Abstract
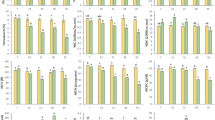
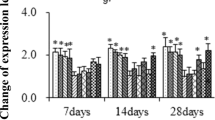
Aquatic ecosystem is greatly affected by metal pollution and global climate change. Mercury (Hg) is one of the most common metal pollutants that pose harmful effects to organisms. In this study, we evaluated the effects of water temperature and Hg2+ on hematological parameters, such as red blood cells (RBCs), hematocrit (Ht) and hemoglobin (Hb) and some indexes involved in energy metabolism, including hexokinase (HK), pyruvate kinase (PK), malate dehydrogenase (MDH), lactate dehydrogenase (LDH), glucose (GLU), electron transport system (ETS) and Na–K-ATPase in grass carp, Ctenopharyngodon idella. Fish (45.37 ± 3.58 g) were acclimated to 15, 20, 25, 30 or 35 °C and co-exposed to 0.000 or 0.039 mg/L Hg2+ for 4 weeks. Three-way ANOVA revealed that all variables were significantly affected by water temperature, Hg2+ concentration, exposure time and their interactions, except the RBCs value corresponding Hg*Time condition. Based on the significant changes of hematological parameters in Hg2+-free groups, the best health status in fish was approximately at 25 °C, appreciating physiological dysregulation in fish under too low (15 °C)/high (35 °C) temperature, especially at 35 °C. Although our data provide evidences that increased temperatures can potentiate Hg2+ toxicity, the combined effects of temperature and metals on aquatic organisms are complex and unpredictable, so we should not ignore the role of environmental factors (such as temperature) while evaluating the harmful effects of metals on aquatic ecosystem.


Similar content being viewed by others
References
Abdel-Tawwab M, Wafeek M (2014) Influence of water temperature and waterborne cadmium toxicity on growth performance and metallothionein-cadmium distribution in different organs of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). J Therm Biol 45:157–162
Abdel-Tawwab M, Wafeek M (2017) Fluctuations in water temperature affected waterborne cadmium toxicity: hematology, anaerobic glucose pathway, and oxidative stress status of Nile tilapia, Oreochromis niloticus (L.). Aquaculture 477:106–111
Adhikari S, Sarkar B, Chatterjee A et al (2004) Effects of cypermethrin and carbofuran on certain hematological parameters and prediction of their recovery in a freshwater teleost, Labeo rohita (Hamilton). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 58(2):220–226
Agrahari S, Gopal K (2008) Inhibition of Na + -K + -ATPase in different tissues of freshwater fish Channa punctatus (Bloch) exposed to monocrotophos. Pestic Biochem Physiol 92(2):57–60
Akhtar MS, Pal AK, Sahu NP et al (2013) Thermal tolerance, oxygen consumption and haemato-biochemical variables of Tor putitora juveniles acclimated to five temperatures. Fish Physiol Biochem 39(6):1387–1398
Ando M, Seoka M, Mukai Y et al (2011) Effect of water temperature on the feeding activity and the resultant mercury levels in the muscle of cultured bluefin tuna Thunnus orientalis (Temminck and Schlegel). Aquacult Res 42(4):516–524
Arnaudova D, Arnaudov A, Tomova E (2008) Selected hematological indices of freshwater fish from Studen Kladenetsh Reservoir. Bulg J Agric Sci 14(2):244–250
Balbus JM, Boxall AB, Fenske RA et al (2013) Implications of global climate change for the assessment and management of human health risks of chemicals in the natural environment. Environ Toxicol Chem 32(1):62–78
Berntssen MHG, Hylland K, Julshamn K et al (2004) Maximum limits of organic and inorganic mercury in fish feed. Aquacult Nutr 10(2):83–97
Biscere T, Rodolfo-Metalpa R, Lorrain A et al (2015) Responses of two scleractinian corals to cobalt pollution and ocean acidification. PLoS ONE 10(4):e0122898
Borges A, Scotti LV, Siqueira DR et al (2007) Changes in hematological and serum biochemical values in jundia Rhamdia quelen due to sub-lethal toxicity of cypermethrin. Chemosphere 69(6):920–926
Broeg K, Lehtonen KK (2006) Indices for the assessment of environmental pollution of the Baltic Sea coasts: integrated assessment of a multi-biomarker approach. Mar Pollut Bull 53(8–9):508–522
Carvalho CS, Fernandes MN (2006) Effect of temperature on copper toxicity and hematological responses in the neotropical fish Prochilodus scrofa at low and high pH. Aquaculture 251(1):109–117
