Abstract
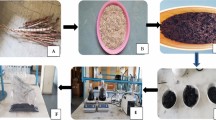
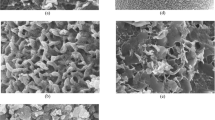
This study aims to investigate the optimal conditions for the elimination of albendazole (veterinary drug) by adsorption on activated carbon, prepared from a plant waste (pericarp of cork oak acorns). This low cost adsorbent was characterized by determining the Brunauer–Emmett–Teller surface area, morphology by using scanning electron microscope and surface chemical properties with Fourier transformed infrared spectroscopy. The pH of solution does not highly affect the adsorption of albendazole, a neutral environment (6.0–7.5) was more favorable. Responses surface methodology, namely Doehlert design was applied to model and optimize the adsorption process. The studied parameters are the pollutant concentration, activated carbon dose and temperature. Two responses were considered, albendazole elimination yield and adsorption capacity. The maximum elimination yield and adsorption capacity were 99.97% and 137.2 mg g−1, respectively. Analysis of variances and Mallows statistic criteria were applied to validate both predictive regression models. Multi-objective methodology using desirability approach was utilized to determine the optimal conditions, which are 50 mg L −1 of pollutant concentration; 1.6 g L −1 of adsorbent dose and 20 °C of temperature, corresponding to elimination yield of 88.8% and adsorption capacity of 82.0 mg g−1. The albendazole adsorption followed pseudo-second order kinetics. All isotherm models applied, namely, Freundlich, Langmuir, Temkin and Dubinin–Radushkevich fitted the experimental data with regression coefficient exceeding 0.930. The albendazole adsorption on the activated carbon was thermodynamically favorable. The application of Boyd’s model showed that the intraparticle diffusion was not the rate limiting step, and the adsorption process may involve several mechanisms.







Similar content being viewed by others
References
Ahmad F, Daud WMAW, Ahmad MA, Radzi R (2012) Cocoa (Theobroma cacao) shell-based activated carbon by CO2 activation in removing of Cationic dye from aqueous solution: kinetics and equilibrium studies. Chem Eng Res Des 90:1480–1490. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cherd.2012.01.017
Araujo P, Janagap S (2012) Doehlert uniform shell designs and chromatography. J Chromatogr B Chemom Chromatogr 910:14–21. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jchromb.2012.05.019
Bártíková H, Podlipná R, Skálová L (2016) Veterinary drugs in the environment and their toxicity to plants. Chemosphere 144:2290–2301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2015.10.137
Bedin KC, Souza IPAF, Cazetta AL, Spessato L, Ronix A, Almeida VC (2018) CO2-spherical activated carbon as a new adsorbent for methylene blue removal: kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic studies. J Mol Liq 269:132–139. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2018.08.020
Benredouane S, Berrama T, Doufene N (2016) Strategy of screening and optimization of process parameters using experimental design: application to amoxicillin elimination by adsorption on activated carbon. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 155:128–137. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2016.04.010
Bhomick PC, Supong A, Baruah M, Pongener C, Gogoi C, Sinha D (2020) Alizarin Red S adsorption onto biomass-based activated carbon: optimization of adsorption process parameters using Taguchi experimental design. Int J Environ Sci Technol 17:1137–1148. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-019-02389-1
Boyd GE, Adamson AW Jr, Myers LS (1947) The exchange adsorption of ions from aqueous solutions by organic zeolites. II. Kinetics. J Am Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01203a066
Callao MP (2014) Multivariate experimental design in environmental analysis. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 62:86–92. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2014.07.009
