Abstract
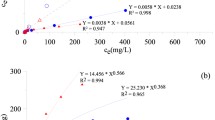
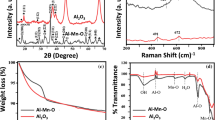
Two synthetic nano-TiO2-based materials, aggregated dendritic anatase nano-TiO2 and polycrystalline rutile nano-TiO2 attached to the surface of SiO2, were analyzed and compared for geo-environmental engineering applications. Characterization of crystal structure, purity, and morphologic, microscopic features of the materials were examined by X-ray powder diffraction, X-ray fluorescence, and scanning electron microscope, respectively. Arsenic removal rates/efficiencies were compared between the two materials in different settings for laboratory batch experiment. The adsorption curve on arsenic was obtained. Subsequently, different concentrations of arsenic solutions were injected in batches at different flow rates 0.67, 0.83, 1.00, 1.25, 1.67, 2.50, 5.00, and 10.00 ml/min to simulate field conditions. Results show that both of TiO2-based materials demonstrate outstanding capabilities for arsenic removal. Removal rates are 83% (± 0.025) and 95% (± 0.024) for aggregated TiO2, while 82% (± 0.031) for 93% (± 0.013) for attached TiO2. Results suggest that attached form of TiO2 is more effective for arsenic removal under fast groundwater flow condition, while aggregated form TiO2 can be suitable for high arsenic concentration and low water flow rate. Both materials are considered cost-effective as both can be recovered and reused after regeneration process.











Similar content being viewed by others
References
Adamson AW, Gast AP (1967) Physical chemistry of surfaces. New York: Interscience publishers 150:180
Bang S, Patel M, Lippincott L, Meng X (2005) Removal of arsenic from groundwater by granular titanium dioxide adsorbent. Chemosphere 60(3):389–397
Bang S, Pena ME, Patel M, Lippincott L, Meng X, Kim KW (2011) Removal of arsenate from water by adsorbents: a comparative case study. Environ Geochem Health 33(1):133–141
Berg M, Luzi S, Trang PTK, Viet PH, Giger W, Stüben D (2006) Arsenic removal from groundwater by household sand filters: comparative field study, model calculations, and health benefits. Environ Sci Technol 40(17):5567–5573
Bravo JL, Chirino H, Mao Y (2017) Heterostructured TiO2@ OC core@ shell photocatalysts for highly efficient waste water treatment. New J Chem 41(22):13600–13610
Camacho LM, Gutiérrez M, Alarcón-Herrera MT, de Lourdes Villalba M, Deng S (2011) Occurrence and treatment of arsenic in groundwater and soil in northern Mexico and southwestern USA. Chemosphere 83(3):211–225
Cheng CL, Perfect E, Mills RT (2013) Forward prediction of height-averaged capillary pressure–saturation parameters using the BC-vG Upscaler. Vadose Zone J 12(3):1–9
Cui J, Du J, Yu S, Jing C, Chan T (2015) Groundwater arsenic removal using granular TiO2: integrated laboratory and field study. Environ Sci Pollut Res 22(11):8224–8234
Garcia E, Li Q, Sun X, Lozano K, Mao Y (2015) TiO2 fibers: tunable polymorphic phase transformation and electrochemical properties. J Nanosci Nanotechnol 15(5):3750–3756
Das D, Samanta G, Mandal BK, Chowdhury TR, Chanda CR, Chowdhury PP, Basu GK, Chakraborti D (1996) Arsenic in groundwater in six districts of West Bengal, India. Environ Geochem Health 18(1):5–15
Ding Z, Zheng B, Long J, Belkin HE, Finkelman RB, Chen C, Zhou D, Zhou Y (2001) Geological and geochemical characteristics of high arsenic coals from endemic arsenosis areas in southwestern Guizhou Province, China. Appl Geochem 16(11–12):1353–1360
Do DD (1998) Adsorption analysis: equilibria and kinetics, vol 2. Imperial College Press, London, pp 13–34