Carvalho CD, Fernandes MN (2008) Effect of copper on liver key enzymes of anaerobic glucose metabolism from freshwater tropical fish Prochilodus lineatus. Comp Biochem Phys A 151(3):437–442
Carvalho CD, Fernandes MN (2019) Effects of copper toxicity at different pH and temperatures on the in vitro enzyme activity in blood and liver of fish, Prochilodus lineatus. Mol Biol Rep 46(5):4933–4942
Diamantino TC, Almeida E, Soares AMVM et al (2001) Lactate dehydrogenase activity as an effect criterion in toxicity tests with Daphnia magna straus. Chemosphere 45(4–5):553–560
Fonseca JD, Marangoni LFD, Marques JA et al (2019) Energy metabolism enzymes inhibition by the combined effects of increasing temperature and copper exposure in the coral Mussismilia harttii. Chemosphere 236:124420
Isani G, Cattani O, Carpene E et al (1994) Kinetic-properties of liver and muscle pyruvate-kinase of a marine teleost, sea bass (Dicentrarchus-Labrax L). Comp Biochem Phys B 107(4):617–624
Kori-Siakpere O, Ubogu EO (2008) Sublethal haematological effects of zinc on the freshwater fish, Heteroclarias sp (Osteichthyes: Clariidae). Afr J Biotechnol 7(12):2068–2073
Kumar N, Krishnani KK, Meena KK et al (2017) Oxidative and cellular metabolic stress of Oreochromis mossambicus as biomarkers indicators of trace element contaminants. Chemosphere 171:265–274
Kumar N, Krishnani KK, Brahmane MP et al (2018) Temperature induces lead toxicity in Pangasius hypophthalmus: an acute test, antioxidative status and cellular metabolic stress. Int J Environ Sci Te 15(1):57–68
Kumar N, Gupta SK, Bhushan S et al (2019) Impacts of acute toxicity of arsenic (III) alone and with high temperature on stress biomarkers, immunological status and cellular metabolism in fish. Aquat Toxicol 214:105233
Kuz’mina VV, Ushakova NV (2013) Influence of temperature and pH on the effects of zinc and copper on proteolytic activities of the intestinal mucosa of planktivorous and benthophagous fishes and their potential preys. Toxicol Environ Chem 95(1):150–162
Lee S, Ji K, Choi K (2014) Effects of water temperature on perchlorate toxicity to the thyroid and reproductive system of Oryzias latipes. Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 108:311–317
Lermen CL, Lappe R, Crestani M et al (2004) Effect of different temperature regimes on metabolic and blood parameters of silver catfish Rhamdia quelen. Aquaculture 239(1–4):497–507
Li ZH, Velisek J, Grabic R et al (2011a) Use of hematological and plasma biochemical parameters to assess the chronic effects of a fungicide propiconazole on a freshwater teleost. Chemosphere 83(4):572–578
Li ZH, Zlabek V, Turek J et al (2011b) Evaluating environmental impact of STPs situated on streams in the Czech Republic: an integrated approach to biomonitoring the aquatic environment. Water Res 45(3):1403–1413
Li ZH, Zlabek V, Velisek J et al (2011c) Antioxidant responses and plasma biochemical characteristics in the freshwater rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss, after acute exposure to the fungicide propiconazole. Czech J Anim Sci 56(2):61–69
Li ZH, Chen L, Wu YH et al (2014) Effects of mercury on oxidative stress and gene expression of potential biomarkers in larvae of the Chinese rare minnow Gobiocypris Rarus. Arch Environ Contam Toxicol 67(2):245–251
Li ZH, Li P, Shi ZC (2015) Chronic exposure to Tributyltin induces brain functional damage in juvenile common carp (Cyprinus carpio). PLoS ONE 10(4):e0123091
Maulvault AL, Custodio A, Anacleto P et al (2016) Bioaccumulation and elimination of mercury in juvenile seabass (Dicentrarchus labrax) in a warmer environment. Environ Res 149:77–85
Monteiro MD, Schwantes MLB, Schwantes AR et al (1998) Thermal stability of soluble malate dehydrogenase isozymes of subtropical fish belonging to the orders Characiformes, Siluriformes and Perciformes. Genet Mol Biol 21(2):191–199
Navas-Acien A, Silbergeld EK, Streeter RA et al (2006) Arsenic exposure and type 2 diabetes: a systematic review of the experimental and epidemiologic evidence. Environ Health Perspect 114(5):641–648
Oruc EO, Uner N, Tamer L (2002) Comparison of Na+-K+-ATPase activities and malondialdehyde contents in liver tissue for three fish species exposed to azinphosmethyl. Bull Environ Contam Toxicol 69(2):271–277
Park K, Han EJ, Ahn G et al (2020) Effects of combined stressors to cadmium and high temperature on antioxidant defense, apoptotic cell death, and DNA methylation in zebrafish (Danio rerio) embryos. Sci Total Environ 716:137130