Cazetta AL, Vargas AMM, Nogami EM, Kunita MH, Guilherme MR, Martins AC, Silva TL, Moraes JCG, Almeida VC (2011) NaOH-activated carbon of high surface area produced from coconut shell: kinetics and equilibrium studies from the methylene blue adsorption. Chem Eng J 174:117–125. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2011.08.058
Charuaud L, Jarde E, Jaffrezic A, Thomas M-F, Le Bot B (2019) Veterinary pharmaceutical residues from natural water to tap water: sales, occurrence and fate. J Hazard Mater 361:169–186. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2018.08.075
Čizmić M, Ljubas D, Ćurković L, Škorić I, Babić S (2017) Kinetics and degradation pathways of photolytic and photocatalytic oxidation of the anthelmintic drug praziquantel. J Hazard Mater 323:500–512. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jhazmat.2016.04.065
Costa NR, Lourenço J, Pereira ZL (2011) Desirability function approach: a review and performance evaluation in adverse conditions. Chemom Intell Lab Syst 107:234–244. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemolab.2011.04.004
Dadou S, Berrama T, Doufene N, Zekkaoui C, Beriber A (2019) Evaluating untreated Clay’s adsorptive capacity to remove an anionic dye from aqueous solution. Arab J Sci Eng 44:9889–9903. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-019-04100-5
Derringer G, Suich R (1980) Simultaneous optimization of several response variables. J Qual Technol 12:214–219. https://doi.org/10.1080/00224065.1980.11980968
Djilani C, Zaghdoudi R, Modarressi A, Rogalski M, Djazi F, Lallam A (2012) Elimination of organic micropollutants by adsorption on activated carbon prepared from agricultural waste. Chem Eng J 189–190:203–212. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.02.059
Dolar D, Pelko S, Košutić K, Horvat AJM (2012) Removal of anthelmintic drugs and their photodegradation products from water with RO/NF membranes. Process Saf Environ Prot 90:147–152. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2011.08.007
Doufene N, Berrama T, Tahtat D, Benredouane S, Nekaa C (2018) Combination of two experimental designs to optimize the dimethylphthalate elimination on activated carbon elaborated from Arundo donax. Arab J Sci Eng. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13369-018-3531-5
Doufene N, Berrama T, Nekaa C, Dadou S (2019) Determination of adsorption operating conditions in dynamic mode on basis of batch study: application for dimethylphthalate elimination on activated carbon prepared from Arundo donax. Chem Eng Commun 206:1015–1034. https://doi.org/10.1080/00986445.2018.1542301
Gaba M, Mohan C (2016) Development of drugs based on imidazole and benzimidazole bioactive heterocycles: recent advances and future directions. Med Chem Res 25:173–210. https://doi.org/10.1007/s00044-015-1495-5
Galarneau A, Villemot F, Rodriguez J, Fajula F, Coasne B (2014) Validity of the t-plot method to assess microporosity in hierarchical micro/mesoporous materials. Langmuir 30:13266–13274. https://doi.org/10.1021/la5026679
Gao Y, Yue Q, Gao B, Sun Y, Wang W, Li Q, Wang Y (2013) Preparation of high surface area-activated carbon from lignin of papermaking black liquor by KOH activation for Ni(II) adsorption. Chem Eng J 217:345–353. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2012.09.038
George AM, Tembhurkar AR (2020) Taguchi experimental design for adsorptive removal of fluoride from water using novel Ficus Glomerata Bark-developed biosorbent. Int J Environ Sci Technol. https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02787-w
Geszke-Moritz M, Moritz M (2016) APTES-modified mesoporous silicas as the carriers for poorly water-soluble drug. Modeling of diflunisal adsorption and release. Appl Surf Sci 368:348–359. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.02.004
Han Q, Wang J, Goodman BA, Xie J, Liu Z (2020) High adsorption of methylene blue by activated carbon prepared from phosphoric acid treated eucalyptus residue. Powder Technol 366:239–248. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.powtec.2020.02.013
Harrington EC (1965) The desirability function. Industrial quality control, pp 494–498
