Abstract
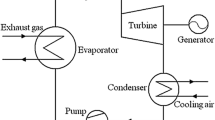
In power plants, a special type of oil is used for the lubrication and cooling of turbine bearings. The temperature of the cooling oil used for heat extraction from the bearings varies between 78 and 90 °C. Using waste heat from this oil will be a great advantage in terms of heat recovery. The overall thermal efficiency of gas turbine in power plants will also increase using this heat. In the literature, there are studies on organic Rankine cycle systems, but it has been seen that there are no studies on the use of waste heat from gas turbine bearings. In this paper, low-temperature organic Rankine cycle using waste heat from gas turbine bearings for different working conditions was investigated as experimentally. For this purpose, a prototype experiment setup was designed and thermodynamic analyses were carried out experimentally. Experimental organic Rankine cycle system was designed to operate in the temperature range of 78–90 °C using the waste heat in the lubricating oil. R134a was used as the working fluid in the prototype organic Rankine cycle system. The thermal efficiency, turbine expansion ratio and turbine power of the prototype organic Rankine cycle system were determined depending on different waste heat source temperatures and working fluid volumetric flow rates. According to experimental results for prototype organic Rankine cycle system, the highest thermal efficiency, turbine expansion ratio and turbine power are 6.84%, 1.94 and 1.22 kW, respectively, at a waste heat source temperature of 86.5 °C and volumetric flow rate of working fluid is 4.7 L/min.





Similar content being viewed by others
Abbreviations
- \({\text{c}}_{{\text{p}}}\) :
-
Specific heat, [kJ/kg K]
- rt :
-
Expander expansion ratio
- h:
-
Enthalpy, [kJ/kg]
- P:
-
Pressure, [kPa]
- \({\dot{\text{m}}}\) :
-
Mass flow rate, [kg/s]
- \({\dot{\text{v}}}\) :
-
Volumetric flow rate, [L/min]
- \({\dot{\text{Q}}}\) :
-
Heat transfer rate, [kW]
- \(\nu\) :
-
Specific volume, [m3/kg]
- \({\dot{\text{W}}}\) :
-
Work, [kW]
- \({\upeta }\) :
-
Thermal efficiency
- I:
-
Current intensity, [A]
- \({\text{n}}\) :
-
Expander shaft rotation speed, [rpm]
- G:
-
Electrical power generation, [W]
- V:
-
Voltage, [V]
- BPHE:
-
Brazed plate heat exchanger
- Cond:
-
Condenser
- Evap:
-
Evaporator
- O:
-
Outlet
- İ:
-
Inlet
- hst:
-
Heat source temperature
- wf:
-
Working fluid
- wfv:
-
Fluid flow rate
- t:
-
Turbine (expander)
- p:
-
Pump
- th:
-
Thermal
- the:
-
Thermal effective
References
Ahmed A, Esmaeil KK, Irfan MA, Al-Mufadi FA (2018) Design methodology of organic Rankine cycle for waste heat recovery in cement plants. Appl Therm Eng 129:421–430. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.10.019
Alshammari F, Pesyridis A, Karvountzis-Kontakiotis A, Franchetti B, Pesmazoglou Y (2018) Experimental study of a small scale organic Rankine cycle waste heat recovery system for a heavy duty diesel engine with focus on the radial inflow turbine expander performance. Appl Energy 215:543–555. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2018.01.049
Bonk CD, Laux C, Rödder M, Neef M (2017) Design of a 1 KW organic Rankine cycle for teaching and research issues. Energy Procedia 129:931–938. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.09.117
Bracco R, Clemente S, Micheli D, Reini M (2013) Experimental tests and Modelization of a domestic-scale ORC (Organic Rankine Cycle). Energy 58:107–116. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2012.12.016
Chul JH, Taylor L, Krumdieck S (2015) An experimental and modelling study of a 1 kW organic Rankine cycle unit with mixture working fluid. Energy 81:601–614. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.energy.2015.01.003
Guangbin L, Yuanyang Z, Qichao Y, Le W, Bin T, Liansheng L (2013) Theoretical and Experimental Research on Scroll Expander Used in Small Scale Organic Rankine Cycle System. Proc Inst Mech Eng, Part E: J Process Mech Eng 229:25–35. https://doi.org/10.1177/0954408913506701
Hoque SME, (2011) Experimental Investigation of an R134a Based Organic Rankine Cycle. Master Thesis, pp. 115, Canada