Perveen S, Hashmi I, Khan R (2019) Evaluation of genotoxicity and hematological effects in common carp (Cyprinus carpio) induced by disinfection by-products. J Water Health 17(5):762–776
Philippe C, Hautekiet P, Gregoir AF et al (2018) Combined effects of cadmium exposure and temperature on the annual killifish (Nothobranchius furzeri). Environ Toxicol Chem 37(9):2361–2371
Sappal R, Fast M, Stevens D et al (2015a) Effects of copper, hypoxia and acute temperature shifts on mitochondrial oxidation in rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss) acclimated to warm temperature. Aquat Toxicol 169:46–57
Sappal R, MacDougald M, Fast M et al (2015b) Alterations in mitochondrial electron transport system activity in response to warm acclimation, hypoxia-reoxygenation and copper in rainbow trout, Oncorhynchus mykiss. Aquat Toxicol 165:51–63
Sappal R, Fast M, Purcell S et al (2016) Copper and hypoxia modulate transcriptional and mitochondrial functional-biochemical responses in warm acclimated rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Environ Pollut 211:291–306
Simcic T, Jesensek D, Brancelj A (2015) Effects of increased temperature on metabolic activity and oxidative stress in the first life stages of marble trout (Salmo marmoratus). Fish Physiol Biochem 41(4):1005–1014
Sokolova IM, Lannig G (2008) Interactive effects of metal pollution and temperature on metabolism in aquatic ectotherms: implications of global climate change. Clim Res 37(2–3):181–201
Stackley KD, Beeson CC, Rahn JJ et al (2011) Bioenergetic profiling of zebrafish embryonic development. PLoS ONE 6(9):e25652
Staurnes M, Rainuzzo JR, Sigholt T et al (1994) Acclimation of atlantic cod (Gadus-Morhua) to cold-water—stress-response, osmoregulation, gill lipid-composition and gill Na-K-atpase activity. Comp Biochem Phys A 109(2):413–421
Sumner AW, Johnston TA, Lescord GL et al (2019) Mercury bioaccumulation in lacustrine fish populations along a climatic gradient in northern ontario, Canada. Ecosystems. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10021-019-00464-9
Talas ZS, Gulhan MF (2009) Effects of various propolis concentrations on biochemical and hematological parameters of rainbow trout (Oncorhynchus mykiss). Ecotoxicol Environ Saf 72(7):1994–1998
Val J, Muniz S, Goma J et al (2016) Influence of global change-related impacts on the mercury toxicity of freshwater algal communities. Sci Total Environ 540:53–62
Waheed R, El Asely AM, Bakery H et al (2020) Thermal stress accelerates mercury chloride toxicity in Oreochromis niloticus via up-regulation of mercury bioaccumulation and HSP70 mRNA expression. Sci Total Environ 718:137326
Wen B, Jin SR, Chen ZZ et al (2017) Plasticity of energy reserves and metabolic performance of discus fish (Symphysodon aequifasciatus) exposed to low-temperature stress. Aquaculture 481:169–176
Woo SJ, Chung JK (2020) Effects of trichlorfon on oxidative stress, neurotoxicity, and cortisol levels in common carp, Cyprinus carpio L., at different temperatures. Comp Biochem Phys C 229:108698
Acknowledgements
The authors wish to thank all who assisted in conducting this work.
Author information
Authors and Affiliations
Corresponding author
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Human and animals rights
All procedures and animal handling were in accordance with the guidelines: OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, No.204: “Fish, Prolonged Toxicity Test: 14-day Study,” adopted April 4, 1984, and OECD Guideline for Testing of Chemicals, No.215: “Fish, Juvenile Growth Test,” adopted January 21, 2000. And the study was approved by the animal ethics committee of Shandong University.
Informed consent
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants included in the study.
Additional information
Editorial responsibility: Jing Chen.
Rights and permissions
About this article
Cite this article
Li, ZH., Li, P. & Wu, Y. Effects of waterborne mercury at different temperatures on hematology and energy metabolism in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Int. J. Environ. Sci. Technol. 18, 1489–1498 (2021). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02906-7
Received:
Revised:
Accepted:
Published:
Issue Date:
DOI: https://doi.org/10.1007/s13762-020-02906-7