Gleick PH (1993) Water and conflict: fresh water resources and international security. Int Secur 18(1):79–112
Guan X, Du J, Meng X, Sun Y, Sun B, Hu Q (2012) Application of titanium dioxide in arsenic removal from water: a review. J Hazard Mater 215:1–16
Gunduz O, Simsek C, Hasozbek A (2010) Arsenic pollution in the groundwater of Simav Plain, Turkey: its impact on water quality and human health. Water Air Soil Pollut 205(1–4):43
Gupta SK, Chen KY (1978) Arsenic removal by adsorption. J (Water Pollut Control Fed) 50:493–506
He G, Zhang M, Pan G (2009) Influence of pH on initial concentration effect of arsenate adsorption on TiO2 surfaces: thermodynamic, DFT, and EXAFS interpretations. J Phys Chem C 113(52):21679–21686
Hering JG, Chen PY, Wilkie JA, Elimelech M, Liang S (1996) Arsenic removal by ferric chloride. J Am Water Works Assoc 88(4):155–167
Indrakanti VP, Kubicki JD, Schobert HH (2009) Photoinduced activation of CO2 on Ti-based heterogeneous catalysts: current state, chemical physics-based insights and outlook. Energy Environ Sci 2(7):745–758
Indrakanti VP, Kubicki JD, Schobert HH (2011) Photoinduced activation of CO2 on TiO2 surfaces: quantum chemical modeling of CO2 adsorption on oxygen vacancies. Fuel Process Technol 92(4):805–811
Jegadeesan G, Al-Abed SR, Sundaram V, Choi H, Scheckel KG, Dionysiou DD (2010) Arsenic sorption on TiO2 nanoparticles: size and crystallinity effects. Water Res 44(3):965–973
Jézéquel H, Chu KH (2005) Enhanced adsorption of arsenate on titanium dioxide using Ca and Mg ions. Environ Chem Lett 3(3):132–135
Kanel SR, Manning B, Charlet L, Choi H (2005) Removal of arsenic(III) from groundwater by nanoscale zero-valent iron. Environ Sci Technol 39(5):1291–1298
Karbassi A, Fakhraee M, Tajziehchi S, Shahriari T, Maddah S (2018) An efficient treatment system for arsenic removal from groundwater. Ambient Sci 5(2):1–5
Kartinen EO Jr, Martin CJ (1995) An overview of arsenic removal processes. Desalination 103(1–2):79–88
Katsoyiannis IA, Zouboulis AI (2002) Removal of arsenic from contaminated water sources by sorption onto iron-oxide-coated polymeric materials. Water Res 36(20):5141–5155
Kim Y, Kim C, Choi I, Rengaraj S, Yi J (2004) Arsenic removal using mesoporous alumina prepared via a templating method. Environ Sci Technol 38(3):924–931
Leal JH, Cantu Y, Gonzalez DF, Parsons JG (2017) Brookite and anatase nanomaterial polymorphs of TiO2 synthesized from TiCl3. Inorg Chem Commun 84:28–32
Ma L, Tu SX (2011) Removal of arsenic from aqueous solution by two types of nano TiO2 crystals. Environ Chem Lett 9(4):465–472
Mao Y, Kanungo M, Hemraj-Benny T, Wong SS (2006) Synthesis and growth mechanism of titanate and titania one-dimensional nanostructures self-assembled into hollow micrometer-scale spherical aggregates. J Phys Chem B 110(2):702–710
Mireles S, Parsons J, Trad T, Cheng CL, Kang J (2019) Lead removal from aqueous solutions using biochars derived from corn stover, orange peel, and pistachio shell. Int J Environ Sci Technol 16:5817–5826
Mohan D, Pittman CU Jr (2007) Arsenic removal from water/wastewater using adsorbents—a critical review. J Hazard Mater 142(1–2):1–53
National Research Council (1977) Medical and biologic effects of environmental pollutants, arsenic. National Academy of Sciences, Washington, p 219
Nicolli HB, Suriano JM, Peral MAG, Ferpozzi LH, Baleani OA (1989) Groundwater contamination with arsenic and other trace elements in an area of the Pampa, Province of Córdoba, Argentina. Environ Geol Water Sci 14(1):3–16
