthil Kumar, P. et al. Effect of physiological and morphological response of Musa acuminata under stress condition with different salinity levels using IoT. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 5227–5238 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03385-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03385-0