Jradi M, Li J, Liu H, Riffat S (2014) Micro-Scale ORC- Based Combined Heat and Power System Using a Novel Scroll Expander. Int J Low-Carbon Technol 9:91–99. https://doi.org/10.1093/ijlct/ctu012
Kane M, Larrain D, Favrat D, Allani Y (2003) Small hybrid solar power system. Energy 28:1427–1443. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0360-5442(03)00127-0
Ko HJ, Kim SW, Han CH, Kim KH (2013) Effects of source temperature on thermodynamic performance of transcritical organic rankine cycle. Int J Mater, Mechan Manuf 1(1):55–59. https://doi.org/10.7763/IJMMM.2013.V1.12
Li L, Ge YT, Luo X, Tassou SA (2017) Experimental investigations into power generation with low grade waste heat and R245fa organic Rankine cycles (ORCs). Appl Therm Eng 115:815–824. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.01.024
Lu Y, Roskilly AP, Smallbone A, Yu X, Wang Y (2017) Design and parametric study of an organic Rankine cycle using a scroll expander for engine waste heat recovery. Energy Procedia 105:1420–1425. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.egypro.2017.03.530
Mondejar ME, Ahlgren F, Thern M, Genrup M (2017) Quasi-steady state simulation of an organic Rankine cycle for waste heat recovery in a passenger vessel. Appl Energy 185:1324–1335. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apenergy.2016.03.024
Muhammad U, Imran M, Lee DH, Park BS (2015) Design and experimental Investigation of a 1 kW organic Rankine cycle system using R245fa as working fluid for low-grade waste heat recovery from steam. Energy Convers Manag 103:1089–1100. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2015.07.045
Seyedkavoosi S, Javan S, Kota K (2017) Exergy-based optimization of an organic Rankine cycle (ORC) for waste heat recovery from an internal combustion engine (ICE). Appl Therm Eng 126:447–457. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2017.07.124
Tarique M.A, (2011) Experimental Investigation of Scroll Based Organic Rankine Systems. Master Thesis, pp.165, Canada
Turunen-Saaresti T, Uusitalo A, Honkatukia J (2017) Design and testing of high Temperature micro-ORC test stand using Siloxane as working fluid. Sch Energy Syst, Finland J Phy: Conf Series 821:012024
Velez F, Chejne F, Quijano A (2014) Thermodynamic analysis of a in an Organic Rankine Cycle for power generation from low temperature sources, Dyna, 81(185) 153–159. https://doi.org/10.15446/dyna.v81n185.37598
Walraven D, Laenen B, D’haeseleer W (2014) Comparison of shell-and-tube with plate heat exchangers for the use in low-temperature organic Rankine cycles. Energy Convers Manage 87:227–237. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.enconman.2014.07.019
Yang SC, Hung TC, Feng YQ, Wu CJ, Wong KW, Huang KC (2017) Experimental investigation on a 3 kW organic Rankine cycle for low-grade waste heat under different operation parameters. Appl Therm Eng 113:756–764. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2016.11.032
Yasa T, (2017) Thermodynamic evaluation of energy recovery system for heavy duty diesel engine by using organic rankine cycle. Anadolu University of Sciences & TechnologyA ,Applied Sciences & Engineering, 18(3), 573–583. https://doi.org/10.18038/aubtda.303809
Zanelli R, Favrat D (1994) Experimental Investigation of a Hermetic Scroll Expander-Generator, International Compressor Engineering Conference. A.B.D, Paper, p 1021
Zhou X, Cui P, Wang X, He L (2017) Thermal investigations into an organic Rankine cycle (ORC) system utilizing low grade waste heat sources. Procedia Eng 205:4142–4148. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.proeng.2017.10.157
Acknowledgments
Project support or financial support have not been received for this study.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Shahid Hussain.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
İpek, O., Mohammedsalih, M.M., Gürel, B. et al. Experimental investigation of low-temperature organic Rankine cycle using waste heat from gas turbine bearings for different conditions. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 19, 1519–1530 (2022). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03172-x
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-021-03172-x