Nickson R, McArthur J, Burgess W, Ahmed KM, Ravenscroft P, Rahmanñ M (1998) Arsenic poisoning of Bangladesh groundwater. Nature 395(6700):338
Nordstrom DK (2002) Worldwide occurrences of arsenic in ground water. Science 296:2143–2145
Oki T, Kanae S (2006) Global hydrological cycles and world water resources. Science 313(5790):1068–1072
Pena M, Meng X, Korfiatis GP, Jing C (2006) Adsorption mechanism of arsenic on nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Environ Sci Technol 40(4):1257–1262
Pena ME, Korfiatis GP, Patel M, Lippincott L, Meng X (2005) Adsorption of As(V) and As(III) by nanocrystalline titanium dioxide. Water Res 39(11):2327–2337
Pierce ML, Moore CB (1982) Adsorption of arsenite and arsenate on amorphous iron hydroxide. Water Res 16(7):1247–1253
Robichaud CO, Uyar AE, Darby MR, Zucker LG, Wiesner MR (2009) Estimates of upper bounds and trends in nano-TiO2 production as a basis for exposure assessment. Environ. Sci. Technol 43(12):4227–4233
Rodríguez-Lado L, Sun G, Berg M, Zhang Q, Xue H, Zheng Q, Johnson CA (2013) Groundwater arsenic contamination throughout China. Science 341(6148):866–868
Rouquerol J, Rouquerol F, Llewellyn P, Maurin G, Sing K (2013) Adsorption by powders and porous solids: principles, methodology and applications. Academic Press, San Diego
Schilling K, Bradford B, Castelli D, Dufour E, Nash JF, Pape W, Schulte S, Tooley I, van den Bosch J, Schellauf F (2010) Human safety review of “nano” titanium dioxide and zinc oxide. Photochem Photobiol Sci 9(4):495–509
Smedley PL, Kinniburgh DG (2002) A review of the source, behaviour and distribution of arsenic in natural waters. Appl Geochem 17(5):517–568
Sultana R, Kobayashi K (2016) Adsorption of arsenic on soil under different soil moisture conditions. Pollution 2(2):211–220
Thamaphat K, Limsuwan P, Ngotawornchai B (2008) Phase characterization of TiO2 powder by XRD and TEM. Kasetsart J (Nat Sci) 42(5):357–361
UNESCO (2018) United Nations World Water Assessment Programme, 2018. The United Nations World Water Development Report 2018: Nature-Based Solutions for Water, pp 154
US EPA (2001) National primary drinking water regulations: arsenic and clarifications to compliance and new source contaminants monitoring. Fed Reg 66:69–76
Watts HD, Tribe L, Kubicki JD (2014) Arsenic adsorption onto minerals: connecting experimental observations with density functional theory calculations. Minerals 4(2):208–240
WHO (1998) Guidelines for drinking-water quality. Vol. 2, Health criteria and other supporting information: addendum (No. WHO/EOS/98.1). World Health Organization, Geneva
Xu Z, Meng X (2009) Size effects of nanocrystalline TiO2 on As(V) and As(III) adsorption and As(III) photooxidation. J Hazard Mater 168(2–3):747–752
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to acknowledge multiple graduate support provided by School of Earth, Environmental and Marine Sciences, the Science Technology and Engineering Partnership for Success (STEPS) Endowment from College of Science, and Graduate College of the University of Texas—Rio Grande Valley.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: M. Abbaspour.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Yin, S., Cheng, CL., Parsons, J. et al. Evaluation of arsenic sorption performance using dendritic anatase and polycrystalline rutile nano-TiO2 for environmental applications. Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 2113–2124 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02963-y
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02963-y