Horvat AJM, Babić S, Pavlović DM, Ašperger D, Pelko S, Kaštelan-Macan M, Petrović M, Mance AD (2012) Analysis, occurrence and fate of anthelmintics and their transformation products in the environment. TrAC Trends Anal Chem 31:61–84. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.trac.2011.06.023
Hu P, Guo C, Zhang Yan, Lv J, Zhang Yuan, Xu J (2019) Occurrence, distribution and risk assessment of abused drugs and their metabolites in a typical urban river in north China. Front Environ Sci Eng 13:56. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11783-019-1140-5
Kuppusamy S, Thavamani P, Megharaj M, Venkateswarlu K, Lee YB, Naidu R (2016) Oak (Quercus robur) Acorn Peel as a low-cost adsorbent for hexavalent chromium removal from aquatic ecosystems and industrial effluents. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-016-2760-z
Langmuir I (1916) The constitution and fundamental properties of solids and liquids. Part I. solids. J Am Chem Soc. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja02268a002
Liang Q, Luo H, Geng J, Chen J (2018) Facile one-pot preparation of nitrogen-doped ultra-light graphene oxide aerogel and its prominent adsorption performance of Cr(VI). Chem Eng J 338:62–71. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.cej.2017.12.145
López FA, Centeno TA, García-Díaz I, Alguacil FJ (2013) Textural and fuel characteristics of the chars produced by the pyrolysis of waste wood, and the properties of activated carbons prepared from them. J Anal Appl Pyrolysis 104:551–558. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jaap.2013.05.014
Martínez-Legaz JE (2014) On Weierstrass extreme value theorem. Optim Lett 8:391–393. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11590-012-0587-0
Mébarki M, Hachem K, Harche MK (2019) Lignocellulosic fraction of the pericarps of the acorns of Quercus suber and Quercus ilex: isolation, characterization, and biosorption studies in the removal of copper from aqueous solutions. Pol J Chem Technol 21:40–47. https://doi.org/10.2478/pjct-2019-0028
Meneghel AP, Gonçalves AC, Rubio F, Dragunski DC, Lindino CA, Strey L (2013) Biosorption of cadmium from water using Moringa (Moringa oleifera Lam.) seeds. Water Air Soil Pollut. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11270-012-1383-2
Nourmoradi H, Moghadam KF, Jafari A, Kamarehie B (2018) Removal of acetaminophen and ibuprofen from aqueous solutions by activated carbon derived from Quercus Brantii (Oak) acorn as a low-cost biosorbent. J Environ Chem Eng 6:6807–6815. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2018.10.047
Oh SJ, Park J, Lee MJ, Park SY, Lee J-H, Choi K (2006) Ecological hazard assessment of major veterinary benzimidazoles: acute and chronic toxicities to aquatic microbes and invertebrates. Environ Toxicol Chem 25:2221. https://doi.org/10.1897/05-493R.1
Pandiarajan A, Kamaraj R, Vasudevan Sudharshan, Vasudevan Subramanyan (2018) OPAC (orange peel activated carbon) derived from waste orange peel for the adsorption of chlorophenoxyacetic acid herbicides from water: adsorption isotherm, kinetic modelling and thermodynamic studies. Bioresour Technol 261:329–341. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.biortech.2018.04.005
Paulo F, Santos L (2017) Design of experiments for microencapsulation applications: a review. Mater Sci Eng C 77:1327–1340. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.msec.2017.03.219
Pausas JG, Woodlands CO (2009) Chapter I. The tree. In: Aronson J, Pereira JS, Pausas S (eds) Cork oak woodlands on the edge. Ecology, adaptive management, and restoration, 1st ed. Island Press, Washinton, pp 11-21
Pintor AMA, Ferreira CIA, Pereira JC, Correia P, Silva SP, Vilar VJP, Botelho CMS, Boaventura RAR (2012) Use of cork powder and granules for the adsorption of pollutants: a review. Water Res 46:3152–3166. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.watres.2012.03.048
Porto RS, Rodrigues-Silva C, Schneider J, Rath S (2019) Benzimidazoles in wastewater: analytical method development, monitoring and degradation by photolysis and ozonation. J Environ Manag 232:729–737. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2018.11.121
Prchal L, Podlipná R, Lamka J, Dědková T, Skálová L, Vokřál I, Lecová L, Vaněk T, Szotáková B (2016) Albendazole in environment: faecal concentrations in lambs and impact on lower development stages of helminths and seed germination. Environ Sci Pollut Res 23:13015–13022. https://doi.org/10.1007/s11356-016-6472-0
Rathod DM, Patel KR, Mistri HN, Jangid AG, Shrivastav PS, Sanyal M (2016) Liquid chromatography–tandem mass spectrometry method for simultaneous determination of albendazole and albendazole sulfoxide in human plasma for bioequivalence studies. J Pharm Anal 6:226–234. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jpha.2016.02.002
Reichenberg D (2002) Properties of ion-exchange resins in relation to their structure. III. Kinetics of exchange. J Am Chem Soc 75:589–597. https://doi.org/10.1021/ja01099a022
Rivera-Utrilla J, Sánchez-Polo M, Ferro-García MÁ, Prados-Joya G, Ocampo-Pérez R (2013) Pharmaceuticals as emerging contaminants and their removal from water. A review. Chemosphere 93:1268–1287. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chemosphere.2013.07.059
Shin HS, Kim J-H (2016) Isotherm, kinetic and thermodynamic characteristics of adsorption of paclitaxel onto Diaion HP-20. Process Biochem 51:917–924. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.procbio.2016.03.013
Tezcan Un U, Ates F, Erginel N, Ozcan O, Oduncu E (2015) Adsorption of Disperse Orange 30 dye onto activated carbon derived from Holm Oak (Quercus Ilex) acorns: a 3 k factorial design and analysis. J Environ Manag 155:89–96. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jenvman.2015.03.004
Thommes M, Kaneko K, Neimark AV, Olivier JP, Rodriguez-Reinoso F, Rouquerol J, Sing KSW (2015) Physisorption of gases, with special reference to the evaluation of surface area and pore size distribution (IUPAC Technical Report). Pure Appl Chem. https://doi.org/10.1515/pac-2014-1117
Tran HN, Wang Y-F, You S-J, Chao H- (2017) Insights into the mechanism of cationic dye adsorption on activated charcoal: the importance of π–π interactions. Process Saf Environ Prot 107:168–180. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.psep.2017.02.010
Viegas R, Campinas M, Costa H, Rosa M (2014) How do the HSDM and Boyd’s model compare for estimating intraparticle diffusion coefficients in adsorption processes. Adsorption. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10450-014-9617-9
Yu L, Luo Y (2014) The adsorption mechanism of anionic and cationic dyes by Jerusalem artichoke stalk-based mesoporous activated carbon. J Environ Chem Eng 2:220–229. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jece.2013.12.016
Yu P, Low MY, Zhou W (2018) Design of experiments and regression modelling in food flavour and sensory analysis: a review. Trends Food Sci Technol 71:202–215. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.tifs.2017.11.013
Zhou Y, Zhang L, Cheng Z (2015) Removal of organic pollutants from aqueous solution using agricultural wastes: a review. J Mol Liq 212:739–762. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.molliq.2015.10.023
Zolgharnein J, Shariatmanesh T, Asanjarani N, Zolanvari A (2015) Doehlert design as optimization approach for the removal of Pb(II) from aqueous solution by Catalpa Speciosa tree leaves: adsorption characterization. Desalin Water Treat 53:430–445. https://doi.org/10.1080/19443994.2013.853625
Acknowledgements
The authors acknowledge the General Directorate for Scientific Research and Technological Development (DGRSDT), Algeria, for facilitating the funding of the current research work and for providing the necessary support for the completion of this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Samareh Mirkia.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Zekkaoui, C., Berrama, T., Kadmi, Y. et al. Insights into the efficient elimination of veterinary drug from water by adsorption on activated carbon: optimization study. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 3635–3650 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03105-0
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-03105-0